IJCRR - 5(8), April, 2013
Pages: 20-31
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BIOENRICHMENT OF LIVE FEED DAPHNIA MAGNA FOR THE SURVIVAL AND GROWTH OF FRESHWATER FISH CATLA CATLA
Author: S. Munirasu, V. Ramasubramanian, V.Uthayakumar, S.Muthukumar
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Daphnia is the potential live feed available in small ponds and lakes. The present study is to evaluate the effect of the Daphnia magna enriched with different micro algae such as Spirulina platensis, Chlorella vulgaris and Spirogyra maximus on growth, survival and biochemical changes of freshwater fish Catla catla. The experimental fishes were fed with Spirulina enriched Daphnia (E1), Chlorella enriched Daphnia (E2), Spirogyra enriched Daphnia (E3), and unenriched Daphnia (E4) as a control and triplicates were maintained for each treatments. After 60 days, the growth rate, survival and Biochemical Compositions such as Protein, Lipids, carbohydrate, amino acids and fatty acids levels were measured. The highest survival rate was recorded as 99.17 % which corresponds to the highest growth rate of fish. Significant differences were observed (P < 0.05) in weight gain, Specific growth rate (SGR), Food conversion ratio (FCR) and Survival (%) (E1) between experimental and control groups. The fishes were fed with diet E1 (S.platensis) was highly significant (P< 0.05) with mean length (1.5 ?0.18 to 4.38 ?0.13) and mean weight (0. 0.210 ?0.01to 2.75 ?0.30) increase in weight gain 273.65% when compared to control (E4) fed fishes. The growth was estimated based on increase in biomass (1.91 + .007) and specific growth rate (3.12 \? 0.06). The Protein, Lipid and Carbohydrates were high in S.platensis enriched D.magna fed fishes. Hence we conclude that S.platensis enriched D.magna is a better food for the larval rearing of Commercial fish C. catla.
Keywords: Spirulina platensis, Chlorella vulgaris, Spirogyra maxima, Daphnia magna, Catla catla, Nutritional values.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Live feeds are one of the major inputs in aquaculture. The success of fish farming depends on the adequate quality of nutritionally balanced feeds (Olsen et al., 1993); Most of the larviculture sector dependent on artemia is the primary food for larval nutrition (Mason 1974; Arthur 1976; Schmidt-Moser and Westphal 1980). The nutritional quality of live feeds can be improved by enriching them with exogenous source of nutrients. For freshwater fish larvae which have a very small mouth and swallow their prey in one bite the size of the nauplii is particularly critical. Cyclops and Daphnia are excellent food source, which could provide quality first feed for fish and crustaceans and the nutritional value on grown and adult D.magna is superior (Sorgeloos, 1980; Leger et al., 1986). The advantages of algae as a food is enormous as algal feeds are easy to culture and it is an excellent feed for the growth of zooplanktons (Bogdan and Gilbert, 1987). Algae are alternative plant feedstuffs that are increasingly being used in aqua feeds because of their nutritional quality, low cost and availability (Mustafa and Nakagawa, 1995). The lower limit of the light intensity for the light type was about 1500 lux and the higher limit for the dim light type was about 1000 lux, although both limit intensities shifted to some extent depending on the freshwater macro algae biochemical investigations show Spirogyra to be rich in nutritive value (Venkataraman, Nigam and Ramanatham, 1980). Freshwater fish larvae, which is unable to synthesize essential amino acid DHA and EPA from the shorter PUFA, has precursor Linolenic acid (18:3n-3) which are required for larval growth and survival as well as contributing to egg and sperm quality when induced in brood stock. Algae are the main sources of highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA) for zooplankton (Witt et al., 1984; Kanazawa et al., 1985; Koven et al., 1992; Sargent et al., 1997). Enrichment or boosting of the aquatic feeds into the organisms has been incorporated in to the larval rearing protocols for many fish species (Sorgeloos et al., 1991). The best materials for enriching Daphnia are different micro algae and these are used because of its easy culturing and excellent food for fishes (Hassina Momotaj et al., 1986). Daphnia which is incapable of synthesizing highly polyunsaturated fatty acid and essential amino acids, it needs to be enriched by micro algal enrichment which contain high level of amino acid in particular, has high biological value during larval development. Catla catla is the fastest growing species (Ravi and Devaraj 1991). The aim of the present investigation is to evaluate the effect of D.manga enriched with different algae feeds phytoplankton’s (S. platensis, C. vulgaris and S.maxima) on survival and growth of C.catla.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The fresh water C. catla fries were collected from Bhavani sagar Government Fish Development Corporation, Erode district, Tamilnadu. They were transported safely and brought to the laboratory in well-oxygenated plastic bags. They were stocked in large cement tank (6’ × 4’ × 3’) and acclimatized to the laboratory condition for 2 weeks before the commencement of experiments. During acclimatization, C. catla were fed with live unenriched D.magna. Water was routinely changed every day in order to maintain a healthy environment for the fishes apart from providing artificial aeration. This ensures sufficient oxygen supply for the fishes and an environment devoid of accumulated metabolic wastes.
