IJCRR - 6(23), December, 2014
Pages: 54-58
Date of Publication: 10-Dec-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF HEALTH INTERVENTION ON GLYCEMIC STATUS OF DIABETIC PATIENTS
Author: M. S. K. Swarupa, Sudha Bala, Vimala Thomas, A. Chandrasekhar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: Diabetes mellitus (Type 2) has been an emerging public health problem in India. Lifestyle related risk factors play an important role in the development of diabetes and its related complications. Therefore, a study has been taken up with an objective to assess the effect of health intervention on glycemic status of diabetics. Methods and material: A descriptive epidemiological interventional study conducted over a period of three months at urban health centres of Deccan College of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad. During this study a health intervention on lifestyle modifications was given and its impact was assessed on the fasting blood glucose levels of already known patients of Diabetes Mellitus. Statistical analysis: Data was entered in Microsoft excel 2007 and interpreted by using SPSS 20. Mean, percentages and paired t test applied wherever appropriate. Results: A total of 104 diabetic patients were enrolled in our study. Majority of them were females (71.15%), belonging to upper lower socioeconomic status according to BG Prasad s classification. Family history of diabetes mellitus was found among 76.42% with higher body mass index and about 72.12% adopted sedentary type of lifestyle. There was a significant improvement in lifestyle and self care practices of the diabetic patients after health intervention. The mean fasting blood sugar level in pre intervention phase was 177.29 \? 72.01 mg/dl. Post intervention, this decreased to 133.29 \? 36.81 mg/dl which is statistically significant. Conclusions: Diabetic patients have to be educated about various risk factors causing diabetes and their modification measures by simple effective strategies to reduce the blood glucose level which has got a greater impact on further development of complications associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes mellitus, Glycemic status, Health intervention
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Many developing countries including India is facing “dual burden of diseases”- both communicable and non communicable disorders due to the epidemiological and the nutritional transition. Among these non communicable diseases, Diabetes Mellitus is one of the most daunting challenge. According to WHO the top three countries in terms of number of type 2 diabetes mellitus individuals with diabetes are India (31.7 million in 2000; 79.4 million in 2030), China (20.8 million in 2000; 42.3 million in 2030) and the USA (17.7 million in 2000; 30.3 million in 2030).1 With this increasing prevalence, type 2 diabetes is posing a major public health problem affecting both mortality and morbidity. Majority of the disability adjusted life years are lost in developing countries due to limited health care budget.2 The rise of diabetes is largely attributed to the epidemic of obesity, unhealthy dietary practices, sedentary lifestyle and genetic factors. It may be a life threatening disease with associated complications such as coronary artery, cerebrovascular, retinal, neurological and renal diseases; but the main initiating factor is the exposure of tissues to chronic hyperglycaemia.3 These are amenable by simple preventive strategy such as lifestyle health education component to reduce the plasma glucose levels. Majority of these education programs including Indian diabetes programme have typically focussed on weight loss, greater intake of fibre content, reduced intake of saturated fat and increased physical activity.4 Hyderabad city, a capital hub of diabetes in India,5 has a higher share of urban slums in Telangana always goes ignored. It is therefore, very important that effort should be made to identify the area that needs urgent attention to modify the lifestyle and promote self care practices about diabetes and its complications. Therefore, the objective of this study was to assess the impact of intervention measures like health education, dietary advice and encouraging physical activity on the glycaemia status of diabetics.
