IJCRR - 7(14), July, 2015
Pages: 40-44
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
CONSEQUENCE OF FULLERENE NANOPARTICLE (C60) ON OXYGEN CONSUMPTION AND BEHAVIOURAL MODIFICATION IN ETROPLUS MACULATUS
Author: N. Sumi, K.C. Chitra
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Fullerenes are nanoparticles composed fully of carbon molecule that are widely used in industry, mostly cosmetics and also play an important role as antioxidants. Aim: The present study was aimed to evaluate the consequence of fullerene toxicity on oxygen consumption and behavioural modification in cichlid fish, Etroplus maculatus. Methods: Fishes were exposed at 100 \?g/ L concentration of fullerene through fish feed for 96 h. Body weight of the animals, weights of gill, liver, brain and gonads along with mucous deposition was observed. Oxygen consumption of control and treatment groups was evaluated. Behavioural modification of fishes after exposure to fullerene was recorded throughout the study. Result: Oxygen consumption was decreased at the end of treatment. Weights of fish were decreased and there was significant increase in mucous deposition throughout the body of treated animal. Weights of gill, liver, brain, ovary and testis decreased significantly than that of control fish. Alterations in behavioural patterns including erratic swimming and surfacing activity, slow opercular movements, reddening of skin and haemorrhage through surface of the body were well marked during the period of trial. However, no mortality was observed throughout the study. Conclusion: The present study accordingly reveals that fullerene induced alteration on oxygen consumption and behaviour in fish.
Keywords: Fullerene, Behaviour, Etroplus maculatus, Oxygen consumption, Fish feed
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Recently nanoscience concerns about carbon-based nanomaterials, among which fullerenes takes one of the first places. Fullerene molecules are composed entirely of carbon, in form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid or tube. Among which spherical cage-like fullerenes also referred to as buckminsterfullerene or bucky balls are important as it contains 60 carbon atoms (C60) were chosen in the present study because most nanoscience particularly nanotoxicological assessment has focused on carbon-based nanoparticles. Fullerenes were discovered experimentally for the first time in September 1985. The Buckminsterfullerene, named after the American architect Buckminster Fuller, whose geodesic dome it resembles was observed by a group of scientists including Richard Smalley, Robert Curl and Harry Kroto at Rice University, Huston and they shared a Nobel Prize in 1996 for their novel discovery (1). Owing to the practical properties fullerenes have become an important molecules in science and technology, particularly on nanotechnology and industrial research. There is an insufficient toxicological data on nano-sized materials, therefore, it makes difficult to determine if there is a risk associated with nanomaterial exposure. Few studies have reported that fullerene possess radical scavenging property and proved as a powerful antioxidant (1), which have been widely used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (2). Fullerene in the range of 1 to 100 ppm is considered as therapeutically relevant concentration to function as antioxidant. On the contrary, some studies have reported that fullerene exposure has been shown to elicit oxidative stress response in embryonic zebrafish (3).
Researchers are widely using several biological models for toxicological assessments of nanoparticles. In the present study the cichlid fish, Etroplus maculatus is used as a piscine model for the rapid estimation of nanoparticle toxicity as it is very easy to rear, feed and are best to lodge in neutral to hard water. There is a growing concern that aquatic environmental pollutants have an impact on the direct behavioral responses on fish. Although numerous literatures have discussed the effect of environmental pollutants on aquatic ecosystem, there is a lack of data stating the outcome of nanoparticles on the behavior of aquatic animals, particularly fish. As behaviour serves as a link between physiological and ecological processes, it may be measured as an ultimate parameter for studying the effect of toxicant in the aquatic environment. In aquatic animals, respiration is an important process that plays a vital role in controlling the energy transformation. Therefore, the metabolic responses of organisms due to the changes in the surrounding environment are an indicator of the acclimatization of the organism, and alteration in the rate of oxygen consumption reflects changes in the internal metabolic activities of the animals. Thus the study was focused on the consequence of fullerene (C60) nanoparticle on the rate of oxygen consumption and behavioural modification in the cichlid fish, Etroplus maculatus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
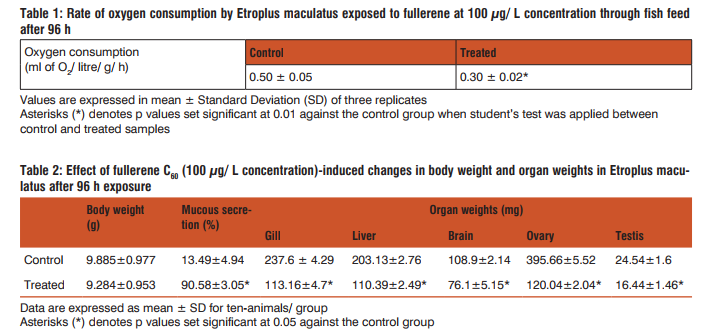