Experimental Setup
The fresh water fish’s C. catla with initial length of 1.2±0.5 cm and initial weights 0.13±0.08g were used. The experimental period was restricted to 60 days. Each experimental trough contained 40L of water capacity. The experimental groups were fed with different algae, Fishes were fed with Spirulina platensis, enriched Daphnia - (E1), Fishes were fed with Chlorella vulgaris enriched Daphnia - (E2), Fishes were fed with Spirogyra maximus enriched Daphnia - (E3), Control fishes were fed with unenriched Daphnia – (E4). Before initializing the experiment, the initial length and weight of the animals were measured; similarly at the end of this experiment (on 60th day) the final length and weight were measured. Similar experimental setup was maintained for several times to study various parameters.
Phytoplankton culture
In the present study important algae such as S. platensis, C. vulgaris and S.maxima were cultured to enrich the Zooplankton (D.magna).
Collection of phytoplankton
The experimental micro algae, S. platensis and C. vulgaris pure culture were obtained from Antenna Green Trust, Antheneri village, Kadachanenthal, Madurai, Tamilnadu. The Spirogyra cultures were collected from IRTC, Palakkad, Kerala. The pure cultures were transferred in oxygen filled polyethylene covers for proper aeration.
Culture of Spirulina platensis
The pure Spirulina cultures were poured into the 24 L plastic tubs and were placed in sun light. Several physico-chemical parameters were maintained in culture medium for the proper culture of Spirulina, such as pH, temperature and dissolved solids. The parameters were checked at every two days interval. Proper aeration was provided through aerators for proper mixing of chemicals and proper growth of Spirulina.
Culture of Chlorella vulgaris
The fresh water green C.vulgaris were cultured in Aquarium tanks. The salt ingredients were dissolved in Ground water. After that, cow dung was mixed with water and filtered with the nylon cloth. The filtrate was put in the culture and mixed well during the culture period. The pH was maintained at 8 and no aeration was provided. The pure C.vulgaris culture were poured into the 24 L plastic tubs and placed in sun light. The culture medium was stirred twice daily for proper distribution of chemicals and good aeration such as pH, temperature, and dissolved solids. to prevent sedimentation and a homogenous exposure of algal cells to light; reduce the nutrient and temperature gradient along depth of culture.
Culture of Spirogyra maxima
The samples were collected just below the water surface in 500 ml plastic containers with screw caps. The Spirogyra was collected and washed thoroughly to remove the adhering dirt. pH of the medium was adjusted to 6.5. Soil-water medium with its variations was excellent for long-term preservation and normal morphology of the above culture.
Calculation of Growth rate in Phytoplankton
After the 20 days S. platensis, C. vulgaris and S.maxima can be viewed as a thin layer on the surface of the medium. At this stage the Spirulina cell count may be calculated by the following equation,
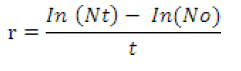
Where,
Nt = final density of phytoplankton, No = Initial density of phytoplankton
t = time interval between the initial and final density estimated
In = Individual animals, r = Growth rate.
Procedures were repeated in several tubs and required quantities of phytoplankton were cultivated.
