IJCRR - 2nd Wave of COVID-19: Role of Social Awareness, Health and Technology Sector, June, 2021
Pages: 63-66
Date of Publication: 11-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Red Cell Distribution Width in Hospitalized Covid Patients - A Study in a Tertiary Care Covid Centre in Eastern India
Author: Dasgupta Senjuti, Osta Manish, Talukdar Manas
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The global pandemic caused by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is associated with a high rate of hospitalisation and mortality in severe cases. This emphasizes the requirement of parameters that can predict the progression of the severity of the disease among COVID-19 infected patients. Red cells distribution width (RDW) is a cheap and easily available parameter included in Complete Haemogram and is associated with an increased risk of mortality with various diseases. Objective: The present study aimed to find out if there is any correlation between RDW and the severity of COVID-19 infection. Methods: The study was conducted on 111 admitted patients of COVID 19 diagnosed by RT-PCR, among those who were 18 years or older and not requiring treatment for anaemia. Eighty-seven of the patients were having moderate and 24 severe diseases. Analysis of the EDTA blood samples was done by Sysmex XT-4000i automated haematology analyser. RDW-CV and RDW-SD along with haemoglobin and haematocrit values were recorded. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad QuickCalcs. Results: Mean value for haemoglobin, haematocrit, RDW-SD and RDW-CV were 11.48 \? 2.22 g/dl, 35.18 \? 6.07 %, 47.26 \? 6.50 fl and 15.69 \? 2.12% respectively. Values for haemoglobin, RDW-CV and RDW-SD were statistically significant when compared between moderate and severe COVID-19 infected patients. Conclusion: Patients with raised RDW values are at a significantly higher risk of developing severe COVID-19 disease which can be fatal.
Keywords: RDW-CV, RDW-SD, Covid-19, Correlation, Prognostic significance, Pandemic
Full Text:
Introduction
The global pandemic of the acute respiratory disease called coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been wreaking havoc since December 2019. It is caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The disease has been associated with a high rate of hospitalisation, the requirement of critical care and mortality.1 It has been reported that 26.1 to 32% of confirmed cases become critical and of these severe cases, the fatality rate is as high as 61.5%.2 These figures emphasize the requirement of parameters that predict the progression of the severity of the disease among COVID-19 patients. In third world countries like India, which has a huge population at risk and limited resources in hospitals, it is especially necessary to define simple and feasible predictors of severity.
The complete hemogram is a baseline investigation undertaken in hospitalized patients and one of the common parameters included in the report is red cell distribution width (RDW). An increase in RDW has been reported to be associated with increased risk of mortality in various diseases ranging from heart diseases, pulmonary diseases, sepsis and carcinomas. This observation led to the assumption that RDW may be a potential marker of risk stratification in COVID-19 as well.3
There is a dearth of studies from India regarding the role of RDW in predicting the prognosis of COVID-19. The present study aimed to find out if there is any correlation between RDW and the severity of COVID-19 infection. Even with the advent of vaccines, it is invariably a matter of substantial time before the entire population is protected from the deadly disease. So, the importance of exploration of the role of cost-effective parameters like RDW which has the potential to guide proper triaging of patients cannot be overemphasized.
Materials and methods
A hospital-based study was conducted in a dedicated tertiary care COVID centre of Eastern India for one month. The study had been approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (Ref no. MC/KOL/IEC/NON-SPON/855/12/2020, dated 22nd December 2020). The study subjects were those adult patients who had been admitted in the COVID ward and COVID ICU (intensive care unit) during this period and had tested positive for COVID-19 by RT-PCR (reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction) test. Those patients who were below 18 years of age were excluded. Patients who were already receiving treatment for anaemia were also excluded.
The patients included in the study were then categorized into “moderate disease” and severe disease” based on criteria defined by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and Director General of Health Services, Govt. of India.4 A patient was classified as “severe” when there was the presence of clinical signs of pneumonia along with any one of the following: respiratory rate >30 breaths/min, severe respiratory distress, SpO2 <90% on room air. When the patients suffered from dyspnoea and/or hypoxia, cough, fever, SpO2 <94% (range 90-94%) on room air, respiratory rate ≥ to 24 per minute (range 24-30 breaths/min), they were categorized as “moderate”. Relevant clinical data for each patient was recorded.
