IJCRR - 6(9), May, 2014
Pages: 131-137
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
SERUM LEVELS OF ANTIOXIDANT TRACE ELEMENTS ZINC AND COPPER IN SENILE MATURE CATARACT
Author: Manoj B., Shubha Jayaram
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: There is much evidence suggesting that nutrition and nutritional factors, especially the trace elements zinc and copper may play a role in the formation of human cataract, a disease that is on the increase due to the growing percentage of elderly persons in the world population. Objectives: The present study was done to estimate levels of antioxidant trace elements zinc and copper in the serum samples of senile mature cataract patients. Methods: This is a case control study carried out in the Department of Biochemistry, PES Institute of Medical Sciences & Research, Kuppam, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh. 30 senile mature cataract patients and 30 normal age and sex matched controls were selected for the study. Serum zinc and copper levels were measured in above groups. Results: Serum Zinc levels in senile mature cataract patients was 126.63+78.40 \?g/dl and in controls 131.01 + 90.2 \?g/dl. serum copper levels in senile mature cataract patients was 85.82 \? 48.1 \?g/dl and in controls it was94.23 \? 52.4\?g/dl. The zinc copper ratio was found to be 1.47 in senile mature cataract patients and 1.39 in controls. There was no significant difference in the zinc and copper levels between the two groups. Conclusions: The present study showed no significant alterations in the levels of zinc and copper in serum samples of senile mature cataract patients. Further studies are required involving a larger study group regarding the nutritional behavior, correlation of antioxidant enzymes with zinc and copper levels and the effect of smoking and alcohol consumption on the levels of zinc and copper in senile mature cataract patients.
Keywords: Zinc, Copper, Trace elements, Senile mature cataract.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In the recent years there has been a steady rise in the mean age of the global population. A rise in prevalence of senile cataract is one of the consequences of expanding elderly population. Cataract is the most common cause of blindness and visual disability worldwide. At the turn of the century, WHO and the International Agency for Prevention of Blindness launched the Vision 2020: the right to sight initiative(1).The most recent estimates from WHO reveal that 47.8% of global blindness is due to cataract and in South Asia region which includes India, 51% of blindness is due to cataract.(2) The causes of cataract, the world’s largest single cause of blindness are multi factorial. Cataract can include cases developmental in origin or secondary to trauma, systemic diseases, drugs and age related factors. Senile or age related cataract is responsible for more than 80% of all cataracts.(3) . Cataract being age related disorder; it is but natural that its incidence increases as longevity increases. For example, in the west, the incidence of cataract in people over 50 years is 15% while in developing countries it is about 40%.(4).The absolute number of cataract blind would increase from 7.75 million in 2001 to 8.25 million in 2020 due to a substantial increase in the population above 50 years in India over this period(5). There is much evidence suggesting that nutrition and nutritional factors especially trace elements zinc and copper may play a role in the formation of human cataract and also in causation and acceleration of cataract.(6) Recent studies have showed increased lipid peroxidation due to oxidative stress as an important causative factor for cataract. The lens is under constant oxidative stress from reactive species of oxygen. These species can damage the lens cellular membrane and macromolecule, as well as enzymes involved in energy production and membrane transport. With ageing, enzymatic and non enzymatic antioxidant capabilities change. The excessive free radical attack implicated in the development of cataract can be protected by dietary intake of micronutrients with antioxidant capabilities. . It appears possible that in cataract the oxidant antioxidant equilibrium is shifted towards oxidant stress and there might be an increased demand for antioxidant micronutrients (vitamins and trace metals) and enzymes concerned with meeting such oxidant stress. Zinc and Copper are important cofactors for antioxidant enzymes like super oxide dismutase, which is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes which combat against this increasing oxidative stress in senile cataract.