Harvesting of phytoplankton
Productivities rarely exceed 30-200 gm per day and cell densities of 2g/ L. The Spirulina and Chlorella were harvested by filtration through meshes having size about 10µm. After harvesting, the algal biomass was dehydrated by sun during. The harvested Spirulina and Chlorella powders were stored in clean, and air tight containers. During weight measurements of algae powders were calculated in gram per liter by during the biomass in an oven at 105?C for two hours. This Spirulina powder was used to enrich the Daphnia.
Harvesting and drying
The cultured Spirogyra were filtered with the help of net of mesh size 30µm and washed thoroughly with the clean water and dried in a hot oven at 60?C. After drying Spirogyra were powdered into fine particles, properly weighed and then stored in clean containers for further use.
Zooplankton culture
The live feed of present investigation D.magna collected from Muthanna Lake, P.N.Pudur, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, and India. During collection period the dip net was swept through the surface water near the shore. Collected mixed zooplanktons were stored in a container. The sample was diluted (5 times) by adding water. Using the plankton net Daphnia were isolated from other zooplanktons. Transferred to a cement tank which was prefilled with soil (5 cm depth), poultry manure (0.4 kg/ton), lime powder (1 kg) and water of 15cm height for further culture.
The density of Daphnia were calculated as follows
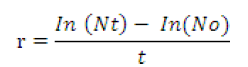
Where
Nt = Final density of the Daphnia, No = Initial density of Daphnia.
t = time interval between the initial and final density estimation.
In =Individual animals.
Enrichment
D.magna was enriched with S. platensis, C. vulgaris and S.maxima to feed the commercially important fish C.catla, cultured in laboratory. The 48 hours adult nauplii of Daphnia were fed with each type of food at same concentration 0.5 mg/ml/d. The powdered feeds are taken at 0.5 mg concentration, mixed with distilled water and stirred for 2-3 minutes vigorously. D.magna (50/ml) was introduced into 500ml culture flasks containing freshwater and mild aeration was provided. After 6 hours of enrichment D.magna (adult nauplii) were fed to experimental fishes (C. catla) twice a day. Daily observations were done. After 60days, the final length, weight and percentage of survival were determined.
Nutritional analysis
Protein, lipid and carbohydrates were determined by the following methods. The basic procedures followed were for protein (Lowry et al., 1951), lipids (Folch et al., 1957) and carbohydrates (Roe 1987).
Amino acids analysis
Total Amino acid composition was determined using a High Performance Thin Layer Liquid Chromatography (Hess and Sherma, 2004).
Fatty acid analysis
Fatty Acid Analysis was done using Gas Chromatography described by Nichols et al.., 1995.
Growth analysis
The growth parameters were calculated by using the following formulae according to (Felix and Sudharsan 2004; Venkat et al. 2004).
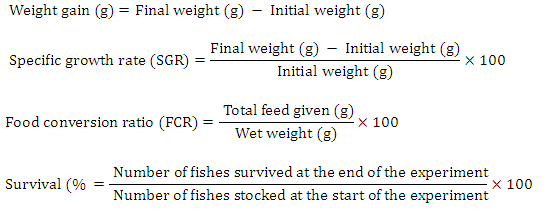
Statistical analysis was performed using analysis of variance (One-way ANOVA) and Student’s t-test, to determine differences between experimental levels. Levels of significance are expressed as (P < 0.05). All analyses were performed using the Statistical Analysis System (SAS computer software, North Carolina, USA) program.
RESULTS
Physico-chemical parameters of rearing water
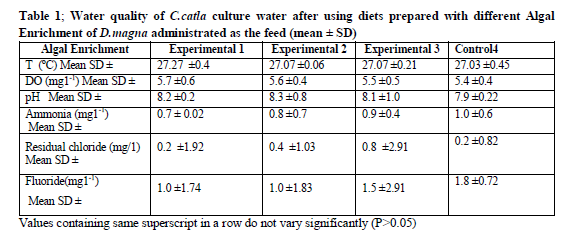
Mean physico-chemical parameters like water temperature (ºC), dissolved oxygen (mg l-1), pH, ammonia–nitrogen(mg1-1), residual chloride (mg1-1) and Fluoride (mg1-1), were recorded in ranges from (27.03±0.45 to 27.27±0.4 ºC), (5.4±0.4 to 5.7±0.6 mg 1-1), (7.9±0.22 to 8.3±0.8), (0.7 ± 0.02 to 1.0 ± 0.6 mg 1-1), (0.2 ± 0.82 to 0.8 ± 2.91 mg 1-1) and (1.0 ± 1.74-1.8 ± 0.72 mg1-1) respectively (Table 1).