At admission, blood samples were collected from each patient in an EDTA vial. Analysis of the blood samples was done by Sysmex XT-4000i automated haematology analyser. RDW-CV (coefficient of variation) and RDW-SD (standard deviation) were both noted for each patient included in the study. The haemoglobin and haematocrit values were also recorded. All collected data were meticulously tabulated.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was done online with the help of Graphpad Quickcalcs software. Unpaired t-test was done to compare the haemoglobin, haematocrit and RDW values between moderate and severe groups of Covid patients (p-value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant).
Results
A total of 120 patients were initially included in the study. It was found that anaemia was present in 6 patients and another 3 patients refused to give consent for the study. So, finally, the study population consisted of 111 patients.
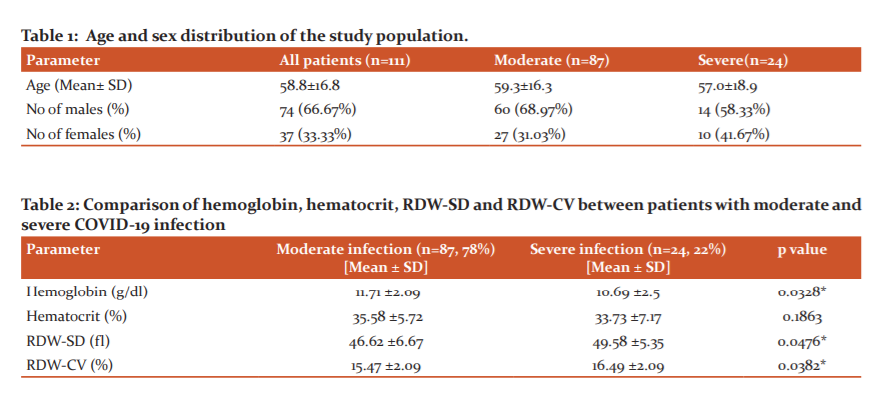
The mean age of the study participants was 59 ± 16.8 years. Among the patients, 74 were males (67%) and the rest (37, 33%) females. The mean value of haemoglobin of these patients was 11.48 ± 2.22 g/dl with values ranging from 5.4g/dl to16.9 g/dl. The mean value of haematocrit was 35.18 ± 6.07 % and the values ranged between 17.8% and 47.2%. The range of RDW-SD varied between 32.7fl and 65.3fl, the mean being 47.26 ± 6.50 fl. The mean RDW-CV was noted to be 15.69 ± 2.12 % with a range between 12.2% and 22.4%.
The number of patients suffering from moderate Covid infection was found to be 87 (78%) and the rest (24, 22%) were diagnosed to have severe disease. The age and sex distribution in the two groups have been shown in table 1. The mean values of haemoglobin, haematocrit, RDW-SD and RDW-CV in both groups have been shown in table 2. The difference in haemoglobin, RDW-SD and RDW-CV between the two groups was found to be statistically significant.
Discussion
SARS-CoV-2 is more contagious than the SARS-CoV that caused the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2003. It is also more infectious than MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus) which was responsible for MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) outbreak in 2012.5 This is perhaps a “once in a century pandemic” mainly due to two reasons – first, even though the case fatality rate is 1%, COVID-19 has proved to be fatal both to healthy adults and the elderly with pre-existing morbidities, and second, the efficient way in which the virus transmits itself both from sick patients and healthy carriers.6
The majority of the patients of COVID-19 have mild disease but some of the affected people undergo rapid deterioration of condition within a span of 7 to 14 days.7 The need for cost-effective parameters to identify patients with a risk of progression to severe disease is apparent from the fact that the mortality rate of severely affected individuals is 20 times more than that in non-severe patients.8
Gong J et al. found RDW to be an important parameter for the determination of prognosis of COVID-19 patients.9 Previous studies have reported a statistically significant increase in RDW in patients with critical illnesses.10,11 It is interesting to note that RDW has been considered to be a prognostic predictor of patients with sepsis.12 Foy BH et al. stated in their study that a raised RDW during admission and increasing value of RDW during hospital stay were both adverse risk factors for COVID-19 patients. They concluded that RDW is a helpful parameter for the risk stratification of these patients.3
The basis of increase in RDW in severe COVID-19 infection has been sought for. RBCs are reservoirs of cytokines.13 In severe illnesses, the deformability of red blood cells (RBCs) is compromised leading to their breakdown and thereby release of the inflammatory cytokines. These mediators may further shorten the life span of RBCs and cause enhanced morphological variations in RBCs, which are reflected in the increased value of RDW.14 Other authors have suggested that inflammatory conditions are associated with the suppression of erythropoiesis. The structural and functional changes of RBCs in such inflammatory states lead to their early demise. IL-1 (Interleukin-1) and TNF-α (Tumor necrosis factor-α) are released and they reduce the synthesis of erythropoietin. These cytokines also play a role in attenuating the response of erythroid precursors to erythropoietin. INF-γ (Interferon-γ) is instrumental in causing apoptosis of erythroid progenitor cells and reduction of expression of erythropoietin receptors.15 So, a combination of early destruction and reduced production of RBCs has been implicated for increased variation of RDW in critical illnesses.