Etroplus maculatus weighing 8.5 ± 1.5 g and length 9 ± 1 cm were collected from a fish farm, Kaloos Aquarium, Kottakkal, Kerala. Fishes were then transported to the laboratory and were acclimatized to the laboratory conditions before the start of experiments. Constant supply of dechlorinated water and good lighting system (12: 12 h; light: dark) was maintained throughout the experiments. The physico-chemical features of the tap water were estimated as per APHA (4). Water temperature in the test ranged from 28 ± 2°C during the experiment, oxygen saturation of water ranged between 70 and 100 %, pH is 7.6 which were monitored using a standardized measures. Fullerene C60 (CAS No. 99685-96-8) of 99.9% purity was a generous gift obtained from Suzhou Dade Carbon Nanotechnology Co. Ltd., China. DMSO (1%) was used as a solvent to dissolve fullerene which was sonicated in SonicsVibracell VX-400 at 35 Hz for 30 min at 3 sec pulse interval to attempt uniform dispersion before adding to the exposure tanks to reach 100 µg/ L. It is also important to point out that the present study was specifically designed to evaluate interactions between the nanoparticle fullerene and the biological system as fish model, not to mimic, for example, an environmental exposure scenario. Therefore the above concentration was chosen for the present study. All other chemicals were of high purity and analytical grade. Experiments were carried out with 10 animals per group maintaining 3 groups of animals. In the present study the nanoparticle fullerene was exposed to animal through fish feed. For this initially total food consumption per fish per day was recorded and it was observed that 74.4 mg of feed (i.e. approximately 24 fish pellets) are required per fish (weighing 8.5 ± 1.5 g and length 9 ± 1 cm) per day. In our laboratory standard fish feed was used that was obtained from Grost and Bumpk Suppliers, Cherthala, Kerala, India. Then the nanoparticles fullerene (100 µg/ L concentration) was added to prior weighed fish feed, mixed, and dried in oven as per standard procedure and were used in the treatment group. Group I is non-treated group where fishes were fed without toxicant and maintained for 96 h. Group II is control group where fishes are exposed to feed prepared with vehicle only (1% DMSO) and maintained for 96 h. For this 350 µl solvent was used and previous findings in our laboratory have demonstrated that no adverse biological effects of DMSO (Dimethyl sulphoxide) at this concentration; however, use of a solvent will likely increase the uptake of material into the animal. Group III is fullerene-treated group where fishes were fed with fullerene dissolved in 1% DMSO at 100 µg concentration per litre and was also retained for 96 h. Every treatment tanks were covered with monofilament net to prevent the specimens from jumping out of test solutions. The mortality as well as the behaviour of fishes was recorded throughout the study. Oxygen consumption was determined by Winkler’s method (5). Before starting the experiment initial sample was collected immediately from each group without causing any damage to the animal. Then at every six hours sample was collected up to 96 h of exposure and the rate of oxygen consumption in each samples were calculated considering net weight of fish by using formula given by Winkler’s method. Briefly, the samples to be tested was collected in a 300 mL BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) bottle taking special care to avoid adding air to the liquid being collected and it was stopper. Then bottle stopper was removed and 1 mL of the manganous sulfate solution was added at the surface of the liquid and followed by the addition of 1 mL of the alkaline-potassium iodide-sodium azide solution. The stopper was replaced avoiding trapping of air bubbles, shaken well by inverting the bottle several times. Concentrated sulfuric acid 1 mL was added to run down the neck of the bottle above the surface of the liquid and shaken well until the precipitate has dissolved. The volume of treated sample was titrated, which corresponds to 200 mL of the original sample as this corrects for the loss of some sample during the addition of reagents (4). The volume was calculated using the formula: mL of sample to titrate = 200 x [300/(300-2)] = 201 mL Then 201 ml of sample was poured from the BOD bottle into a flask and titrated against 0.0250 N sodium thio-sulfate to the first disappearance of the blue color and the total number of mL of sodium thiosulfate used was recorded and the dissolved oxygen was estimated by the formula mg/L oxygen consumption = (mL titrant x normality of titrant x 8000)/equivalent volume of sample titrated. The difference in dissolved oxygen content between initial and final water samples represents the amount of oxygen consumed by the fish. Thus the rate of oxygen consumption was expressed as ml of O2 / litre/ g/ h. However, in the present study the final results of oxygen consumption only at 96 h were given from the collected control and treated samples. Statistics were compiled using SPSS, version 19.0, where Students t-test was used to determine significant difference between control and treated groups (p < 0.05; p < 0.01). All exposure groups consisted of 10 animals (N = 10) and data are expressed in Mean ± Standard Deviation (SD).