Biochemical analysis of experimental diets and tissues
Chemical compositions of the experimental tissues were reported in (Table 2). Variation in the values of crude protein content of feed was (34.46±0.89 to 43.26±1.47 %), crude lipid content (15.03±1.08 to19.27±2.18) crude carbohydrate content (30.3±0.31 to 39.7±7.07), Ash Content (15.07±1.83 to 16.83±0.62) and Moisture content (68.93±1.82 to 73.82±0.68) recorded respectively. Tissue crude lipid content was recorded within the range of (3.27–3.6%).
Growth parameters
The growth parameters recorded in this experiment were presented in (Table 3).
The S.platensis performed the best in all the growth-related parameters. The fish fed with diet E1 (S.platensis) showed a high significant (P< 0.05) mean length (1.5 ±0.18 to 4.38 ±0.13) and mean weight (0. 0.210 ±0.01to 2.73±0.30) and increase in weight gain 273.65% over control. The highest survival rates were recorded as 99.17 % which also corresponds to the highest growth rate of fish.
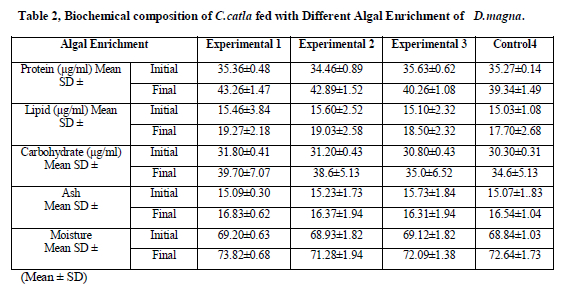
Values are means of three replicates per treatment
Values containing same superscript in a row do not vary significantly (P < 0.05)
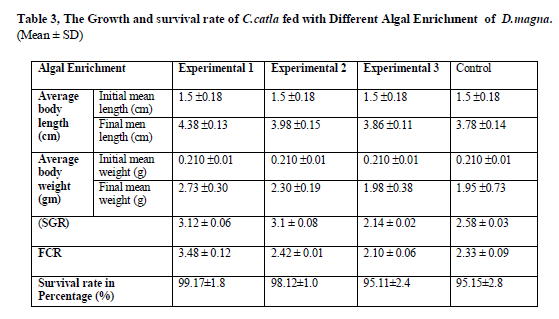
Values are means of three replicates per treatment
Values containing same superscript in a row do not vary significantly (P< 0.05)
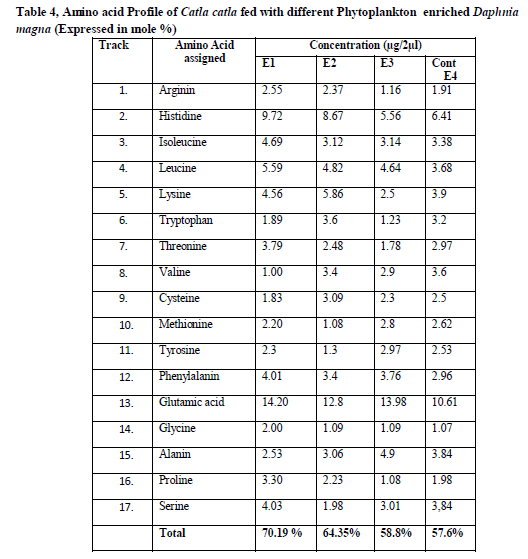
Amino acid analysis using HPTLC
The Protein and amino acid estimation of the different algae enriched D.magna fed fishes was carried out by using HPTLC.17 amino acids were found to be present in the fresh fed with a total of 12.57mg/g tissue (Table 4). The concentration of amino acids in the fishes fed with S.platensis enriched D.magna were of Arginin 2.55, Histidine 9.72, Isoleucine 4.69, Leucine 5.59, Lysine 4.56, Tryptophan 1.89, Threonine ,3.79, Valine 1.00, Cysteine 1.83, Methionine 2.20, Tyrosine 2.3, Phenylalanin 4.01, Glutamic acid 14.20, Glycine 2.00, Alanin 2.53, Proline 3.30 and Serine 4.03 and total amino acids were 70.19 % respectively.