(7) Senile cataracts were found to have low levels of Zinc and high levels of Copper(8). Plasma levels of Zinc and Copper are significantly low in cataract patients (9). Trace element analysis of diets consumed by Indians has revealed the inadequacy of copper and zinc as compared to recommend daily intakes. Thus copper and zinc deficiency might play an important contributory role in cataract risk. While some studies have shown normal serum zinc levels, other studies have shown a decreased serum zinc levels and there are very few studies regarding the status of these trace elements in senile cataract in a rural population. Hence the present study to estimate the serum levels of zinc and copper in senile mature cataract patients
OBJECTIVES
1. Estimation of serum levels of zinc and copper in senile mature cataract patients
2. Comparing the same with healthy normal controls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted in Department of Biochemistry, PES Medical College and Department of Ophthalmology, PES Institute of Medical Sciences & Research, Kuppam, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh. The study was approved by the ethical committee of the institution. Total number of subjects taken up for the study was 60, out of these 30 cases, diagnosed as senile mature cataract patients were included as cases.30 normal,age and sex matched healthy subjects were considered as controls.This sample size was arrived at by keeping 5% significance and allowable error of 20%. The subjects for the study were divided into 2 groups namely: Group – I Cases with senile mature cataract. Group – II normal healthy controls
Sample collection
All the samples were collected from the Ophthalmology OPD. After obtaining informed consent, 5 ml of venous blood was collected from cubital vein taking aseptic precautions. The sample was centrifuged for 10 minutes at 3000 rpm and serum was separated. All the samples were analyzed on the same day of sample collection. The following biochemical parameters were assayed: 1. Serum zinc 2.Serum Copper 3. Blood glucose (FBS) All the biochemical parameters were assayed using chem well fully automated analyzer. Estimation of Blood Glucose levels were done to rule out diabetes mellitus .Blood glucose estimation was done by glucose oxidaseperoxidase method.Serum Zinc levels were estimated by nitro PAPS colorimetric method. Nitro-PAPS react with zinc in alkaline solution to form a purple colour complex, and theintensity of the complex formed is directly proportional to the amount of zinc present in the sample at 570 nm(10) . Serum Copper levels were estimated by Di-BrPAESA colorimetric method. 3, 5-Di-Br-PAESA combines with Copper to form a blue–violet complex, the absorbance is measured at 580 nm(11). Statistical methods: the results were tabulated, data was analysed , mean,standard deviation was calculated and the results were compared by using student t test using instat statistical software.
RESULTS
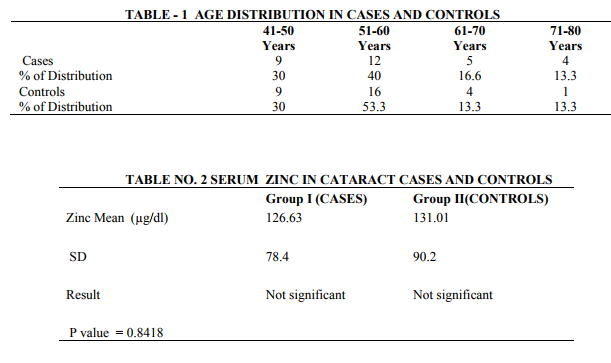
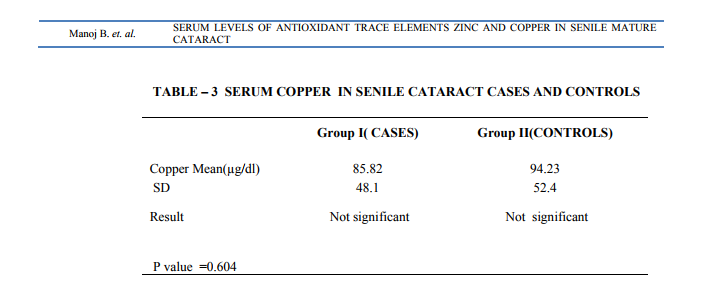
The study was carried out at PES Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Kuppam, Chittoor (District), A.P. The salient findings in the present study are the study of zinc and copper in senile mature cataract patients. In the present study zinc and copper levels were analyzed in serum samples of subjects with senile mature cataract and the levels were compared with normal healthy individuals. In the current study 60 subjects wereselected out of this 30 are senile mature cataract cases and 30 normal healthy individuals. Samples were age and gender matched. More number of cases was found in age group 51 -60 years (40%). This has been shown in table no.1. The mean Serum Zinc value in senile mature cataract patients was126.63+78.40 µg/dl and in controls the mean value was 131.01+ 90.2 µg/dl. The difference between the mean values between the two groups was not statistically significant.(p=0.841). This has been shown in table no.2 The mean serum copper values in senile mature cataract patients was 85.82 ± 48.1 µg/dl and in controls it was 94.23 ± 52.4µg/dl. The means of cases and control values was not statistically significant. This has been shown in table no. 3. The zinc copper ratio was found to be 1.47 in senile mature cataract patients and 1.39 in controls .there was no significant difference between the zinc copper ratio between the two groups.
