IJCRR - 4(17), September, 2012
Pages: 172-180
Date of Publication: 14-Sep-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF XANTHAN GUM BASED FLOATING TABLET OF TRAMADOL
HYDROCHLORIDE
Author: Somnath Patil, Swati Jagdale, Shailendra Kela, Varsha Divekar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The aim of the present work was to prepare floating tablets of Tramadol HCl (TH) using xanthan gum as carrier. TH is a centrally acting oral analgesic that blocks pain through opoid receptor binding and inhibition of nor epinephrine and serotonin reuptake. It has elimination half-life of about 6 hrs. It has an oral bioavailability of about 70% which is suitable for developing gastro retentive floating drug delivery system. The formulations were prepared by varying the concentrations of xanthan gum and sodium bicarbonate. The tablets were prepared by direct compression technique. Xanthan gum and Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) were used as alone and in combination as matrix forming agent and sodium bicarbonate for development of CO2. The prepared floating tablets were evaluated for tablet properties such as hardness, thickness, weight variation, floating property. In vitro dissolution was carried out for 8 hrs in 0.1N HCl at 37\?0.50C using USP paddle type dissolution apparatus. It was noted that, all the prepared formulations had desired floating lag time and constantly floated on dissolution medium by maintaining the matrix integrity. The drug release from prepared tablets was found to vary with varying concentration of the polymer, xanthan gum and HPMC K4M. From the study it was concluded that floating drug delivery system can be prepared by using xanthan gum as a carrier.
Keywords: Floating Tablet, HPMC K4M, in- vitro dissolution, Tramadol HCl, Xanthan gum.
Full Text:
Introduction:
The real issue in the development of oral controlled release dosage forms is not just to prolong the delivery of drugs for more than 12 hours, but to prolong the presence of the dosage forms in the stomach or upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract until all the drug is released for the desire period of time [1] . Rapid GI transit could result in incomplete drug release from the drug delivery device in the absorption zone leading to diminished efficacy of the administered dose [2]. Several approaches are currently used to retain the dosage form in the stomach. These include bio adhesive systems [3]. swelling and expanding systems,[4? 5] floating drug delivery systems (FDDS),[6? 7] and other delayed gastric emptying devices.[8] FDDS, also called hydrodynamically balanced system, is an effective technology to prolong the gastric residence time in order to improve the bioavailability of the drug.[9] This technology is suitable for drugs with an absorption window in the stomach or in the upper part of the small intestine,[10] drugs acting locally in the stomach,[11] and for drugs that are poorly soluble or unstable in the intestinal fluid.[12] FDDS have a bulk density lower than the gastric fluid and thus remain buoyant in the stomach, without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly. Based on the mechanism of buoyancy, two distinctly different technologies, i.e. noneffervescent and effervescent systems, have been utilized in the development of FDDS. The effervescent system utilizes matrices prepared with swellable polymers and effervescent components, e.g. sodium bicarbonate and citric acid or stearic acid. The matrices are fabricated such that in the stomach carbon dioxide is liberated by the acidity of the gastric contents and is entrapped in the gellified hydrocolloid. This produces an upward motion of the dosage form and maintains its buoyancy. In noneffervescent FDDS, the drug is mixed with a gel?forming hydrocolloid, which swells on contact with the gastric fluid after oral administration and maintains relative integrity of shape and a bulk density of less than unity within an outer gelatinous barrier. The air trapped by the swollen polymer confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. [13? 14] TH is a centrally acting oral analgesic that blocks pain through opoid receptor binding and inhibition of nor epinephrineand serotonin reuptake. TH is having short plasma half life 6 hrs which is suitable for developing gastro retentive floating drug delivery system.
Materials and Methods:
Materials:
Tramadol hydrochloride was provided as a gift sample from JCPL, Jalgaon and hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose K4M and xanthan gum obtained as a gift sample from Vapi Care Pharma Pvt Ltd. Vapi. Other excipients and chemicals were of analytical grade and purchased from Pure Chem. Laboratories, Pune.