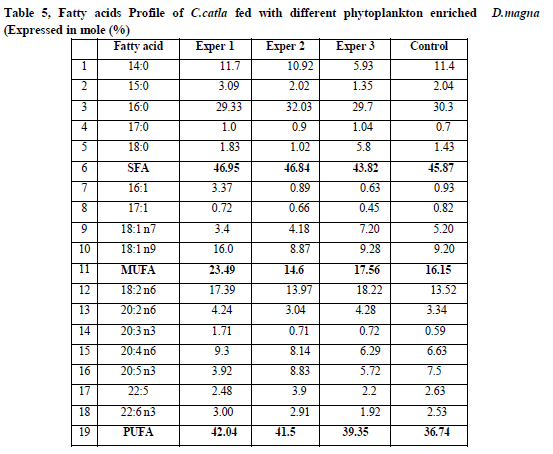
Fatty Acid Profile:
Fatty acids Profile of C.catla fed with different phytoplankton enriched D.magna (Expressed in mole %) were tabulated in Table.5. In the S.platensis enriched D.magna the total saturated fatty acid content was (SFA) 46.95%, total MUFA was 23.49%, and total PUFA and HUFA was 42.04 %. The C.vulgaris enriched D.magna had total SFA 46.84%, total MUFA as 14.6%, total PUFA and HUFA as 41.5%. In the S.maxima enriched D.magna, the total SFA content was 43.82 %, total MUFA was 17.56%, total PUFA and HUFA was 39.35% and unenriched Daphnia had the total SFA as 45.87 %, total MUFA as 16.15%, total PUFA and HUFA as 36.74% respectively.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, variations in nutritional composition among planktons were observed. The studies indicated that the sufficient densities of S.platensis are important for the normal growth and development of larval C.catla during the early development (Lu, J. and Takeuchi, T. 2004). The S.platensis contains high protein compared to C.vulgaris and S.maxima (Table 3). The biochemical composition of S.platensis revealed that they have high amount of protein between 55-70% depending on the source (Phang et al, 2000). S.platensis is rich in high quality protein, vitamins, minerals and many biologically active substances (Becker, 1994). S.platensis can be used in the diets of domestic animals (Vekataraman 1972). Despite on the high nutritive value of algae, little information has been published on their use as a protein source for fishes (Appler, 1985; Nakagawa et al., 1987; Cho and Kaushik, 1990). The present study recommends that algae enriched D.magna and copepod (M.aspericornis) can be exclusively used as an important alternate or supplementary feed for commercial seed production of C.catla. Larvae of nearly all marine and of many freshwater fish species require live feed organisms as first food for many fish species live food still gives better results in terms of growth and survival than artificial diets (Dabrowski, 1984). After 60days of experiment the biochemical composition of fish enriched with S. platensis enriched Daphnia was found to contain maximum level of protein. These results indicated that S. platensis is best food for enrichment of D.magna suitable for the growth and survival of commercial fish C.catla (Nandeesh et al., 1993). There is great difference found between the feeds enriched fed fish and control. Protein is the most important and expensive component of the aquaculture diets. Protein is required in the diet to provide indispensable amino acids and nitrogen for synthesis of dispensable amino acids (Balazs and Ross., 1976; Colvin and Brand, 1977). They supply the major portion of energy required by living cells. If a large percentage of the metabolic energy requirements of the animal can be met from the carbohydrate, it have the potential for delivering a low cost source of energy that could spare protein for growth (Cedric Simon, 2009). Lipids are substances found in both plants and animals (Harrison, 1990). Lipids fall into two basic categories (glycerol-based and nonglycerol-based). The lipids are important sources of metabolic energy adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and are the most energy-rich of all classes of nutrients. (Teshima 1972; Pillay and Nair, 1973; Galois, 1984). Among the 17 Protein in body tissues, 10 amino acids are essential and must be supplied through the diet since animals including fish cannot synthesis them (Watanabe, 1993; Coloso and Cruz, 1980; Kanazawa