DISCUSSION
At the turn of the century, WHO and the International Agency for Prevention of Blindness launched the Vision 2020: the right to sight initiative. Since cataract is a major cause of avoidable blindness in the developing countries, the key to the success of the Global Vision 2020: the right to sight initiative is a special effort to tackle cataract blindness(5). It has been observed in most of the studies that the metabolism and status of micronutrients are altered in senile mature cataract patients(1). There is much evidence suggesting that nutrition and nutritional factors, especially the trace elements zinc and copper may play a role in the formation of human cataract, a disease that is on the increase due to the growing percentage of elderly persons in the world population(6).
Serum Zinc
There was no significant difference between zinc values of cases and controls in the present study. Karcioglu(12) in 1982 described the knowledge about zinc metabolism in the eye as fragmentary and quite confusing .This statement is still appropriate as there has been a good amount of controversy regarding the status of these trace elements in serum as well as in the tissue of the eye like aqueous humor and lens and their possible role in senile cataractogenesis. Akyol(13) on a study of cataract patients reported serum Zn concentration within the normal range (80-140 µg/dl) and no significant difference was found. Bhat(14) in a study in India showed that plasma levels of Zn and Cu were lower in patients compared to controls, but Mohan and his colleagues in a larger study were unable to demonstrate such an association(15). IssaNourmohammadi et al(16), have also shown lower serum zinc levels in cataractous patients compared to controls. Indranilchakraborthy et al, have also found a decreased serum zinc levels in cataract patients compared to controls(17). The present study is in concordance with that of Akyol et al(13)and mohan et al(15), who have also reported no significant changes between zinc levels of cataract patients and controls. A study by K. N. Sulochana, R. Punitham, and S. Ramakrishnan(18) has also shown no significant changes in zinc levels of cataract patients and controls. But it has shown significant difference in zinc levels between smokers with cataract and non smokers with cataract. This shows that zinc supplementation may be of help in such patients. Zinc being chiefly an intracellular metal is stored in various intracellular protein and enzymes, SOD (superoxide dismutase) being one of them. Although circulating zinc in plasma and serum often has been shown to indicate human zinc deficiency, it does not always accurately reflect the whole body zinc status. The diagnosis of zinc deficiency is difficult due to the lack of a single specific and sensitive biochemical index of zinc status. The most reliable method for diagnosing marginal zinc deficiency in humans is considered to be a positive response to zinc supplementation. An alternative approach is to use a combination of biochemical and functional tests to evaluate zinc status. Serum or plasma zinc on its own is neither sensitive nor specific. A number of comprehensive reviews have been published on the subject of assessing zinc status in the human population. This may be the reason for the inconclusive nature of serum zinc levels in the present study. There has been a few studies on estimation of zinc levels in cataractous lenses, which have shown increased zinc levels in cataractous lenses. In contrast, some studies have reported a significant decline in lens zinc concentration in the zincdeficient rats. This series of reports linking zinc to the lens suggests that the physiologic function of zinc in the lens should be explored as well as the impact of zinc deficiency on cataract development. Serum copper In the present study Mean Serum copper value in controls is 94.23+52.4 μg/dl where as the value in cataract patients is 85.8 ± 48.1 μg/dl . The difference between the means of patients and controls is not statistically significant. (p=0.60) Our study is concordant with that of Jacques et al(19) who studied serum Cu levels and increased risk of cataract but the association was not statistically significant. andakyol et al(13), and mohan et al(15) who have found the same results. A recent study by K.N.Sulochana et al(18) , has also shown no significant difference in blood copper levels and ceruloplasmin levels between cataract patients and controls. How everbhat et al(14), reported decreased levels of copper in serum samples of cataract patients compared to controls. Conflicting results have been reported in the literature regarding serum copper levels in cataract cases. Several epidemiological studies from various countries on elderly subjects showed lower Zn levels with values ranging from 18% lower levels to 40%. However, whether these concentration changes are the actual cause of cataract development or are the consequence of disease itself must be further studied. Therefore further assessment should be carried out on the safety and efficacy of Zn and Cu dietary supplementation in the treatment of senile cataract The present study has shown a zinc copper ratio of 1.47in cataract patients and 1.39 in control group. Nasiruddin. M et. al(20), using the data compiled from several studies has shown the normal zinc copper ratio to be 1.07 and have observed that the ratio remains normal in cataract cases, which is concordant with the present study. A slightly higher ratio in the present study may be due to smaller group size.
