IJCRR - 5(14), July, 2013
Pages: 77-82
Date of Publication: 29-Jul-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DETECTION OF HEAVY METAL TOXICITY IN GILLS AND FLESH OF LABIO ROHITA AND EDAPHODON KEWAI IN RIVER YAMUNA AT ALLAHABAD
Author: Rajeev Kumar, R.M.Tripathi, Lav Kesharwani, Amit Chattree, A.K.Gupta
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The concentrations of Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr), Lead (Pb), Manganese (Mn) and Aluminium (Al) in water, sediments , gills and flesh of both Labio rohita and Edaphodon kewai from River Yamuna in Allahabad, U.P., India, were determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. The pattern of distribution of the heavy metals showed a prevalence of Cr and Mn over other metals in the organs of the two fish species as well as in the water and sediment samples. The highest concentration of Mn was in the sediment and low in water. The unexpectedly high concentration value obtained for Cr and Mn calls for medical alertness since it exceeded the WHO recommended acceptable limits for consumption. Al was not detected in the organs of fish species, water and sediment. Cd and Pb distribution in all the samples was lower than the WHO recommended acceptable limits for consumption.
Keywords: Labio rohita, Edaphodon kewai, Heavy Metals, Fishes, Sediment
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Heavy metals in water, vegetation, fishes and other marine food, are one of the main reasons for the environmental contamination. Due to this reason, the detection of heavy metals and their ill effects on the human being are always of concern of a scientist/toxicologist. The toxic effects of heavy metals are long lasting, reason being the non degradation properties of heavy metals. The heavy metals can?t be degraded whereas organic contaminants decompose into other chemicals with time. Heavy metals have toxic effects even at low concentration, which may prove lethal to any living being. Their concentration in biota can be increased through bio-accumulations (Ganagaiya et al, 2001). Heavy metals are classified as essential (if they play basic role as components of vital biochemical or enzymatic activities in human body e.g. Fe, Mn, Mo, Cr, V, Zn ) and as nonessential (if the metals are classified as with no biological, chemical and physiological importance in man. Deficiency or high concentrations of these metals may have detrimental effect on health. Once liberated into environment, man-made chemicals and products of heavy metals are taken up into the body via inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption. Heavy metals on exposure may not necessarily produce a state of toxicity in the body as they accumulate in the tissues over time until they reach toxic concentration. Exposure to toxic metals is associated with many chronic diseases. As per available report, when meta llic toxicant finds their way into the body, there are possible mechanisms through which they act. Some of which are: (a) Inhibition of Enzymatic Activities: This is so because some metals such as Pb, Hg and Cd have affinity for sulphur and therefore attack sulphur bonds in enzyme, thus immobilizing them. Other site of attack include the free amino (- NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) groups in protein. (b) Attacks on Cell Membrane and Receptor: The heavy metals bind to cell membrane and receptor, thereby altering their structures. This affect transport and other inter or intra cellular processes in the body. Cd inhibits oxidative phosphorylation in the body. (c) Interference with Metabolic Cations: Heavy metals interfere with the metabolism of essential cations such as absorption, transportation, decomposition and storage. Cd follows the pathway of Zn and Cu metabolisms. Pb replaces Ca in bones. (d) Action on the Artery: Heavy metals can increase the acidity of the blood. The body draws Ca from the bones to help restore blood pH. Further toxic metals set up conditions that lead to inflammation in arteries and tissues, causing more Ca to be drawn to the area as a buffer. The Ca, coats the inflamed area in the blood vessel but creating another by the hardening of the artery walls and its progressive blockage of the arteries. This leads to osteoporosis. Various studies have reported various levels of heavy metals pollutants as detected in water bodies in Allahabad. The heavy metals get into the aquatic environment via different ways of weathering process or mass activities such as agricultural and industrial waste disposal (Okoye, 1991). Due to the easy availability and being inexpensive fish is the common food for human being. Fish is often the last link in aquatic food chain therefore it is the need of time to determine its toxic metal concentration. According to (AbouArab et al., 1996) fish accumulate these heavy metals from the surrounding water and sediment. Many disease conditions in man are linked to the consumption of fishes contaminated with toxic metals (Ganagaiya et al., 2001) Cadmium (Cd) and Lead (Pb) in any concentration can cause kidney damage, their symptoms of chronic toxicity include impaired kidney infection, poor reproductive capacity, hypertension etc. Chromium as Cr (VI) penetrates cell membranes and can cause geno-toxic effect and cancer (Iwegbue, 2004). Prayag (Allahabad), UP India has “Triveni Sangam”, which has two physical rivers Ganges, Yamuna, and the invisible or mythic Saraswati River. It is a place of religious importance and the site for historic Kumbh Mela held every 12 years. Tourists from all over the world mark their presence for religious bath in Triveni Sangam. River Yamuna is the largest river of the Ganges (Ganga) in northern India with length of 1,376 km and Basin of area 366,223 km2 . River Yamuna is chosen in this present work for the sample collection in this present study. The main aim of our work is to determine the levels of Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr), Lead (Pb), Magnesium (Mn) and Aluminium (Al) in different organs of fish species, water and sediment as well as their potential health effects on human. An Atomic Absorption Spectrometer from „Varian Company? was used to analyse the samples.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Labeo rohita and Edaphodon kewai fishes were the target species for the heavy metal detection. The brief introduction of both fishes is as follows: Labeo rohita Scientific Name: Labeo rohita; Etymology: Labeo: Latin, labeo = one who has large lips. Identification: All species in the genus labeo have a Dorsal fin with 12-14 1/2 branched rays; lower profile of head conspicuously arched; short dorsal fin with anterior branched rays shorter than head; 12-16 predorsal scales ; snout without lateral lobe (Froese et al., 2013).