and Tsshima, 1981). A large proportion of the amino acid consumed by animals is catabolized for energy. Amino acids play important and versatile roles in fish nutrition and metabolism. (Peng Li et al., 2008). Since high protein diets are needed for good growth of most aquatic animals (NRC, 1993), estimation of minimum requirements of essential amino acids (EAA) is indispensable to formulate cost effective diets. The quantitative EAA requirements of fish and crustaceans are often determined by feeding experiments with diets containing graded levels of the particular amino acid to be examined (Wilson, and Halver, 1986; Tang and Hwang, 1966 and Cobb et al., 1975). Both the absolute amounts of individual fatty acids and their relative proportion are important in the nutrition of fish larvae (Sargent et al., 1997). In particular, the DHA/EPA ratio may affect larval growth and survival, possibly because high amounts of EPA in relation to DHA may create an imbalance in the structural composition of the phospholipids that are essential components of biological membranes (Rainuzzo et al., 1994). In the present study, DHA/EPA ratios ranged from 4.7:1 for A. sinjiensis to 2.2:1 for P. crassirostris. All three species therefore met or exceeded the recommended DHA/EPA ratio of about 2:1 formarine finfish larval feeds (Sargent et al., 1997). The improvements in larval growth, survival and rates of normal are generally attributed to levels of DHA, EPA and or arachidonic acid (ARA) in the diet (Castell et al., 1994; Reitan et al., 1994).
CONCLUSION
The present investigation on nutritional evaluation of different algal diets for the survival and growth of C.catla showed best results especially with reference to biochemical compositions. We have used 3 important algae for the enrichment of live feed, D.magna and obtained detailed results. The biochemical compositions of different algae S. platensis, C. vulgaris and S.maxima, the fatty acids of algae enriched D.magna , Amino acid analyses of algae enriched live feeds D.magna were done for feeding the live feeds enriched with these algae to commercial fish C.catla, for ensuring the S. platensis as a better protein supplement for fish larvae. The results clearly indicates that the green algae enriched D.magna are the best candidate species for practical aquaculture.
References:
- Appler, N. H., 1985. Evaluation of Hydrodictyun reticulaturn as a protein source for Oreochromis (Tiiapia) nilotica and Tilapia zillii. Journal of fish biology. 27: 327-333.
- Arthur, D.K. 1976. Food and feeding of larvae of three fishes occurring in the California Current, Surdinops sugux, Engruulis mordux and Truchurus symmetricus. Fish. Bull., U.S. 74517-530.
- Balazs, Ross E, and Brooks C.C 1973. Preliminary studies on the preparation and feeding of crustaceans diets. Aquaculture, 2,369-376.
- Becker, E.W. 1994. Microalgae. In Nutrition., Cambridge, Cambridge University Press. pp. 196–249
- Bogdan.K.G. and Gilbert,J.J. 1987. Quantitative composition of food niches in some freshwater zooplankton. A multi-tracer-cell approach. Oecologia (Berlin), 72, 331-340.
- Castell, J.D., Bell, J.G., Tocher, D.R., Sargent, J.R., 1994. Effects of purified diets containing different combinations of arachidonic and docosahexaenoic acid on survival growth and fatty acid composition of juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Aquaculture 128: 315– 333
- Cedric J. Simon, 2009. Identi?cation of digestible carbohydrate sources for inclusion in formulated diets for juvenile spiny lobsters, Jasus edwardsii. Aquaculture 290 275–282.