Method:
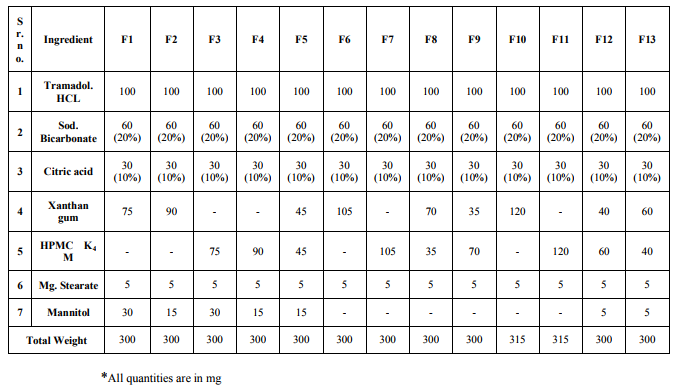
Floating tablets containing TH were prepared by direct compression technique using variable concentrations of Xanthan gum and HPMC K4M with sodium bicarbonate. Different tablets formulations were prepared by direct compression technique. All the powders were passed through 60 mesh sieve. Required quantity of drug, and low-density polymer were mixed thoroughly. Magnesium stearate was finally added as lubricant. The blend was directly compressed (9mm diameter punches) using tablet compression machine. Each tablet contained 100mg of TH and other pharmaceutical ingredients as listed in table-1. Table 1: Composition of Floating Tablet of TH
Evaluation of powder blend:
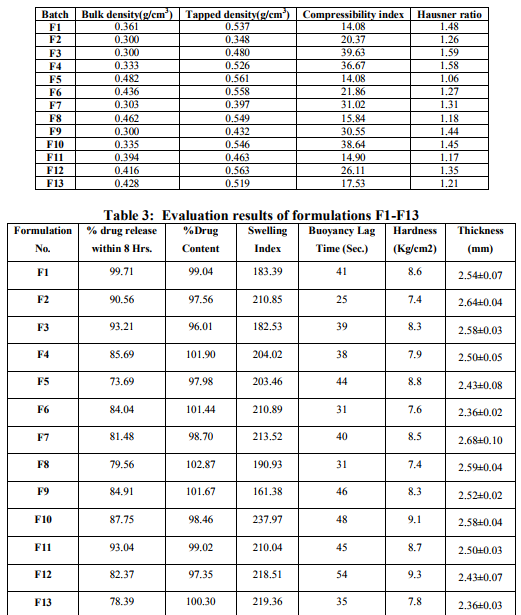
The powder blend used for preparation of tablets was evaluated for angle of repose, and compressibility index. Angle of repose: The angle of repose is a relatively simple technique for estimation of the flow property of a powder. Powders with low angle of repose are free flowing and those with a high angle of repose are poorly flowing powders [7]. 10 gm of powder was passed through funnel and the pile was formed. The height and weight of the pile was measured and the angle of repose was calculated by using the formula:- Angle of repose (θ) = tan-1 (height /radius) The angle of repose less than 300 usually indicate a free- flowing material and more than 400 suggest a poorly flowing material [8] . Carr`s compressibility index: The Carr?s compressibility index was calculated by calculating the tapped and bulk density using the 100 ml measuring cylinder. Compressibility is calculated by the formula. Carr`s compressibility index = (TBD-LBD)/ TBD X100 Where, TBD is tapped bulk density and LBD is loose bulk density. A carr`s index greater than 25 is considered to be an indication of poor flowability, and below 15, of excellent flowability. [9] Table 2: Characterization of precompresion parameters of table.
Evaluation of Tablets:
All the formulations were evaluated for various parameters such as hardness, friability, weight variation, % drug content, buoyancy lag time, swelling index, in-vitro drug release, release experiments, IR spectroscopy and optimized formulation were evaluated for in-vivo study. Hardness: Hardness of tablets was determined using monsanto hardness tester. Friability: For each formulation, the friability of 20 tablets was determined using the Roche friabilator. In this test tablets were subject to the combined effect of shock abrasion by utilizing a plastic chamber which revolves at a speed of 25 rpm, dropping the tablets to a distance of 6 inches in each revolution. A sample of pre weighted 20 tablets was placed in Roche friabilator which was then operated for 100 revolutions i.e. 4 mins. The tablets were then dusted and reweighed. Percent friability (%F) was calculated as follows, % F= (loss in weight / initial weight) x 100 Conventional compressed tablets that lose less than 0.5 to 1.0% of their weight are generally considered acceptable.
Thickness:
Thickness of all tablets was measured using a vernier calliper. Weight variation: The weight of 20 tablets was taken on electronic balance and the weight variation was calculated. The weight variation tolerance allowed for tablet weighing 324 mg and more is 5%.
Drug content:
To calculate the drug content, the tablets were triturated in the mortar. 30mg of the tablet powder (10mg Tramadol HCL) was added to 10 ml of distilled water and drug solution was filtered through Whatman paper no.1. The sample was analyzed for drug content by UV spectrophotometer (Varian Cary 100) at 270 nm after suitable dilutions. Drug stability in the 0.1 N HCl and distilled water was checked using UV spectrophotometer for a period of 10 hours. Buoyancy Studies: In vitro buoyancy was determined by buoyancy lag time. The tablets were placed in a 100 ml beaker containing 0.1N HCl. The time required for the tablet to rise to the surface and float was determined as floating lag time. Swelling index: The swelling index of the tablets was calculated in order to find out the swelling ability of the tablets. For calculating the swelling index, the previously weighed tablets were placed in the 100 mL beaker containing 0.1 N HCl. The tablets were removed at the time interval of 1 hr for 8 hours and weighed. The swelling index of the tablets can be measured by studying its dimensional changes, weight gain or water uptake. Hence swelling index was calculated by the formula; Swelling index= (Wt-Wo) X 100/Wo Where, Wt= Final weight of tablets at time„t? Wo= Initial Weight of tablets.
