IJCRR - 2nd Wave of COVID-19: Role of Social Awareness, Health and Technology Sector, June, 2021
Pages: 48-54
Date of Publication: 11-Jun-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Public Opinion and Practices Regarding Social Distancing During COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross Sectional Study in a Major City of India
Author: Kumar V, Rizvi JZ, Saini M, Mishra P
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Indian government appealed to the citizens to adhere to preventive health behaviours including social distancing, wearing face masks, maintaining hand hygiene and others. Social distancing at public places is an important measure to control the spread of disease. Objective: Current study was carried out with the objectives to evaluate public opinion and their practices regarding social distancing in a major city of India. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted using an online questionnaire in the form of Google Forms and the link to the survey was distributed through WhatsApp and also via e-mail. All the eligible participants were requested to forward the questionnaire to as many contacts as possible. A total of 560 participants were approached out of which 452 responded. Data were entered into Microsoft Excel and analyzed using SPSS version 15. Results: Among the total study participants, 92.9% were practising social distancing outside the home. Although most of the participants (79.2%) believed that it provides self-protection from COVID-19, only 43.8% of them were aware of the minimum recommended distance for social distancing. Only 12.6% of participants attended cultural gatherings and 20.4% had visited gym, restaurants or bars. Conclusion: Awareness regarding social distancing was higher among males than females. Only about one-third of the study participants were satisfied regarding social distancing followed in their area. Approximately three-fourths of the participants felt stress and anxiety to be the impact of social distancing. Future prospective studies need to be conducted with a larger sample size and among all classes of society to generalize the study findings.
Keywords: Novel coronavirus, COVID-19, Awareness, Opinion, Practice, Social distancing
Full Text:
Introduction
There is a lot to discover about the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that has led to a pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Recent studies revealed that not only people with symptoms but also those without any symptoms of coronavirus disease were likely to play role in the spread of COVID-19. The disease transmission is well known to occur more commonly through respiratory droplets than through objects and surfaces including doorknobs, countertops, keyboards and toys. Current evidence has suggested that SARS-CoV-2 might stay viable for the variable period on surfaces made from a variety of materials.1 A consistent feature of every national response to the COVID-19 pandemic was issuing the guidelines to the public regarding social distancing. Different countries had different minimum distances which they advised their citizens to maintain.2 Since SARS-CoV-2 emerged as a new virus, currently, pharmaceutical interventions like vaccines are not available. Therefore, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have been the mainstay for the prevention and control of COVID-19. In the United Kingdom as well as other developed nations, the key NPIs being used in relation to the COVID-19 pandemic were social distancing and social isolation besides maintenance of personal hygiene including regular and thorough hand washing.3 A systematic review and meta-analysis including 172 observational studies across 16 countries and six continents were done to investigate the optimum distance required to prevent person-to-person virus transmission. The findings supported physical distancing of 1 m or more.4 In India, an advisory on social distancing was proposed on 31st March 2020 to avoid contact between people.5,6 However; public response to social distancing norms in India was yet to be assessed. This study was conducted with the objectives to evaluate public opinion and practices regarding social distancing in a major city of India.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cross-sectional study was conducted in Lucknow city of India between August-September 2020. The target participants were those above the age of 18 years, who were able to understand the English language and more specifically among those having some digital equipment with internet access, setting a non-probabilistic sample with convenience bias.7 All information regarding the study, participant’s rights and investigator’s contact details were provided on the first page of the questionnaire. Participants were required to give mandatory consent before proceeding to the next page. Permission to conduct the study was obtained from the institutional ethics committee vide letter Ref. no. MIMS/EX/2020/209.
Data Collection tools
An online questionnaire (survey) was developed using Google Forms and the link to the survey was distributed through WhatsApp contacts of the authors of this study and also via e-mails between 26th August to 10th September 2020. All the eligible participants were requested to forward the questionnaire to as many contacts as possible. Respondents that followed the link were first provided with a clear declaration of their rights as participants, including voluntary non-obligated participation or the right to refuse. Further, the confidentiality of the data and strict anonymity of participant’s identity was assured. Non-responders were sent a reminder and the link to the questionnaire at an interval of 15 days. At the end of one month, acceptance to any further response was stopped. The questionnaire was structured into three parts: a) Questions regarding the respondents’ socioeconomic profile including age, gender, religion, education, occupation, marital status, type of family and income; b) Questions on opinion regarding social distancing and c) Questions about their practices to maintain social distancing.