Gong et al. suggested that the symptom of fatigue which is experienced by severe COVID-19 patients may be explained by the raised value of RDW.9 Wang C et al. found both RDW-SD and RDW-CV to be significantly higher in patients with severe COVID-19 infection than those with moderate disease.16 Similar results were found in the present study. Other studies have reported the rise of RDW to be a predictor of the occurrence of complications in COVID-19 infection.17,18
Conclusion
Both RDW-SD and RDW-CV are simple and easily available parameters, which may be used to triage patients with COVID-19 infection. Those with raised RDW values are at a significantly higher risk to develop a severe illness which can lead to serious complications and even prove to be fatal. In developing countries with limited resources, a simple parameter like RDW has the potential to provide life-saving information.
Acknowledgments: The authors thank all patients who participated in the study.
Conflict of interest: Nil.
Funding: Nil.
Author’s contributions
-
Dasgupta Senjuti had contributed by developing the concept and the design of the study. She defined the intellectual content of the paper and undertook a literature search. She also contributed to data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing and manuscript review.
-
Osta Manish had contributed to formulating the design of the study. He undertook literature search and helped in data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing and manuscript review.
-
Talukdar Manas had defined the intellectual content of the paper. He undertook literature search and contributed to data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing and manuscript review.
References:
1. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel corona virus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061-9.
2. Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H, et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centre, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(5):475-81.
3. Foy BH, Carlson JCT, Reinertsen E, Valls RPI, Lopez RP, Palanques-Tost E, et al. Association of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width With Mortality Risk in Hospitalized Adults With SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Netw Open 2020;3(9):e2022058.
4. Clinical Management Protocol for COVID19. https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19.pdf.
5. Gralinski LE, Menachery VD. Return of the Coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses 2020;12(2):135.
6. Gates B. Responding to Covid-19-A Once-in-a-Century Pandemic? N Engl J Med 2020;382(18):1677-9.
7. Feng Z, Yu Q, Yao S, Luo L, Duan J, Yan Z, et al. Early Prediction of Disease Progression in 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Patients Outside Wuhan with CT and Clinical Characteristics. medRxiv 2020: 2020.02.19.20025296.
8. Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 2020;395(20): 507-13.
9. Gong J, Ou J, Qiu X, Jie Y, Chen Y, Yuan L, et al. A tool to early prediction of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a multicenter study using the risk nomogram in Wuhan and Guangdong, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(15):833-40.
10. Wang B, Gong Y, Ying B, Cheng B. Relation between Red Cell Distribution Width and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019:1942078.
11. Havens JM, Seshadri AJ, Salim A, Christopher KB. Red cell distribution width predicts out of hospital outcomes in critically ill emergency general surgery patients. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2018;3:e000147.
12. Mahmood NA, Mathew J, Kang B, DeBari VA, Khan MA. Broadening of the red blood cell distribution width is associated with increased severity of illness in patients with sepsis. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4(4):278-82.
13. Karsten E, Breen E, Herbert BR. Red blood cells are dynamic reservoirs of cytokines. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:3101.
14. Janz DR, Ware LB. The role of red blood cells and cell-free haemoglobin in the pathogenesis of ARDS. J Intens Care 2015;3:20.
15. Sarkar M, Rajta PN, Khatana J. Anemia in Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Prevalence pathogenesis, and potential impact. Lung India 2015;32(2):142-51.
16. Wang C, Deng R, Gou L, Fu Z, Zhang X, Shao F, et al. Preliminary study to identify severe from moderate cases of COVID-19 using combined haematology parameters. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(9):593.
17. Lu G, Wang J. Dynamic changes in routine blood parameters of a severe COVID-19 case. Clin Chim Acta. 2020; 508:98-102.
18. Vaid A, Somani S, Russak AJ, Freitas JDK, Chaudhry FF, Paranjpe I, et al. Machine learning to predict mortality and critical events in COVID-19 positive New York City: Model Development and Validation. J Med Internet Res. 2020;6;22(11):e24018.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License