IJCRR - 7(8), April, 2015
Pages: 39-44
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A COMPARATIVE STUDY BETWEEN ELECTRICAL STIMULATION IN ADDITION TO PASSIVE STRETCHING THAN ALONE PASSIVE STRETCHING ON SPASTICITY IN PATIENTS WITH SPASTIC DIPLEGIC CEREBRAL PALSY CHILDREN
Author: Ghazi Sharique Ahmad, Md Haider Ali, K. Sambhu Nath, Md Sarfraz
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: An electrical stimulation and passive stretching were used to reduce spasticity in spastic diplegic cerebral palsy children patient. Methodology: Intervention for four weeks which consisted of 30 minutes of electrical stimulation of antagonistic muscles and 30 seconds of passive stretching of the agonist muscles (bicep brachi) 3 times per week of spastic diplegic child patients. Pre and Post treatment Spasticity of the bicep brachi was measured using the modified Ashworth scale.
Results: The mean value 1.43 of Group A post treatment was compared to the mean value 1.93 of Group B post treatment then the P value found to be 0.0057. Conclusions: Spasticity of diplegic cerebral palsy children are greatly reduced by using electrical stimulation combined with passive stretching. This suggests that electrical stimulation with passive stretching are more reliant to reduce spasticity than alone passive stretching.
Keywords: Electrical stimulation, Muscle spasticity, Diplegic cerebral palsy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cerebral palsy is an “umbrella term covering a group of non-progressive, but often changing, motor impairment syndromes secondary to lesions or anomalies of the brain arising in the early stages of its development1 . The traditional definition of cerebral palsy is a non progressive impairment in movement or posture caused by injury or anomaly of the developing brain2 . CP is classified by the types of motor impairment of the limbs or organs, and by restrictions to the activities an affected person may perform3 .There are three main CP classifications by motor impairment: spastic, ataxic, and athetoid / dyskinetic.3 Additionally there is a mixed type that shows a combination of features of the other types. These classifications also reflect the areas of the brain that are damaged3 . Spastic cerebral palsy, or cerebral palsy where spasticity (muscle tightness) is the exclusive or almost-exclusive impairment present, is by far the most common type of overall cerebral palsy, occurring in upwards of 70% of all cases4 . People with this type of CP are hypertonic and have a neuromuscular mobility impairment (rather than hypotonia or paralysis) stemming from an upper motor neuron lesion in the brain as well as the corticospinal tract or the motor cortex4,5. Spasticity as defined by Lance (1980) is “a motor disorder characterized by a velocity dependent increase in muscle tone with exaggerated tendon jerks, resulting from hyper excitability of stretch reflex as one of the component of upper motor neuron syndrome”.6,7,8 The upper limb adopts an adducted posture at the shoulder and a flexed posture at the elbow and wrist, with the fingers flexed into the palm. In patients with no functionally useful voluntary limb movement, spasticity can maintain an abnormal resting limb posture leading to contracture formation. In the arm, severe flexion deformity of the fingers and elbow may interfere with hand hygiene and dressing, as well as affecting self-image.9,10 Numerous studies say that the effectiveness of stretching depends upon the frequency and duration of the applied stretch11,12,13. This raises the question as to whether the effectiveness of stretch can be enhanced with electrical stimulation7. Functional electrical stimulation (FES) or neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) is the application of continuous current of electricity administered through a surface electrode at the nerve or motor point of a muscle to elicit a muscle contraction.14,15 Many authors have employed that use of functional electrical stimulation and have achieved success in terms of improved upper extremity function. Electrical stimulation has been shown to have positive effects on motor performance.16, 17 , 18 It has also been claimed that spasticity reduction with electrical stimulation is achieved without any muscle weakness or paralysis. It was found that electrical stimulation may increase sensory inputs into the central nervous system and so accelerate nervous plasticity and lead to faster improvement19,20. It has been proposed in various studies that neuromuscular electrical stimulation enhances motor recovery with reduction in spasticity, increase in range of movement of joints and strengthening of muscles, and prevention or correction of contractures.21,22 Electrical stimulation of the antagonistic muscles may improve the efficacy of stretching by providing an additional stretch to the agonistic muscles. It may also reciprocally inhibit the stretched muscle.7 The explanation of these results is that When electrical stimulation is added to passive stretching, is more effective than alone passive stretching for decrease in spasticity in patients with cerebral palsy.7 Therefore, it is predicted that in the current study, Patients with elbow flexors spasticity with Grade between 2- 4 in Modified Ashworth Scale of cerebral palsy children would show greater reduction of spasticity with application of electrical stimulation and passive stretching.
METHODS
Subjects
A total of 30 patients with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy patients, with stage 2 - 4 modified aswarth scale, age 3-5 years were selected. All participants were on phase of medication, tested after an overnight abstinence of at least 12 hours from their usual medication regimen. All participants were naive with respect to the experimental design.
Study design
The study has two groups (Group A and Group B). Each group was 15 patients of both the genders of cerebral palsy. Group A received neuromuscular electrical stimulation to elbow extensors (triceps) and passive stretching of elbow flexors (biceps). And Group B patients received only passive stretching to elbow flexors (biceps). Both the groups were trained for thrice a week for 4 weeks. The approximate duration of each session is 30minutes. All the subjects received a total of 12 sessions.
