IJCRR - 6(11), June, 2014
Pages: 18-23
Date of Publication: 13-Jun-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF PERCEPTION OF NURSES ON WORKING ENVIRONMENT IN TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN MUMBAI
Author: Vijaykumar S. Singh, Smita Chavan, Subita Patil, Vikas Jaiswal, Sagar Kamble
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Nurses forms an important health care delivering force in tertiary care hospitals.Positive working environment in hospital has enhancing effect on work efficiency and quality of care provided by nurses. Aim: The aim was to find out perception of nurses on working environment and related problem of tertiarycare hospital in Mumbai. Objectives: To know the perception of nurse on problems related to work load, patient related problems and problems due to lack of resources. Materials and Methods: A work site cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted amongst 202 consented nurses of tertiary care hospital in Mumbai. Data was collected by personal interview. Pre-designed semi-structured standardized interview schedule consisting of questions related to Socio-demographic factors, work load, patient related problems and to lack of resources included. Results:In this study 104/202(51.5%) subjects always perceived work load was too much. 84/202 (41.6 %) subjects had to always compromise quality of work because of work load.47/202 (23.3%) subjects always face difficulty in dealing with serious patient33/202 (16.3%) always face difficulty when patient do not recover for long time.136/202(67.3%) subjects always feel that the staff was inadequate to accomplish work properly.97/202 (48.0%) subjects always feel that equipments and supplies were never adequate. Conclusions: Components of working environment in the present tertiary care hospital play a majorrole interfering with work efficiency of nurses and patient care. Proper training and management support needed to make service successful perceived by nurses.
Keywords: Working environment, work load, tertiary hospital, work efficiency performance, patient care.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Working environment of the hospital is sum of prevailing external factors which has bearing on the working population. Nursing profession is recognised as stressful profession involvesskilful and multitasking work which include to follow orders of clinicians, timely management of patients, the wards, getting work done by class four employees, communicating with patient, relatives, higher authorities and administration etc. Nurses face difficult working conditions with limited resources, health hazards, over work and certain special situation causing detrimental effects on physical, mental and social health.1 Healthy work environment is very important to potentiate the work efficiency and for providing quality care.A number of studies conducted within past decade have shown that the nurses in hospitals with better care environments reported more positive job experiences and fewer concerns
with care quality.2 This study was undertaken in tertiary care public hospital which has speciality departments such as Medicine, Surgery, Paediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynaecology etc. and super speciality departments such as Neurology, Cardiology, Neurosurgery, Plastic Surgery etc. The hospital is catering to the large number of population, often exceeding to its bed and human resource capacity which result in overburdening of work on nursing staff. Thus the present study was conducted among nursing staff to explore different components in hospital care environment which may have influence on work efficiency of nurses and the quality of patient care. Outcome of this study might enable concern authority to provide the appropriate environment, supervision, guidance and training programs and to evaluate the additional human resource need for healthcare facilities.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This is a cross-sectional, questionnaire based, observational study carried out in a tertiary care hospital under Municipal Corporation, Sion, Mumbai, India. The sample size comprised of 202 staff nurses, Permanent employee of place of study, working at least for two years, were selected using a convenience sample. Thestudy toolwas a Pre-designed,Pre-tested, semi-structured questionnaire. Confidentiality was assured interview schedule consisting of questions related to Socio-demographic factors, questions related to work load, problems related to patient care and lack of resources are included. The ethics committee of the institute approved the study. The pilot study was done in which questionnaire was pre-tested on subsample of 20 nurses. None of the subject was forced or reimbursed. The Subjects who were on any leave or in probation period or on contractual basis and staff nurses intermittent night duties every 3 months were excluded from the study Data was collected by personal interview method by visiting the subjects at their workplace by prior appointments i.e. wards, operation theatres, and departments or at nursing station. The care was taken that they do not get disturbed during emergency care of patients. Attempts