METHODOLOGY
The study was conducted at two Owaisi urban health centres namely Bhavani Nagar and Hassan Nagar, a field practice area of department of community medicine of Deccan College of medical sciences, Hyderabad, India. It was a four months interventional study conducted from October 2012- December 2012.All the type 2 diabetic patients attending the urban health centres over a period of two weeks were interviewed using semi structured interviewed schedule which was relevant to the study. This interview schedule was pretested by pilot study on twenty patients attending outpatient clinic at Owaisi hospital. A questionnaire schedule was developed after pilot test and the necessary changes were incorporated. Voluntary consent form was prepared in urdu language. Among the total one thousand and hundred patients attending the urban health centre during two weeks, identified existing cases of type 2 diabetes of at least one year duration and on treatment for at least an year among resident adults>20 years of age based on history of disease or history of taking anti diabetic drugs or documentary proof (prescription or report of blood sugar levels) of type 2 diabetes were included ie a total of hundred and four patients were taken. The information was collected about various socio demographic factors, family history, addictions, duration of disease, physical activity(daily activity + exercise), associated disorders, complications, symptoms, lifestyle, self care factors by the investigator. Height, weight, blood pressure and fasting blood sugar were measured using appropriate technique. Body mass index was calculated as a measure of obesity as per Asian guidelines of obesity. At the same sitting educational intervention with counselling was done on one to one basis in local vernacular Urdu language. A pamphlet with health education information regarding diabetes printed in Urdu is distributed to all patients. After a period of three months, their improvement in their lifestyle and self care factors were assessed using the same proforma for over two weeks along with their fasting blood sugar level after intervention at urban health centre. Intervention measures include: 1. Health education: patients were given basic information about diabetes and its complications and how to control blood sugar levels and prevent its complications. Patients were given information about hypoglycaemia, how to prevent it and what to do during the episodic spell. 2. Dietary advice: they were given information on different types of foods which are beneficial or harmful, spacing of meals and frequent intake of small quantity of food. Restriction of sweets and oily food. 3. Physical activity: Patients were asked to practice at least 45minutes of walk or practicing yoga at regular intervals for thrice a week on daily basis were advised. 4. Self care of foot, cutting down the addictions, importance of regular eye checkups and importance of regular treatment.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The collected data was numerically coded and entered in Microsoft excel 2007 and then analysed using SPSS version 20. The statistical measures obtained were proportions, percentages, mean scores and paired t test wherever appropriate to see the association between various parameters both pre and post intervention.
RESULTS
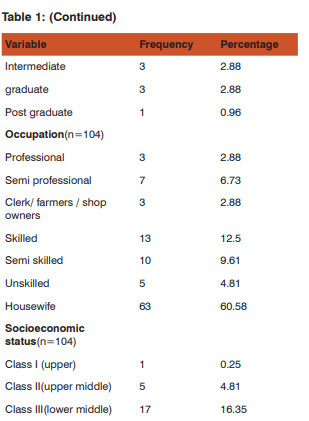
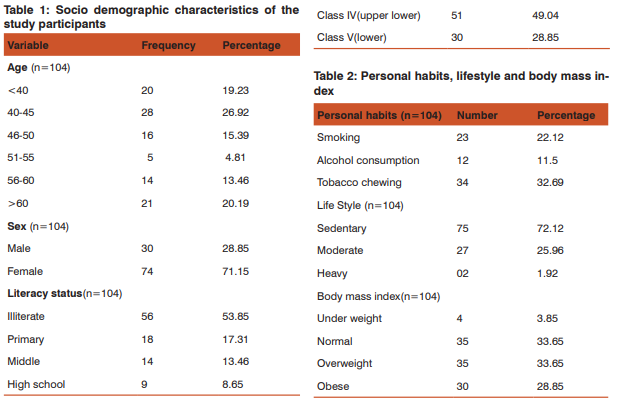
Socio demographic characteristics: A total of 104 diabetic patients were examined, consisting of 30(28.85%) males and 74(71.15%) females. Majority of patients 28(26.92%) were in the age group of 40-45 years with the mean age of patients was 50.21± 11.32yrs ; 51(49.04%) subjects were from upper lower socio economic status(according to Modified BG Prasad classification). Most of the patients 56 (53.85%) were illiterate. Housewives accounted the highest 63 (60.58%), followed by skilled workers 13 (12.5%) and semi skilled 10 (9.6%);family history of diabetes was reported by 80(76.92%). Table 1 Personal habits, life style and Body Mass Index: Among these diabetic patients more than half of them 69(66.39%) had personal habits such as tobacco chewing 34(32.69%), 23(22.12%) were smoking and 12(11.50%) consumed alcohol. Majority of them had adopted sedentary lifestyle 75 (72.12%) followed by moderate lifestyle 27(25.96%). As per Asian standards classification of Body Mass Index, about 35(33.65%) were overweight and 30(28.85%) were obese. Table 2 After assessing their knowledge about symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus, it was found that 62(59.61%) had polyphagia,54(51.92%)
had fatigue,48(46.15%) had Polyurea,45(43.27%) polydypsia and 37(35.58%) had weight loss. Regarding complications, it was found that peripheral neuropathy was found among 56(53.81%), diabetic retinopathy among 13(9.62) and cardiovascular diseases among 10(9.29%).