In Vitro Dissolution Studies:
The release rate of Tramadol HCl from floating tablets was determined using United States Pharmacopeia (USP) 24 dissolution testing apparatus 2 (paddle method). The dissolution test was performed using 900 mL of 0.1N HCl, at 37 ± 0.5°C and 60 rpm. A sample (5 mL) of the solution was withdrawn from the dissolution apparatus hourly for 10 hours, and the samples were replaced with fresh dissolution medium. The samples were filtered through a 0.45-μ membrane filter and diluted to a suitable concentration with 0.1N HCl. Absorbance of these solutions was measured at 270 nm using double beam UV spectroscopy. Cumulative percentage drug release was calculated using PCP disso software.
Results:
Evaluation of tablets:
Hardness:
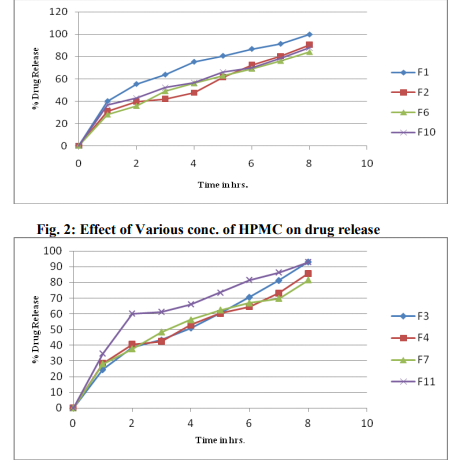
Hardness of the formulations F1-F13 was observed within the range of 7.4-9.3 as shown in table 3.
Friability:
Friability of the tablets was observed below 0.30% for all batches which was in the acceptable limit. Thickness: The thickness of all the tablets was found within the range of 3 ± 0.5 mm. Weight variation: The weight of all the tablets was found within the range of 300 mg ± 5mg. Hence the weight of all formulations was found within the limit. Drug content: The range of % drug content of the formulations F1-F13 was found between 96.01 and 102.87. The tablets showed hardness, friability, thickness, weight variation and % drug content within the limit. The in-vitro buoyancy study shows that all the formulations shows good floating property.
In Vitro Buoyancy Studies:
The in-vitro buoyancy study showed the good floating ability of the tablets as shown in the table 3. Buoyancy lag time indicates the time required for the formulation to float in the medium. From table 2, it was observed that formulations F10 and F12 shows comparatively more floating lag time as compared to other formulations. It was further observed that formulation F2 shows lowest floating lag time among the all formulations.
Swelling index:
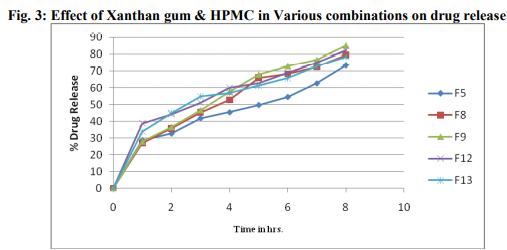
From the swelling index study of all the batches, it was observed that the increase in the concentration of polymers increases the swelling property of the tablets as shown in table 3. Further the formulation containing optimized swelling index was obtained. From the formulation batches, it was observed that the formulations F10 and F13 showed maximum swelling index. In Vitro Dissolution Studies: The drug release patterns from all the formulations are shown in table 3. The percent drug release after 8 hours is as shown in figure 1, 2 and 3. It was observed that the drug release was retarded from the formulations containing more concentration of Xanthan gum and HPMC K4M. The drug release profile of formulations F1-F13 indicates that as the concentration of polymer increases, the drug release was retarded. From the comparison of release profile of all the batches, it was observed that the formulations containing combination of polymers shows more retardation in drug release in less concentration as compared to Xanthan gum and HPMC K4M alone. This indicates that combination of polymers is more efficient in formulating the sustained release dosage form. Table 3: Evaluation results of formulations F1-F13 Fig.1: Effect of Various conc. of Xanthan gum on drug release Fig. 2: Effect of Various conc. of HPMC on drug release Fig. 3: Effect of Xanthan gum and HPMC in Various combinations on drug release
Discussion:
The flow properties of the powder blends were studied and formulation F5 was found to have comparatively good compressibility index and hausner ratio than other formulations. From the results of floating properties it was shown that all tablets had good floating properties. From the results of swelling study it was concluded that swelling index increases as time passes because the polymer gradually absorbed water due to hydrophilic in nature and swell. The swelling index increases with time up to 2 hours in some batches which might due to low viscosity of polymer and after 2 hours, the polymer chain relaxation was dominating phenomenon as swelling reaches thresholds resulting in lowering of swelling index. Thus the viscosity of polymer had a major role on swelling process, matrix integrity as well as floating capability. From the swelling study of the formulations, formulation F10 was found to have good swelling properties. The in vitro dissolution was carried out for all batches. From the dissolution studies of the formulations, formulation F10 was found to have better drug release profile than other formulations. Formulation F10 was also found to have better swelling capacity and floating time than other formulations. The drug release was extended for more than 8 hours from the floating drug delivery formulations.