- Cho, C.Y. and Kaushik, S.J. 1990. Nutrition energetics in fish: energy and protein utilisation in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri). World Rev. Nutr. Diet., 61: 132-172
- Cobb, B.F., Conte, F.S., Edwards, M.A., 1975. Free amino acids and osmoregulation in penaeid shrimp.J. Agric. Food Chem. 23 6, 11721174.
- Coloso, R. M. and Cruz, L. J 1980. Preliminary studies in some aspects of amino acid biosynthesis in juveniles of Penaeus monodon Fabricus I- Incorporation of 14C from (U-14C) acetate in amino acids of perceptible proteins. Bull. Phil. Biochem. Soc., 3: 12–22.
- Colvin L.B. and Brand C.W. 1997. The protein requirement of penaid shrimp at various life cycle stages in controlled environment systems. Proc. World Maricul.Soc,. 8. 821-840.
- Dabrowski, K., 1984. Influence of initial weight during the change from live to compound feed on the survival and growth of four cyprinids. Aquaculture 40:
27–40.
- Dey and Chandra, R .K Dey and S .Chandra 1995. Preliminary studies to raise diseases resistant seed (fry) of Indian major carp Catla catla (ham.) through herbal treatment of spwan, fish .chimes ,pp23-25.
- Felix N, Sudharsan M 2004. Effect of glycine betaine, a feed attractant affecting growth and feed conversion of juvenile freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac Nutr 10:193–197
- Folch, J., Less, M., Bloane stanly, G. H. 1957. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues.J.Biol.Chem.PP.266, 467-509.
- Galois, R., 1984. Variations de la composition lipidique tissulaire au cours de la vitellogenese chezla crevette Penaeus indicus Milne Edwards. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 84, 155–166.
- Harrison, K.E., 1990. The role of nutrition in maturation, reproduction and embryonic development of decapods crustaceans: a review. J. Shellfish Res. 9, 1–28
- Hassina Momotaj and Dr A Z M Iftikhar Hussain, 1986. Effect of Spirulina on Arsenicosis Patients in Bangladesh ,Aquaculture, 53: 95-99
- Hess, B., &Sherma, J., (2004). Quantification of arginine in dietary supplement tablets and capsules by silica gel high-performance thin-layer chromatography with visible mode densitometry. ActaChromatographica., 14: 60-69.
- Kanasawa, A., 1985. Essential fatty acid and lipid requirement of fish. In C.B. Cowey, A.M. Mackie & J.G. Bell (eds), Nutrition and Feeding in Fish, Academic Press, London: …281–298.
- Kanazawa, A., Teshima, S., 1981. Essential amino acids of the prawn. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 17, 1375– 1379.
- Kanazawa, A., Teshima, S., Sakamoto, M. 1985. Effects of dietary lipid, fatty acids and phospholipids on growth and survival of prawn (Penaeus japonicus) larvae. Aquaculture 50, 39– 49
- Koven,W.M., A. Tandler, G.W. Kissil & D. Sklan, 1992. The importance of n3 highly unsaturated fatty acids for growth in larval Sparus aurata and their effect on survival, lipid composition and size distribution. Aquaculture 104: 91–104.
- Léger, P.H., D.A. Bengtson, K.L. Simpson & P. Sorgeloos. 1986. The use and nutritional value of Artemia as a food source. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 24: 521-623.
- Lowery. O.H., Rosebrough. N.J., Farr. A. L, and Randall. R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with Foliphenol Reagent. J. Biol . Chem . pp. 193, 263-275.
- Lu, J. & Takeuchi, T. 2004. Spawning and egg quality of the tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus fed solely on raw Spirulina platensis throughout three generations. Aquaculture, 234: 625–640.
- Mason, J.C. 1974. Behavioral ecology of chum salmon fry in a small estuary. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 31233-92.
- Mustafa, M.G., Nakagawa, Y.H., (1995). A review: dietary benefits of algae as an additive in fish feed. Isr. J. Aquac. 47, 155–162.
- Nakagawa, H., Kashahara, S. and Ugiyama, T. 1987. Effect of ulva meal supplementation on lipid metabolism of black seabream (Acanfhopagrus schlegek Bleeker). Aquaculture, 62: 109-121.