RESULTS
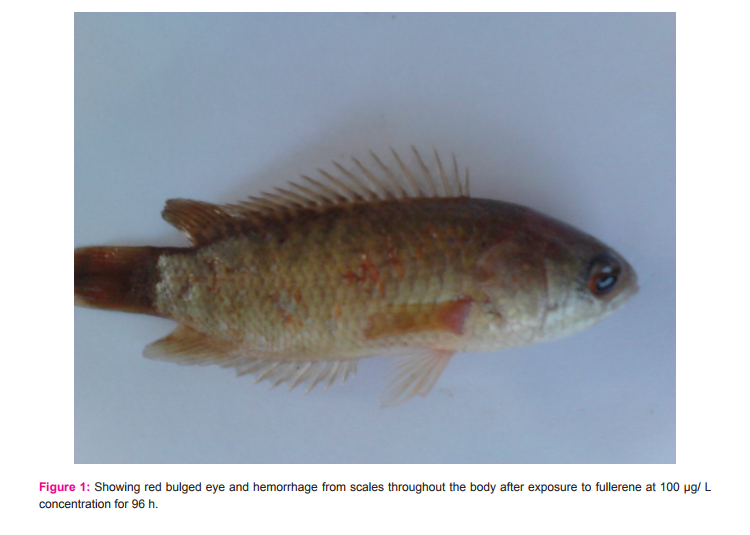
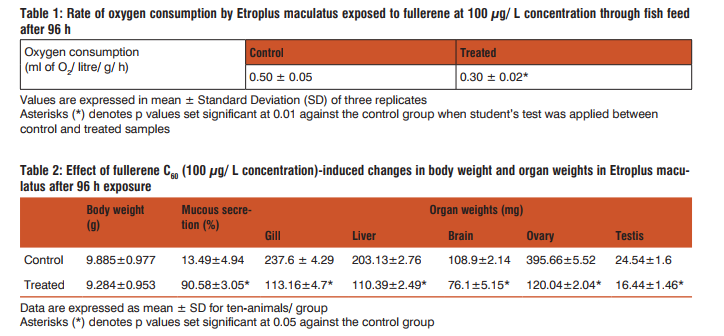
Oxygen consumption was found to be decreased at the end of fullerene treatment when compared to the corresponding control groups; however, the data of vehicle control (DMSO) was not shown (Table 1). The weights of fish were decreased and there was mucous deposition throughout the body of treated animal (Table 2). Weights of gill, liver, brain, ovary and testis decreased significantly than that of the control fish (Table 2). DMSO treatment did not show any significant changes in the body weights or organ weights and the results were found similar to non-treated control group, therefore the data was not represented in the present study. Alterations in behavioural patterns including erratic swimming and surfacing activity, slow opercular movements, reddening of skin and haemorrhage on surface of the body through scales were well marked during the period of trial (Figure 1). However, no mortality was observed throughout the study.