Edaphodon kewai Scientific Name: Edaphodon kewai; Etymology: Its scientific name, kawai, means "fish" in the language of the Moriori, a Pacific tribe who inhabited the islands. Identification: firm, silvery fish with a rigid body. Their backs have black spots or ripple patterns. Young fish up to 25cm have in addition, vertical rows of spots below the lateral line. They are easily distinguished from similar sized kingfish by the high spiny dorsal fin that is joined to the soft rayed portion of the fin (Consoli, 2006).

sampling of water, fishes and sediments were conducted at the River side. Water and sediment samples were collected and preserved.
The samples of fish were collected from the fisher men and were put in plastic bags and refrigerated in the laboratory. Gills and muscular section were removed using a plastic knife and then dried in an oven at 105± 200C for about 24 hours, after which the samples were weighed prior to digestion. The dried gills and flesh of fish species were pounded and milled with a mortar and pestle until a powder was obtained. They were then put in plastic containers and stored in desiccators until digestion. 10 ml. conc. H2SO4 and 5 ml. conc. HNO3 were added. The sample was digested in fume cupboard until the solution volume was reduced to 2 ml. The digestion continued until the solution was colourless. This ensured the removal of all HNO3. The sample was allowed to cool, and 15 ml. of distilled water was added with gentle swirling. 1M NaOH was added drop wise until a pink- brown or colourless solution was produced. The solution was filtered using a Whatman filter paper No. 41, followed by dilution to the mark in a 25 ml. volumetric flask. The water and sediment were digested according to the method prescribed by (Sreedevi et al.,1992), Following the digestion, all samples were analyzed for Cd, Pb, Cr, Mn and Al in ppm level.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The distribution of Cd and Pb in the gills and flesh of Labio rohita and Edaphodon kawai fish species was generally low when compared to WHO ( WHO,1996) recommended levels as portrayed in Table 1 and 2
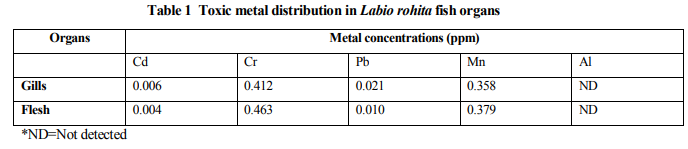
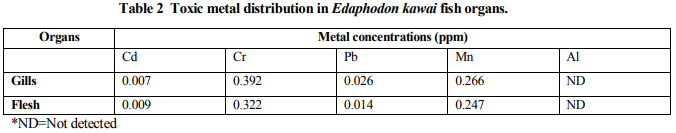
Al is not detected in the organs of all the fish species. This shows that the study area is unpolluted with Aluminium. The concentration of Cr in all the fish species is higher in the gills than in the flesh, while the concentration of Mn in synodyntis is higher in the flesh than the gills. The concentrations of Cr and Mn in all the fish species are higher than the permissible consumption limits. Table 2 shows the concentration of Cr and Mn in gills higher than in flesh of Edaphodon kawai fish species. The specificity of concentrations of heavy metals is irrespective of the locality of fish capture and uptake route of the metals (Alinnor, 2005).