- Nandesha M.C., De Silva S.S. and D.Krishnamurthy, 1993. Evaluation of mixed feeding schedules in two Indian major carps, catla (Catla catla) and rohu (Labeo rohita). Aquaculture. pp. 753-765.
- Olsen, Y., Reitan, K.I. and Vadstein, O. 1993. Dependence of temperature on loss rates of
- Peng Li . Kangsen Mai . Jesse Trushenski . Guoyao Wu. 2008. New developments in fish amino acid nutrition jurnal of review article Aquaculture 309-46
- Phang, S.M., Miah, M.S., Chu, W.L. & Hashim, M. 2000. Spirulina culture in digested sago starch factory waste water. J. Appl. Phycol., 12: 395–400.
- Pillay, K.K., Nair, N.B., 1973. Observations on the biochemical changes in the gonads and other organs of Uca annulipes, Portunus pelagicus, and Metapenaeus affinis Decapoda: Crustacea during the reproductive cycle. Mar. Biol. 18, 167–198.
- Rainuzzo, J. R., Reita, K. I., Olsen, Y., 1994. Lipid Composition in turbot larvae fed live feed cultured by emulsions of different lipid classes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 107A, 699-710.
- Ravi J. & Devaraj K.V. 1991. Quantitative essential amino acid requirements for growth of catla, Catla catla (Hamilton). Aquaculture 96, 281-291..
- Reitan, K. I., Rainuzzo, J. R., Olsen, Y., 1994. Influence of lipid composition of live feed on growth, survival and pigmentation of turbot larvae. Aquaculture Int 2., 33-48.
- Roe. J.H., (1955). The determination of blood sugar and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J. Biol. Chem., 212 :335-343.
- Sargent, J. R., Mc Evoy, L. A., Bell, J. G., 1997. Requirements presentation and sources of polyunsaturated fattyacids in marine fish larval feeds. Aquaculture. 155, 117-127.
- Sargent, J. R., R.J. Henderson and D.R. Tocher, 1989. The lipids. In J. Halver (ed.), Fish Nutrition, 2nd edn., Academic Press: 153–217.
- Sargent, J.R., McEvoy, L.A., Bell, J.G., 1997. Requirements, presentation and sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine fish larval feeds. Aquaculture 155, 117–127.
- Schmidt-Moser, R., and . Westphal. D, 1980. Relationships of gobies (Gobiidae, Pisces) and their prey in the brackfish foerde schlei (Baltic coast of Western Germany). 15th European Symposium on Marine Biology, Kiel 471-478.
- Sorgeloos, P., 1980. The use of the brine shrimp Artemia in aquaculture. In: G. Persoone, P. Sorgeloos, O. Roels and E. Jaspers (Editors), The Brine Shrimp, Artemia, Vol.3, Ecology, Culturing, Use in Aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, pp.25-46.
- Tang, Y., and Hwang, T.L., 1966. Evaluation of the relative suitability of various groups of Techniques 13: 601–603.
- Venkat HK., Sahu NP., Jain KK, 2004. Effect of feeding Lactobacillus-based probiotics on the gut microflora, growth and survival of postlarva of Macrobrachium rosenbergii(de Man). Aquac Res 35:501–507
- Venkataraman L.V., Nigam BP, and Ramanathan PK, 1980. Rural oriented fresh water cultivation and production of algae in India. In:Shelf G and Soeder CJ (Eds), Algae Biomass, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 81-95.
- Venkataraman, S., 1972. Algal Biofertilizers for Rice Cultivation. Today & Tomorrow, New Delhi, 75.
- Watanabe, T., 1993. Importance of docosa hexaenic acid in marine larval fish. J. World Aquac, Soc.24(2) :152-161.
- Wilson, R.P., Halver, J.E., 1986. Protein and amino acid requirements of fish. Annu. Rev. Nutr., 6: 225-244
- Witt, U., G. Quantz, and G. Kuhlmann, 1984. Survival and growth of turbot larvae Scophthalmus maximus L. reared on different food organismswith spesial regard to longchain polyunsatturated fatty acids. Aquacult. Eng. 3: 177–190.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License