DISCUSSION
Toxicity effects of fullerene C60 through fish feed was assessed in the cichlid fish, Etroplus maculatus as biological model. Present investigation clearly demonstrates that exposure to fullerene through fish feed efficiently target the model organism and it was proved through various parameters including rate of oxygen consumption and behavioural modification in the cichlid fish. In the present study the potential toxicity of fullerene was evaluated by observing the total body weight gain or loss of the animal for the exposed period. It was renowned that at acute exposure of fullerene for 96 h showed a decrease in the total body weight of the fish when compared to the control groups. The reduction in the body weight may be due to treatment related effect but it was observed that no animals are noticed with anorexia as the food consumption was not decreased throughout the study and no pellets were found left at the end of each day observations in both control and treatment groups. In addition, there was a significant increase in the deposition of mucous throughout the body of fullerene-treated animal than that of control groups. The present observation reveals that when fullerene was exposed through fish feed it enters into gut and as soon as it reaches other vital organs as gill, liver, brain (as nanoparticles can passes through the blood-brain barrier) and also the reproductive organs could have caused the animal to secrete mucous throughout the body as the first line of defensive mechanism to dispose the toxicant from the body. Our previous study on the exposure of one of the nanoparticles, silicon dioxide to Oreochromis mossambicus had shown a comparable observation (6). Moreover the presence of mucous is an indicator of existence of toxic substances in the water and this could lead to the functional alterations and intrusion in fundamental process such as osmoregulation (7). Fullerene treatment significantly decreased the weights of gill, liver, brain, ovary and testis than that of control groups and it was evidenced that fullerene through fish food could seriously affect the vital organs of the animal. A change in respiratory rate is common physiological responses of fish to any toxicants. It can be detected easily through changes in rate of oxygen consumption, which was frequently used to evaluate the changes in metabolism under environment deterioration. In the present study the decrease in the rate of oxygen consumption by Etroplus maculatus at 96 h of fullerene exposure through fish feed may be due to internal action of nanoparticle fullerene C60. Thus it was evident that fullerene exposure disrupts the osmotic regulation of fish and this may be possibly due to the adverse effect of nanoparticle on gills and could have caused disruption in the efficiency of oxygen uptake, which could induced respiratory stress and impaired oxidative metabolism, and also may be due to mucous secretion on body surface upset osmoregulation (8). Nanoparticles are known to cause biochemical changes in the brain of fish, which can lead to behavioural changes (9). Nanoparticles can be taken up through gut or gill and via blood are transferred to several organs, including the brain. Therefore, fishes in the present study when exposed to fullerene through fish feed are known to cause several behavioural changes. Immediately after the fullerene exposure fishes showed air engulping behaviour and vigorous swimming to tide over the stress. After few hours fishes fight among themselves and they tried to escape from the aquarium tank followed by sinking behaviour. At the end of the treatment period, hemorrhage was noticed on scales as well as on the pectoral fin. Red bulged eyes, shedding of scales, slow opercular movement was also noticed.
CONCLUSION
In the present study the exposure to fullerene C60 even at therapeutically proven concentration as antioxidant is measured as toxic to aquatic animals as fish. An emerging nanoscience have the market growth of fullerene through several applications, such as creams used on skin, or for drug delivery, but there is a widespread concerns about their adverse effects on human health. The present investigation clearly portraits that fullerene C60 at 100 µg/ L concentration through fish feed imbalance osmotic regulation as well as caused behavioural modifications in cichlid fish, Etroplus maculatus.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge the funding agency, University Grants Commission-Special Assistance Programme, Government of India for this study. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.

References:
1. Tong J, Zimmerman MC, Li S, Yi X, Luxenhofer R, Jordan R, Kabanov AV. Neuronal uptake and intracellular superoxide scavenging of a fullerene (C60)-poly(2-oxazoline)s nanoformulation. Biomaterials 2011; 32: 3654-65.
2. Cai X, Jia H, Liu Z, Hou B, Luo C, Feng Z, et al. Polyhydroxylated fullerene derivative C60(OH)24 prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in an MPP+ induced cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 2008; 86: 3622- 34.
3. Usenko CY, Harper SL, Tanguay RL. Fullerene C60 exposure elicits an oxidative stress response in embryonic zebrafish. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2008; 229: 44-55.
4. APHA. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water, 20th Edition, Washington, DC. 1998.
5. Welsh JH, Smith RI. Laboratory Exercise in Invertebrate Physiology. Burgess Publishing Co., Minneapolis. 1961.
6. Vidya PV, Chitra KC. Elevation of reactive oxygen species in hepatocytes of tilapian fish when exposed to silicon dioxide: A potential environmental impact of nanomaterial. Int J Recent Sci Res 2015; 6(3): 2990-5.
7. Bernet D, Schmidt H, Meier W, Burkhardt-Holm P, Wahli T. Histopathology in fish: proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J Fish Diseases 1999; 22: 25-34
. 8. Mukadam M, Kulkarni A. Acute toxicity of cypermethrin, a synthetic pyrethroid to estuarine clam Katelysia opima (Gmelin) and its effect on oxygen consumption. J Agri Chem Environ 2014; 3: 139-43.
9. Smith CJ, Shaw BJ, Handy RD. Toxicity of single walled carbon nanotubes to rainbow trout, (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Respiratory toxicity, organ pathologies, and other physiological effects. Aquatic Toxicol 2007; 82: 94-100.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License