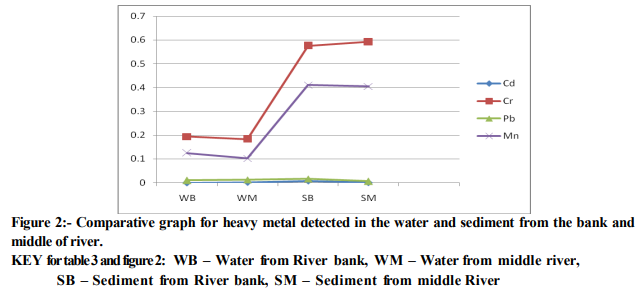
The distribution of the concentration of metals in both water and sediment was observed in the order of Cr>Mn>Pb >Cd as shown in Table 3. The result of this study shows that the concentration of metals in the sediment is higher than in water. Heavy metals entering an estuary in the solid form adhere to sediments whereas, the soluble form is precipitated to increase the sediment metal load and decrease the open water column concentration. The concentration of Cr and Mn in sediment is higher than WHO standard as reported by Bhatia (Bhatia, 2001). The presence of Cr in soaps and detergents used for washing and bathing in the River could be responsible for Cr highest level in sediment. The Cr concentration level above WHO limit is a threat to human health as people were actually using the water from the River for drinking and domestic purpose. The high concentration of Mn in both water and sediment could be attributed to its presence in many types of rock (ATSDR, 2000). It is above the permissible limits for drinking water. The heavy metal detection in the fish, water, vegetation and in other consumables should be carried out in the water bodies and necessary update is required to check the whether the heavy metal concentration is below or above the permissible limits. The detection is compulsory around the globe as the consumption of eatables provided by the water bodies is common in all countries.
CONCLUSIONS
This study revealed that Cr and Mn levels in all the test samples were not only high but above the permissible limits as recommended by World Health Organisation. The bioaccumulation of these metals may pose great hazard to health of humans and animals that rely on the fish and water from River Yamuna. The concentrations of Cd and Pb in all the samples were however, low and below the standard limit. Al was not detected in all of the samples.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The corresponding author is deeply oblidge to University Grants Commission for granting scholarship to pursue Research and Development work in Forensic Science. The authors are thankful to Dr. R. Krishnamurthy, Director of Chemistry Division, Geological Survey of India, Hyderabad, India for permission of Sample analysis in their reputed organization.
References:
1. Ganagaiya, P.I., Tabudrawa, T. R., Suth, R. and Satheesrraran (2001) „Heavy metal contamination of Lami coast al Environment, Fiji, Southern Pacif ic, Journal of Natural Sciences, 19: 24 – 29.
2. Iwegbue, C. M . A., Nwanjei, G. E. and Eguavoen, I. O. (2004)„Distribution of Cadmium, Chromium, Iron, Lead and mercury in water, Fish and aquatic plants from Ewalu River, Nigeria, Advances in Natural and Applied Science Research, 2(1): 72-82.
3. Abou-Arab, A. A. K., Ay esh, A. M ., Amra, H. A. and Naguib, K. (1996) „Characteristic levels of some pesticides heavy metals in imported fish, Food Chemistry , 57(4): 487- 492.
4. WHO – World Health Organisation (1996) Health criteria other supporting information in Guideline for drinking water quality, edition Geneva, 2: 31-388.
5. ATSDR (2000) „ Toxicological profile for manganese Agency for toxic substances and disease Registry, US department of Health and human services, public health services, G. A.
6. Sreedevi, P. A., Suresh, B., Sir aramkrishna, B., Prebhavarhi, B. and Radhakrishriaiah, K. (1992) „Bioaccumulation of Nickel in organs of the fr esh water fish, Cyprinocarpio and the fresh water mussel Lamethdeimar ginalis under lethal and sublethal nickel stress, Chemosphere, 24: 29-36.
7. Alinnor, I. J. (2005) „Assessment of elemental contaminants in water and fish samples from Aba river, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 102(1-3): 15- 25.
8. Bhatia, C. S. (2001) Environmental pollution and control in chemical process industries, First edition. Khanna publishers, Naisarak, Delhi, India.
9. Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2013). "Labeo rohita" in FishBase. May 2013 version.
10. Consoli, C.P. (December, 2006). Edaphodon kawai, sp. Nov. (chondrichthyes: holocephali): a late cretaceous chimaeroid from the chatham islands, southwest pacific. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26(4):801–805.
11. Okoye, B. C. O. (1991) „Heavy metal and organisms in the Lagos Lagoon, International studies, 37: 285 – 295
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License