Conclusion:
Regulated drug release attained in the current study indicates that the matrix tablets of Tramadol hydrochloride, prepared using various polymers, can successfully be employed as a once-a-day oral controlled release drug delivery system. High floating ability of the formulation is likely to increase its GI residence time, and eventually, improve the extent of bioavailability. However, appropriate balancing between various levels of the 2 polymers is imperative to acquire proper controlled release and flotation of the formulation. Formulation F10 shows good in vitro gastro retentive floating drug delivery of Tramadol HCl.
Acknowledgements:
Authors are thankful to JCPL, Jalgaon for providing the drug sample of Tramadol hydrochloride, also thankful to Vapi care pharma Ltd. for providing Xanthan gum and HPMC K4M. Authors are very much thankful to Principal and management of MAEER?s Maharashtra Institute of Pharmacy, Pune for their help and support. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
[1] Bardonnet P, Faivre V, Pugh WJ, Piffaretti JC, Falson F. [2006] Gastro retentive dosage forms: Overview and special case of helicobacter pylori. J. Control. Release 111:1 – 18.
[2] Obaidat AA, Obaidat RM. [2001] Controlled release of tramadol hydrochloride from matrices prepared using glyceryl behenate, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 52: 231-235
[3] Brunton L. Parker K. Blumenthal D. I. Buxton, Goodman and Gilman`s: Manual of pharmacology and therapeutics, Mc Graw Hill, New York. 358-367.
[4] Tiwari SB, Murthy TK, Pai MR, Mehta PR, Chowdhary PB. [2003] Controlled release formulation of Tramadol hydrochloride using hydrophilic and hydrophobic matrix system AAPS PharmSciTech 31: 1-6
[5] Narendra C, Srinath MS, Ganesh B. [2006] Optimization of bilayer floating tablet containing Metoprolol tartrate as a model drug for gastric retention. AAPS PharmSciTech 34:E1-E7.
[6] Dave BS, Amin AF, Patel MM. [2004] Gastroretentive drug delivery system of ranitidine hydrochloride: formulation and in vitro evaluation AAPS PharmSciTech 34: 1- 6.
[7] Aulton ME. [2008] Aulton`s Pharmaceutics-The design and manufacture of medicine, second ed., Churchill Livingstone Elsevier:. 133, 441-450.
[8] Lachman L, Lieberman HA, [2009] the theory and practice of industrial pharmacy, CBS publishers and distributors, special Indian edition, New Delhi. 300,301,317,299.
[9] Allen LV, Popovich NG, Ansel HC. [2008] Ansel`s pharmaceutical dosage form and drug delivery system, Lippincott William and Wilkins: 186-203.
10] Jain NK. Response surface optimization of drug delivery system, CBS Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi.
[11] Singh B. [1998] Comprehensive computer program for the study of drug release kinetics from compressed matrices. Ind. J. Pharm. Sci. 60: 358-362.
[12] Singh B, Chakkal SK, Ahuja N. [2006] Formulation and optimization of controlled release Mucoadhesive tablets of atenolol using response surface methodology. AAPS PharmSciTech 3: E1-E10.
[13]. Davis SS, Stockwell AF, Taylor MJ. The effect of density on the gastric emptying of single and multiple unit dosage forms. Pharm Res.1986; 3:208?213.
[14]. Urguhart J, Theeuwes F. Drug delivery system comprising a reservoir containing a plurality of tiny pills. US patent 4 434 153. February 28, 1994.
[15]. Mamajek RC, Moyer ES. Drug dispensing device and method. US Patent 4 207 890. June 17, 1980.
Table Caption:
1. Table 1: Composition of Floating Tablet of TH
2. Table 2: Characterization of precompresion parameters of table
3. Table 3: Evaluation results of formulations F1-F13
Figure Caption:
1. Fig.1: Effect of Various conc. of Xanthan gum on drug release
1. Fig. 2: Effect of Various conc. of HPMC on drug release
2. Fig. 3: Effect of Xanthan gum and HPMC in Various combinations on drug release
Table 1: Composition of Floating Tablet of TH
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License