were made to establish good rapport with the study subjects by personal contact. The objectives and of the study were explained in details to the subjects in the language understand best and written informed consent is taken from the participants. Even after prior appointments, if subjects were found busy in their emergency work, care was taken not to interrupt them in their work and again suitable time was taken. Study tool was filled personally by interviewing the subjects. Recruitment and collection of data continued for six months and the process was carried out by the author and one assistant professor and one second year resident medical officer who were previously trained. The details regarding socio-demographic factors, work load problems, patient related difficulties, work place problems, problems due to lack of resources, conflict with other health professionals were obtained from study subjects. Lastly study subjects were asked to give their suggestions too
RESULTS
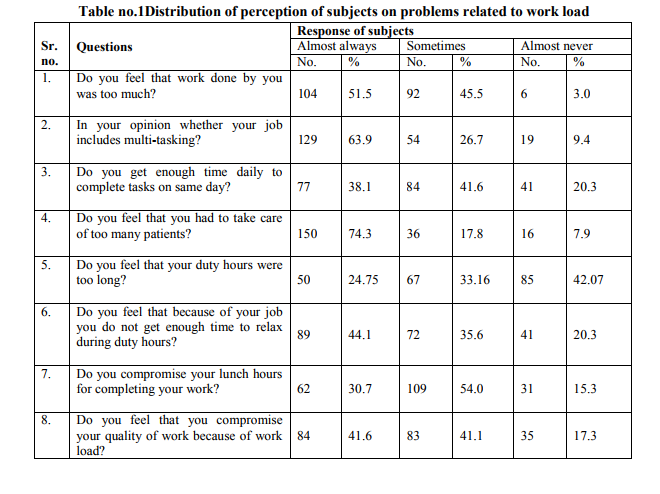
In relation to workload problems it was observed from table no.1 that104/202(51.5%) subjects always perceived work done by them was too much.129/202 (63.9%) of subjects feel that their job is multitasking.41/202(20.3%) subjects felt that they never get enough time to complete task on the same day.150/202(74.3%) feel that they always had to take care of too many patients.50/202(24.75%) feel that their duty hours were always too long and 67/202 (33.16%) feel the same sometimes.89/202 (44.1 %) of subjects always feel that they do not get time to relax during duty hours and72/202 (35.6%) feels the same sometimes.62/202 (30.7%) subjects always compromise lunch hours for completing their work while 109/202 (54%) do the same sometime.84/202 (41.6%) subjects had to always compromise quality of work because of work
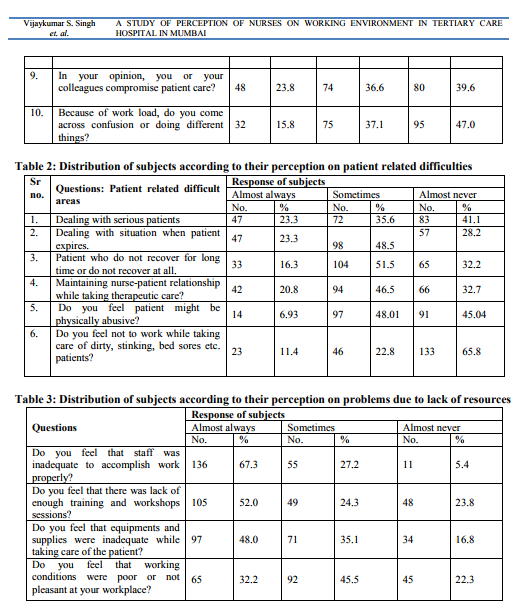
load.48/202 (23.1%) perceived that they or their colleagues always compromise patient care. 32/202 (15.8%) always came across confusion for doing different things because of work load and 75/202 (37.1%) sometimes while97/202(47%) never came across confusion. Patient related problems as perceived by study subjects shown in table no.2, it shows that 47/202 (23.3%) subjects always and 72/202 (35.6%) sometimes face difficulty in dealing with serious patients.47/202(23.3%) subjects always 98/202 (48.5%) sometime face difficulty in dealing with situation when patient expires.33/202 (16.3%) always and 104/202 (51.5%) sometimes face difficulty when patient do not recover for long time 42/202 (20.8%) always and 94/202 (46.5%) sometimes face difficulty in maintaining nursepatient relationship.14/202 (6.93%) always and 97/202 (48.01%) sometimes feel that patient might be physically abusive. 23/202 (11.4%) always and 46/202( 22.8) sometimes feel not to work while taking care of dirty, stinking, bed sores patients. As regards with perception on lack of resources, observation in table no.3 shows that136/202(67.3%) subjects always feel that the staff was inadequate to accomplish work properlyand 55/202 (27.2%) sometimes and 11/202 (5.4%) never feels the same.105/202 (52.0%) subjects always feel that there was lack of enough training and workshops sessions and49/202 (24.3%) sometimes while48/202 (23.8%) never feels the same 97/202 (48.0%) subjects always feel that equipments and supplies were always inadequate while taking care of the patient 71/202 (35.1%) sometimes while34/202 (16.8%)never feels the same 65/202 (32.2%) subjects always feel that working conditions were always poor or not pleasant at workplace and92/202 ( 45.5%) sometimes while 45/202 (22.3%) never had such feeling
DISCUSSION
As shown in Table no 1, 51.5% subjects always perceived work done by them was too much and 74.3% perceived that they always had to take care of too many patients. 44.1 % of subjects always perceived that they do not get time to relax during duty hours.30.7% always and 54% sometimes had to compromise lunch hours for want of completing their work. 41.6% accepted that they had to always compromise quality of work because of work load. 15.8% of the subjects always and 37.1% sometimes came across confusion because of work load. Lambert V.A. Lambert C.E. Ito M. (2002) in their study showed workload on the first step of regression analysis and it was accounted for 1.7%.3 This study also support current study
findings of workload was a major factor.A study by Al-HussamiM et al4 supports the findings of present study who examined concentration as one of the psychological concepts related to work environment that 28% of respondent felt that their concentration is low. The nurses experience physical and mental workload since their job involves standing, walking, bending, lifting and making decisions about patient care and other administrative work. All this leads to exhaustion, which disturbs concentration.103 Present study finding also comparable with study by O. Orji et al which revealed that 83.3% of health care workers had work-related stress.5 Table no 2 shows that23.3% subjects always face difficulty in dealing with serious patients and in case of death of a patient. 