CONCLUSION
The present study has tried to estimate Antioxidant trace elements like zinc and copper in the serum samples of senile mature cataract patients and the comparative study of these parameters with controls . In conclusion no significant alterations of zinc and copper levels were found in the serum of senile mature cataract patients in the present study. Further studies are required involving a larger study group regarding the nutritional behaviour, correlation of antioxidant enzymes with zinc and copper levels and the effect of smoking and alcohol consumption on the levels of zinc and copper in senile mature cataract patients. A complete understanding of the role of zinc and copper at the molecular level is required to plan intervention studies to establish firm criteria for zinc and copper supplementation aimed at prevention of senile mature cataract.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of all the patients who have taken part in the project. This study was conducted with support from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) as Short Term Studentship (ICMR-STS) program for Manoj B. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
REFERENCES
1. Foster A. Vision 2020: The Cataract Challenge. Community Eye Health 2000;13:17-21.
2. World Health Organization. Global initiative for the elimination of avoidable blindness: An informal consultation. WHO/PBL/97.61. Geneva: WHO; 1997.
3. Evans J, Minassian DC. Epidemiology of Age-related Cataract. J Comm Eye Hlth 1992;9:2-6.
4. Ohrloff C. Epidemiology of senile cataract. In Hockwin O, Sasaki K, Leske MC (eds). Risk factors for cataract development. Karger: Basel, 1989.pp1-5.
5. Murthy G, Gupta SK, John N, Vashist P. Current status of cataract blindness and Vision 2020: The right to sight initiative in India. Indian J Ophthalmol 2008;56:489-94
6. West Sk, Val Madrid CT. Epidemiology of risk factors for age related cataract. Survophthalmol 1995;39:323-34.
7. Minassian DC, Mehra V. 3.8 million blinded by cataract each year: Projections from the first epidemiological study of Incidence of Cataract Blindness in India. Br J ophthalmol 1990;74:341-3
8. Nath B, Srivastava SK, and Singh K. accumulation of copper and inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase activity in human senile cataractous lens. Indian J Exp Biology. 7:25-26,1969.
9. Bhat K. S. Nutritional Status of Thiamine, riboflavin and pyridoxine in cataract patients. Nutr Rep Int. 36:685-692,1987.
10. Makino T .A sensitive, direct colorimetric assay of serum zinc using nitro-PAPS and using micro well plates .Clinchem acta1991; 197:209-220.
11. Abe, Akita, S. Yamashita, and A. Noma. "Sensitive, direct colorimetric assay for copper in serum."Clinical chemistry 35.4 (1989): 552- 554.
12. Karcioglu ZA: Zinc in the eye. SurvOphthalmol 1982;27:114–122.
13. Akyol N, Deger D, Keha EE, Kilis S, et al. Aqueous humor and serum zinc and copper concentrations of patients with Glaucoma and Cataract. Br. J. ophthalmol.1988; 74:661-2.
14. Bhat K. S. plasma calcium and trace metals in human subjects with mature cataract. Nutr. Rev. Interanat. 1998:37:157-63.
15. Mohan M. Study design and data of WHONPCB blindness survey-1986-88. In Lim ASM (ed): World’s major Blinding conditions. Published by XXVI international congress.Opthalmol. Singapore, 1990, PP. 182187.
16. IssaNourmohammadi, Mansour Mirsamadi. Serum zinc and copper concentration in human age related cataract. MEJAA, Nov 2004, vol 1, issue 2 :10-14.
17. IndranilChakraborty, SanjoyKunti, MousumiBandyopadhyay, AnindyaDasgupt, Gopal Deb Chattopadhyay and SandipChakraborty. Evaluation of serum zinc level and plasma and activity in senile cataract patients under oxidative stress. Indian J. Clin.Biochem., 2007; 22: 109-13.
18. K.N.sulochana, R. Punitham, S. Ramakrishnan, Effect of cigarette smoking on cataract: Antioxidant enzymes and constituent minerals in the lens and blood of humans. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 2002; 34: 428-431.
19. Jacques PF, Hartz SC, Chylack LT Jr, et al. Nutritional status in persons with and without senile cataract: blood vitamins and minerals levels. Am J clinNutr. 48:152-158,1988.
20. Nasiruddin, M. "XXXV Annual Conference of the Indian Pharmacological Society, Gwalior, November 26-29, 2002, Abstracts of Research Papers (Part-Vi)." Indian Journal of Pharmacology 36.1 (2004): 54
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License