The questionnaire mainly contained closed-ended questions with tick-box options, 5 points Likert scale and yes/no responses. A 5-point scale was used to measure the opinion of the participants about social distancing being followed in their respective areas, in which 1 referred to “highly satisfied”, 2 to “just satisfied”, 3 to “neutral”, 4 to “not satisfied” and 5 to “highly dissatisfied”. The questionnaire also contained few open-ended questions.
Data analysis
Data from the completed surveys were entered into Microsoft Excel and analyzed using SPSS version 15. The data was analysed descriptively by calculating frequency and percentage. Pearson’s Chi-square test, which calculates the value of the chi-square variable and the p-value of that sample, was applied for each relationship between categorical variables.
Results
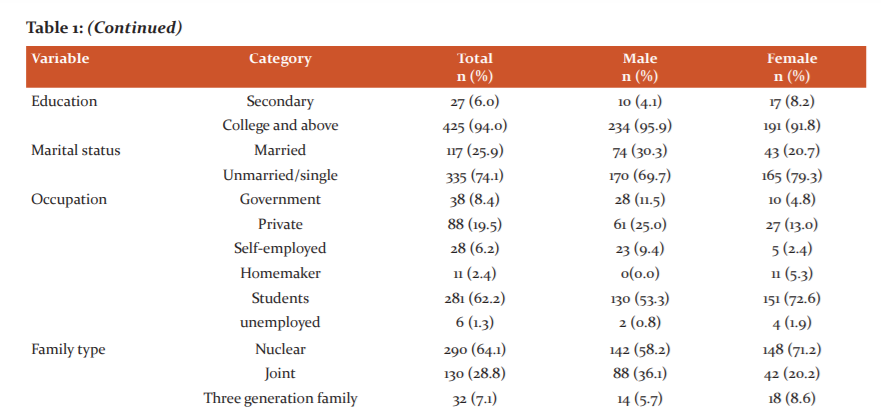
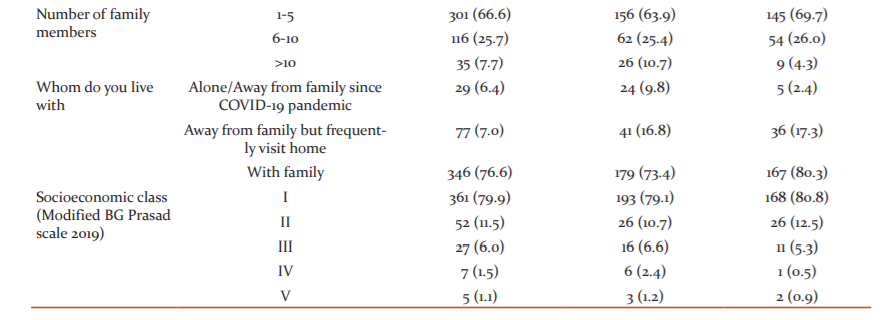
A total of 560 individuals fulfilling the eligibility criteria were approached out of which 452 individuals participated in the study. Hence, the non-response rate was 19.3%. Approximately two-thirds of the participants were aged up to 25 years (64.4%) and more than three-fourth belonged to the Hindu religion (79.0%). Based on educational status, the majority of the participants were from college and above level (94.0%) and the rest have completed secondary level of education (6.0%). Further, out of the total 244 (54.0%) males and 208 (46.0%) females, 234 (95.9%) and 191 (91.8%) were having college and above level education respectively. In terms of marital status, approximately three-fourths of the participants were unmarried/single (74.1%) and about their occupation, 62.2% of the participants were students and 19.5% had a private job. Nuclear family was the common type of family among the participants (64.1%) especially among females (71.2%) than males (58.2%). The socio-demographic details of the participants are shown in Table 1.