16.3% when patient do not recover for long time.20.8% in maintaining nurse-patient relationship and 6.93% always feel that patient might be physically abusive while11.4% always feel not to work while taking care of dirty, stinking, bed sores patients.The survey of 2,00,000 physicians and nurses from 130 general hospitals in Netherlands revealed that 90% have suffered mental and physical violence, 78% have sexual intimidation and over 50% hospital staff have been threatened with weapons.6 Our study finds less percentage of perception of physical violence which may be due to poor patients taking treatment from this public hospital who are usually helpless and dependent on hospital staff. The above table 3 shows that out of total study subjects (n=202), majority i.e. 67.3% feel that staff was always inadequate to accomplish hospital work.48.0% feel that equipments and supplies were always inadequate while taking care of the patient.52.0% feel that there was always lack of enough training and workshops sessions. 32.2% feel that working conditions were always poor or not pleasant at workplace.Study by Pratibha Kane indicated that 66% percent of the nurses were interested in training for new skills and 60% desired more training for their present job. Ongoing training and job rotation are yet not an established initiative taken up by HR mangers in hospitals.7The current study findings about perception of lack of enough training sessions supported by this study. Our study shows even higher percentage for need of training and workshop sessions.Similar findings like current study stated by Nikbakht8who found that Iranian nurses were confronted with many difficulties in two domains: (1) difficulties relating to work settings, such as personnel shortages, heavy workloads, unclear tasks, lack of registered and auxiliary nurses, equipment deficiencies and low salary; and (2) difficulties relating to a poor public image and a low social status of nurses8 .In India, some of the issues related to nurse retention still remain to be tackled – job insecurity for the contractual staff, low pay in both the government and private sectors, lack of a conducive work environment and infrastructure facilities.9 This statement of WHO strongly support our current study findings related to problems due to lack of resources.
CONCLUSION
Workload of the indoor patients in the hospital is the one of the main factor as perceived by the nurses. Dealing with serious, chronically ill and in case of death of patients is another major factor perceived by them causing physical and mental stress. Inadequate staff, inadequate equipment and supplies make the work of the nurses and working conditions poor and unpleasant. It can be concluded that components of working environment in the present tertiary care hospital play a major role interfering with work efficiency of nurses and patient care.
RECOMMENDATIONS
There should be limit of admitting patients in municipal hospitalswhich distort the nurse patient ratio or by increasing indoor facilities including increasing the nursing post so that more patients can be admitted. In service training in personal management, communication skill, stressmanagementand support by the administration needed to make service successful perceived by nurses.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors expresses the sense of gratitude to Dean, the staff and research society,Prof and head,Dept of community medicine, Matron and nursing schoolof LTMMC and GH, Sion, Mumbai for permitting, ethical clearance and helping to do the above study. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in the references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals, books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
REFERENCES
1. Occupational Health Hazards Of Hospital Staff Nurses. Part II Physical, Chemical And Biological Stressors. Triolo PK, American Association of Occupational Health Nurses Journal 1989 July; 37(7); 274-9.
2. Aiken LH et al, Effects of nurse staffing and nurse education on patient deaths in hospitals with different nurse work environments. J NursAdm, volume 42, page S10.
3. Lambert V.A. Lambert C.E.. Ito M.. ‘Work place stressors, ways of coping and demographic characteristics as predictors of physical and mental health of Japanese hospital nurses’, Int. J. Nurse Stud. 2004: 41: 85-97.
4. Al-Hussami M., Saleh M.Y.N., Abdalkader R.H. andMahadeen A.I. Predictors of nursing faculty members organizational commitment ingovernmental universities, Journal ofNursing Management(2011), 19, 556–566.
5. O. Orji. O. B. Fasubaa. Occupational health hazards among health care workers in an obstetrics and gynaecology unit of a Nigerian teaching hospital 2002; Vol. 22, No.l:Pp75-78.
6. Franx Occupational Health And Safety Management. Nurses article pg 10-11. 2005
7. Pratibha Kane ,Stress causing psychosomatic illness among nurses, American Journal of Nursing 2009 Vol 13 Issue 1: Pp 28-32
8. Nikbakht , Emami, ParsaYekta, Nursing experience in Iran, International Journal of nursing Practice, 2003(9):78-85
9. Hewitt JB et al 1993 Health hazards of nursing: identifying workplace hazards and reducing risks. A WHO NNS Clinical Issues in Perinatal And Women’s Health Nursing 4(2): 320-7
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License