Modification factors in pre and post intervention phase:
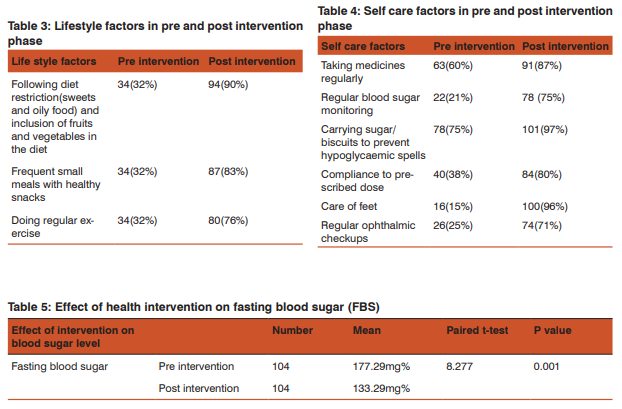
Table 3 and 4 show significant improvement in lifestyle factors and self care adoption after interventions. Diet restriction has improved from 32% (pre intervention) to 90% (post intervention); frequent meal intake from 32% (pre intervention) to 83% (post intervention); regular exercise from 34% (pre intervention) to 76% (post intervention); regular intake of medicine from 60% (pre intervention) to 87% (post intervention; regular blood sugar monitoring from 21% (pre intervention) to 75% (post intervention; treating hypoglycaemic spells from 75% (pre intervention) to 87% (post intervention); care of feet from 15% (pre intervention) to 96% (post intervention) and compliance to the dose from 38% (pre intervention) to 80% (post intervention).
Effect of health intervention on fasting blood sugar (FBS)
Table 5 depicts the mean fasting blood sugar level in pre intervention phase was 177.29 ±72.01 mg/dl. After health intervention the mean fasting blood sugar level decreased to 133.29 ± 36.81 mg/dl which is statistically significant (P value 0.001).
DISCUSSION
The present descriptive epidemiological interventional study was conducted at an urban health centre in Hyderabad, which is a field practice area of department of community medicine, Deccan College of Medical Sciences. It was conducted over a period of three months selecting 104 known cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus by adopting simple random sampling method. Total 104 diabetic subjects were examined with mean age of 50.2yrs.In the present study, majority of the diabetic patients attending the urban health centre were females(71.15%). Also noted that most of them (49.04%) belonged to upper lower socio economic status as per modified BG Prasad’s classification and about 53.85% were illiterates. Housewives catered the majority (60.58%), followed by skilled workers(12.5%) and semi skilled workers (9.6%) respectively. Similar findings were observed by George. H et al in their study conducted among diabetics attending secondary care hospital in Vellore, Tamil Nadu where the majority attending the centre were females (61%) and the mean age of the participants was 54.45 years (SD 6.1). Of the study participants, 25.5% had not received any formal education. Housewives accounted for 45% of the study participants, unskilled workers 17% and farmers, shop owners, and clerical job holders 11.3%.6 It was observed in our study that 76.92% of them had positive family history of diabetes mellitus and had personal habits such as to tobacco chewing 34(32.69%), 23(22.12%) smoking and 12(11.50%) alcohol consumption. Priya D et al had found 44.2% of them had family history of diabetes mellitus among diabetics attending diabetic clinic at government medical college, Nagpur, Maharashtra. In the same study they also found current tobacco chewing, smoking and alcohol consumption among 19%, 10.2% and 30.3% respectively.7 According to Asian classification of nutritional status we found 33.65% of them over weight and 28.85% of them obese. Similarly Hemant Mahajan et al in their study conducted in urban slums of Mumbai depicted total 178 (59.3%) had Body mass index (BMI) more than or equal to 25 kg/m2.8 Present study had observed significant improvement in lifestyle, self care practices and fasting blood glucose status of patients after health intervention. Bhuwan Sharma et al has conducted study in eastern suburb of Mumbai in the field practice area of Grants medical college had observed an improvement in their lifestyle and self care factors after health intervention such as maintaining diet from pre intervention 28.68% to post intervention 56.62%; doing regular exercise from 33.46% to 43.04% ; regular treatment from 59.2% to 81.98%; regular checking of blood sugar levels from 20.22% to 31.61% and treating hypoglycaemic spells from 12.5% to 26.11%.9 Similarly Sultan R Ahmed also found significant improvement in lifestyle, self care practices and glycaemia status of patients (both fasting and post prandial blood glucose levels) after health intervention.10 Balagopal et al in their diabetes prevention and management program me in rural India found that the lifestyle modifications were effective in reducing some of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes and improving self management of the disease.11 Englert.H observed that 35% of fasting blood sugar reduction among diabetics in their 4-week, communitybased intensive educational lifestyle intervention programme (CHIP) at Rockford, Illinois, USA.12