As depicted in Table 2, awareness about minimum recommended distance for social distancing was higher in males (48.4%) as compared to females (38.5%) and this was found to be statistically significant (p=0.034). Regarding the impact of social distancing in human life, the majority of the participants believed that it protects COVID-19 (79.2%). Although, other responses regarding the impact of social distancing were stress (35.4%), anxiety (36.3%), drop-in day to day activities (42.9%) and no impact (9.9%). More males (86.5%) than females (81.7%) responded that COVID-19 can be prevented by maintaining required social distancing but it was not statistically significant. Similarly, more males (63.6%) than females (56.7%) had the opinion that eating outside food can spread COVID-19 disease. Most of the participants (83.4%) responded that meetings, conferences, seminars or workshops can lead to the spreading of disease while few participants (10.4%) were not sure about it. Statistically, a significant difference was found between males and females regarding their opinion whether working outside can also pose the risk of COVID-19 to their family members (p=0.017). The majority (90.9%) considered work from home to be a better idea to avoid the COVID-19 spread.
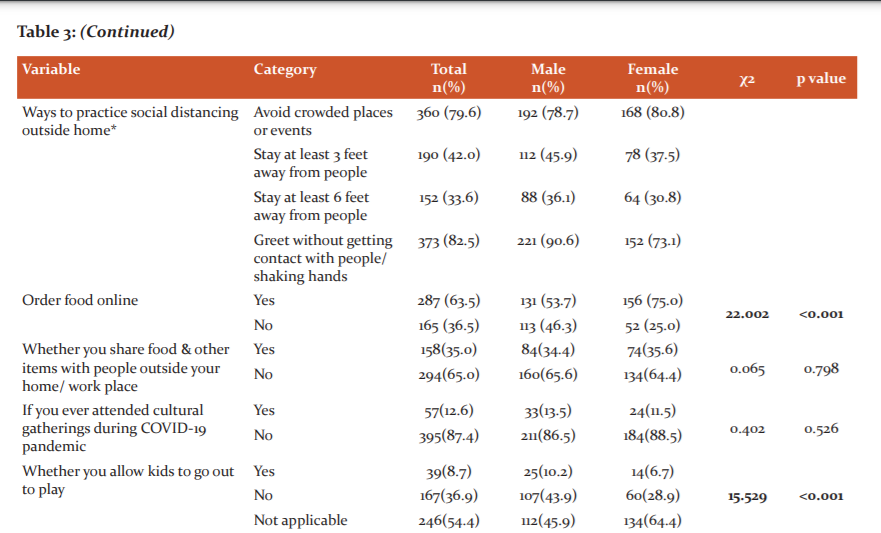
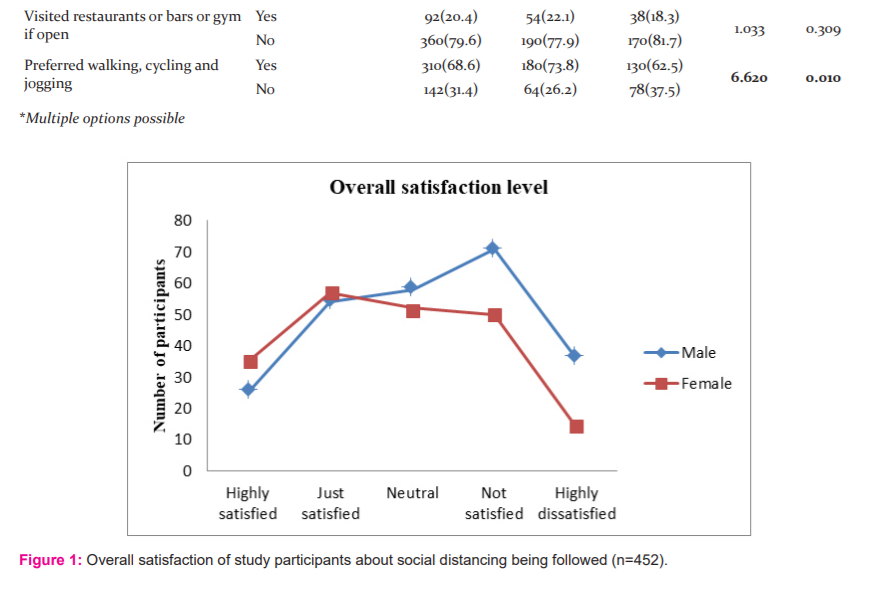
As shown in Table 3, males went out of home for work, business or essentials more than their female counterparts and this difference was found to be statistically significant (p<0.001). However, there was no significant difference between males and females as far as practising social distancing outside the home is concerned. In our study, the majority of the participants avoided crowded places or events (79.6%) and greeted people without shaking hands or any physical contact (82.5%). Less than half of them (45.2%) stayed 3 feet away from people and only 36.2% stayed 6 feet away. More females (75.0%) than males (53.7%) ordered food online and this difference was statistically significant (p<0.001). The majority of the participants did not attend cultural gatherings during the COVID-19 pandemic (87.4%). When asked if they allowed their kids to go out to play, only 8.7% said “yes”. Further, more males than females allowed kids to go out to play and the difference was statistically significant (p<0.001). 20.4% of the participants visited restaurants or bars or gym during the pandemic. Also, there was a statistically significant difference between males and females in terms of preference to walking, cycling and jogging during the pandemic (p=0.010).
When asked about satisfaction with social distancing being followed in their area, only 37.8% of the study participants were satisfied (Table 2). The difference in satisfaction level between males and females was found to be statistically significant (p=0.013) as shown in Figure 1.
Discussion
Awareness and opinion among the public regarding social distancing besides other preventive measures became crucial in controlling the spread of COVID-19, both at regional and national levels since it could affect the current trend in COVID-19 cases across the country. In the current study, the opinion and practices of the eligible population regarding social distancing during COVID-19 were assessed in Lucknow city of India. Our study showed that less than half (43.8%) of the participants were aware of the minimum recommended distance for social distancing similar to a study conducted by Ahmed et al where 41.0% of the participants were knowing the same.8 In the current study, 3.3% of the participants had an opinion that drinking alcohol can prevent COVID-19 which was lesser in comparison to a study conducted by Tomar et al. that reported 14.0% of participants with the same opinion.9 Socio-demographic characteristics especially the association between gender and awareness and opinion regarding social distancing were consistent with the earlier studies on COVID-19.10-12 In this study 92.9% of participants said that they were practising social distancing outside the home which was slightly lesser as compared to a study done by Maheshwari S et alwhere 98.3% participants practised it.10 Another study conducted by Seale Hamong Australian adults13 showed that 66.7% of the 1332 participants kept themselves away from crowded places in comparison to 79.6% of the 452 participants in the current study. Further, in a study conducted by Zhong et al.,14 95.4% males and 96.9% females avoided crowded places which was more than our study that showed 78.7% males and 80.8% females avoiding crowded places or events. Moreover, in our study, 82.5% of the participants avoided getting contact with people during greeting which was lesser as compared to a study conducted by Ha et al. that reported 99.1% of the 464 participants avoiding contact with people especially handshaking and hugging.15 In the current study, 35.4% of the participants believed stress to be an impact of social distancing during the pandemic while in a study done by Singh et al., 28.8 % of participants felt falling in stress or boredom to be associated with COVID-19 pandemic.16 This could be due to loss of a job or decreased social interaction. However, 90.9% of the participants in the current study had an opinion that social distancing was needed even if symptom-free which was lesser in comparison to a study conducted by Singh AK et al. where 98.% participants admitted that social distancing was crucial to stop virus transmission.17 Further, our study revealed that 11.0% of the participants never went out of the home to maintain social distancing while in a study done by Aldarhami et al., 37.8% of the participants never left home during the pandemic of COVID-19.18 In terms of the satisfaction, only around one-third of the participants were satisfied regarding social distancing followed in their area. This could be due to carelessness about social distancing among the general public.
Since data was collected online due to the current situation of the COVID-19 pandemic, by sharing the survey link through e-mail and WhatsApp among more qualified, technically sound people, so results cannot be generalised to the general public. Future prospective studies need to be conducted with a larger sample size and involving subjects from all classes of society to generalize the study findings.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has positively impacted the awareness and opinion of people regarding social distancing in India but the practices of people were not much influenced as can be seen in this study. Findings of the study suggested that awareness regarding social distancing was higher among males than females. This could be due to the slightly better educational, occupational and socio-economic status of males as compared to females. Approximately three-fourths of the participants felt stress and anxiety to be the impact of following social distancing norms and this mindset of participants along with carelessness could have influenced the practices towards social distancing and other guidelines given by the government. There is a need to perform extensive research on the topic with larger sample size and among all classes of society as well as to provide continuous information on the significance of preventive measures so that they could be achieved.