CONCLUSIONS
From the present study we can conclude that significant improvement in the glycaemic status can be achieved among diabetic patients by health interventions such as health education, dietary advice and encouraging physical activity to bring out lifestyle and self care modification. One of the limitation of the study was Glycosylated HB (Hb1Ac) which is a good indicator of glycemic control but in this study it is measured with only fasting blood sugar level due to financial constraints. These findings highlight the need of health intervention programme to improve the quality of life and prevent further complications associated with Type 2Diabetes Mellitus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors sincerely thank Dr Sultan Rizwan Ahmed, Associate professor, Department of Community Medicine, Deccan College of Medical Sciences for his immense support in the study. Authors would also thank Mohammed Faiyazuddin, Medico social worker, Deccan College of Medical Sciences for his contribution in health education among diabetic patients in local language and all the staff members of urban health centre’s for their cooperation. Authors humbly acknowledge all the diabetic participants for their cooperation in the present study
References:
1. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047-53
2. Jonsson B. The economic impact of diabetes. Diabetes care 1998;21: C7-10
3. Diabetes Mellitus. In: K.Park’s, Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine. M/s Banarsidas Bhanot Publication, Jabalpur, 21st Edition 2011:362-366
4. Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Mary S, Mukesh B, Bhaskar AD, Vijay V,Indian Diabetes Prevention Programme (IDPP): The Indian diabetesprevention programme shows that lifestyle modification and metformin prevent type 2 diabetes in Asian Indian subjects with impaired glucose tolerance (IDPP-1). Diabetologia 2006, 49:289–297
5. Mohan and R.Pradeepa. Epidemiology of diabetes in different regions of India. Health Administrator Vol: XXII Number 1and 2 - 2009 : 1- 18 .
6. George H, Rakesh P S, Krishna M, Alex R, Abraham VJ, George K, Prasad JH. Foot care knowledge and practices and the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy among people with diabetes attending a secondary care rural hospital in southern India. J Fam Med Primary Care [serial online] 2013 [cited 2014 Oct 19];2:27-32. Available from: http:// www.jfmpc.com/text.asp?2013/2/1/27/109938
7. Priya D, Hiwarkar P.A,Khakse G.M., Wahab S.N.Self-Health Care Practices Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients Attending Diabetes Clinic in India: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Recent Trends in Science And Technology.2012,4;116-119
8. Hemant Mahajan1,Tejashri Kambali, Manish Chokhandre, Amod Borle, Maya Padvi. Health Intervention Impact Assessment on Glycemic Status of Diabetic Patients International Journal of Diabetes Research 2012, 1(5): 73-80
9. Bhuwan Sharma, Hemant Mahajan and Naresh Gill. impact of health education on knowledge, attitude, self care practices and life style modification factors in diabetic patients . International Journal of General Medicine and Pharmacy 2013;2:29-38
10. Sultan r Ahmad, Gajanan d velhal, Yasmeen k kazi. Impact of life style modifications among diabetics in an urban slum of Mumbai.National journal of community medicine 2012;3:631-636
11. Balagopal P, Kamalamma N, Patel TG, Misra R.A community-based diabetes prevention and management education program in a rural village in India.Diabetes Care 2008;31(6):1097-104
12. Heike S. Englert, Hans A. Dieh, Roger L. Greenlaw, Steve Aldana. The Effects of Lifestyle Modification on Glycemic Levels and Medication Intake: The Rockford CHIP. INTECH Open Access Publisher, 2012
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License