Acknowledgement: The authors are thankful to all subjects who consented to participate in the survey and also those who shared the questionnaire on their social networks. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles and journals from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: None
Source of funding: NIL
Authors’ contribution: All the authors made substantial contributions to the conception, design, analysis and interpretation of data; drafting the article, revising it critically for important intellectual content; and final approval of the version to be published.




References:
-
Cleaning and Disinfection for Households Detailed Disinfection Guidance; 2020. Cdc.gov website https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/cleaning-disinfection.html. Accessed 15 September 2021.
-
Guo ZD, Wang ZY, Zhang SF, Li X, Li L, Li C, et al. Aerosol and surface distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in hospital wards, Wuhan, China, 2020. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(7):1583-91.
-
Williams SN, Armitage CJ, Tampe T, Dienes K. Public perceptions and experiences of social distancing and social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic: a UK-based focus group study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7):1-8.
-
Chu DK, Akl EA, Duda S, Solo K, Yaacoub S, Schünemann HJ, et al. Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-to-person transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2020;395:1973-87.
-
Advisory on Social Distancing Measure because of the spread of COVID-19 disease [Internet]. Mohfw.gov.in. website https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/SocialDistancingAdvisorybyMOHFW.pdf. Accessed September 2021
-
Social Distancing. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 [cited 17 September 2020]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/social-distancing.html
-
Bezerra AC, Silva CE, Soares FR, Silva JA. Factors associated with people's behavior in social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ciência & Saúde Coletiva 2020;25(1):2411-21.
-
Ahmed H, Ahmed A, Saeed MA. Knowledge, attitude and practices (KAP) regarding the prevention against COVID–19 infection at the outset of the outbreak in Pakistan amongst smartphone users. Biomedica 2020;36:267-73.
-
Tomar BS, Singh P, Nathiya D, Suman S, Raj P, Tripathi S, et al. Indian community’s Knowledge, Attitude & Practice towards COVID-19. medRxiv 20092122 [Preprint]. 2020. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.05.05.20092122v1.full.pdf
-
Maheshwari S, Gupta PK, Sinha R, Rawat P. Knowledge, attitude, and practice towards coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among medical students: A cross-sectional study. J Acute Dis. 2020;9(3):100-4.
-
Zhang X, Sun Y, Ye D, Sun Z, Su H, Ni J, et al. Analysis on the mental health status of community residents in Hefei during SARS spread. Chin J Dis Contr Prev. 2003;7:280-2.
-
Jiao J, Tang X, Li H, Chen J, Xiao Y, Li A, et al. Survey of knowledge of villagers in prevention and control of SARS in Hainan Province. Chin Trop Med. 2005;5:703-5.
-
Seale H, Heywood AE, Leask J, Steel M, Thomas S, Durrheim DN, et al. COVID-19 is rapidly changing: Examining public perceptions and behaviours in response to this evolving pandemic. PLoS ONE 2020;15(6):1-13.
-
Zhong BL, Luo W, Li HM, Zhang QQ, Liu XG, Li WT, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices towards COVID-19 among Chinese residents during the rapid rise period of the COVID-19 outbreak: a quick online cross-sectional survey. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(10):1745-52.
-
Ha TH, Schensul SL. Data on early assessment of knowledge, attitudes, and behavioural responses to COVID-19 among Connecticut residents. Data in Brief 2020; 33(2020):1-5.
-
Singh S, Singh RK. Awareness, Attitude and Practices towards COVID-19 among People of Bihar during Lockdown 1.0: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int J Sci Healthcare Res. 2020;5(2):432-43.
-
Singh AK, Agrawal B, Sharma A, Sharma P. COVID?19: Assessment of knowledge and awareness in Indian society. J Public Affairs. 2020;20(4):1-9.
-
Aldarhami A, Bazaid AS, Althomali OW, Binsaleh NK. Public Perceptions and Commitment to Social Distancing “Staying-at-Home” During COVID-19 Pandemic: A National Survey in Saudi Arabia. Int J Gen Med. 2020;13:677-86.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License