Instrumentation
The procedure included the Electrostim T electrical muscle stimulator and Modified Ashworth scale. Electrostim T is a modern solid state and a portable surface electrical muscle stimulation unit. It offers both Faradic and Galvanic currents with a various available waveforms like: Plain Faradic: faradic pulses of 0.7ms with a pulse repetition frequency of 40 cycles per second and Surged Faradic: faradic pulse of 0.7ms pulse duration with a repetitive frequency of 40 cycles per second. Surge rate varies from 0.8 to 3 seconds with a fixed rest time of 0.5 seconds. Electrical muscle stimulation is the elicitation of muscle contraction using electrical impulses. The electrical impulses with a short duration of less than 1ms duration is known as faradic type current and is used to strengthen weak muscles, relax spastic muscles.24 Faradic type current is usually surged for treatment purposes to produce a near normal titanic like contraction and relaxation of the muscle.15,24 The current is surged so that intensity of successive impulses increases gradually reaching a peak and then falls either suddenly or gradually.14,15,24 Modified Ashworth Scale is used to grade spastic hypertonicity. It is basically a subjective, 5 point ordinal scale.42 This scale remains a gold standard scale by which other tests are validated. It has been shown to have good intrarater reliability (0.84) and good interraterreliability(0.83)42
Procedure
The patients were diagnosed to have spastic diplegic cerebral palsy and who fulfilled the above inclusive and exclusive criteria were selected. The attendant of entire subject signed an informed consent approved by ethical committee of Bachcha Hospital, Katihar, Bihar, India. A closed environment with least possible distraction was selected as site for data collection. General demographic data was taken. The research designs used were pre and post experimental design for the study. The selected subjects were randomly assigned into one of the two groups A and B.7,23 Each group consists of 15 patients of both the genders and in the age group between 2 to 5 years. Group A: they received neuromuscular electrical stimulation to elbow extensors (triceps) and passive stretching of elbow flexors (biceps). And Group B: they received only passive stretching to elbow flexors (biceps) Both the groups were trained for thrice a week for 4 weeks. The approximate duration of each session is 30minutes. All the subjects received a total of 12 sessions. A portable, surface electrical muscle stimulation unit (Electrostim T) is used in the study. The experimental methods used are non-invasive and pose no hazards to the health of the patient.21
Treatment Intervention
The technique for application of passive stretching was based on passive range of motion therapeutic exercises by Kisner and Colby.29 The passive range of motion consists of moving the elbow passively and holding it in position for 60 seconds. The procedure of passive stretching is given in every treatment session in all the patients, both in group A and B.25 The assessments of spasticity using Modified Ashworth Scale of elbow flexors were carried out at the commencement of the treatment session (pre-treatment). These assessments are also carried out at the end of 4th week (post treatment) on all the patients. The subjects who were included in the research are the patients of spastic diplegic cerebral palsy affecting the elbow flexors muscle i. e biceps with a grade ranging from 2-4. The subjects who are not having normal tactile and pain sensation are not included in the research. In the group A, combination of electrical stimulation and passive stretching is used. The subject is placed in the sitting position and electrical stimulation is given to the elbow extensors i. e triceps brachii for 30minutes in a single session and thrice a week which is followed by passive stretching of the elbow flexors. The triceps is stimulated by placing an active electrode over its motor point of the tendon at the elbow. The therapist was explained the procedure of the stimulation to the participant so that he can be familiarize with the apparatus. A two channel electrical stimulator is applied to the antagonist muscle (triceps) of the subjects of Group A through square 2.5 cm surface electrodes. A stimulator with surging is used to produce near normal tetanic like contraction and relaxation of the muscle and it will be more comfortable which in its self may reduce the tone. The stimulation frequency used is 40 Hz and pulse duration 0.7ms which produces a smooth and comfortable contraction. The rest time is 0.5 sec with a surge rate ranging from 0.8 to 3 sec. The intensity is set according to the subject tolerance and it should produce a visible contraction. The current amplitude will be adjusted according to the subject comfort. During the application of the electrical stimulation the subjects were positioned with elbow semi flex so that biceps is not in lengthened position as recommended by Benton (1981) and therefore to reduce the amount of stimulation required attaining a forceful contraction. After the stimulation, three brief stretches are applied to the elbow flexors for 60sec with a 1 min rest in between the three stretches.13 In the Group B, passive stretching to the elbow flexors for thrice a week is given. Neither the subjects of both the groups received any other form of treatment for spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. At the end of 4 weeks outcome measures are collected immediately after the last intervention by therapist.13,25
Statistical Analysis
A pretest-posttest experimental group design is used for the study. The pretest treatment values of modified aswarth scale on day 1 and post treatment values on day 5 was taken. The data was analyzed using the SPSS 18 Software. Paired T- test applied for comparison of pre test treatment values and post test treatment values within and each groups respectively. The results were taken to be significant if p<0.05.
RESULTS
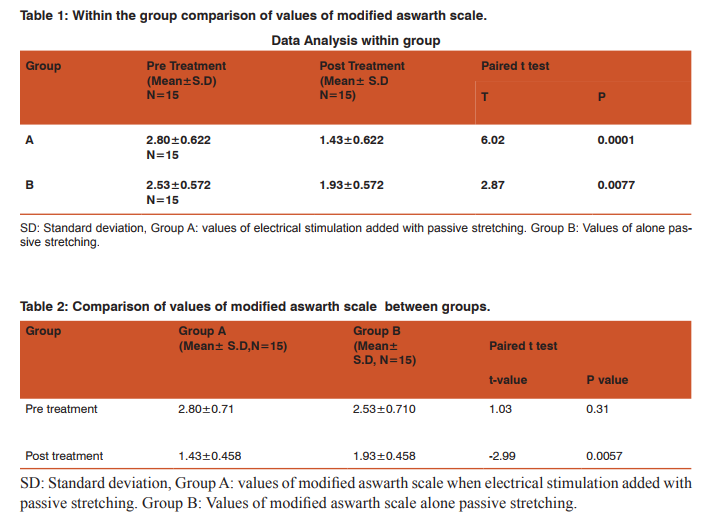
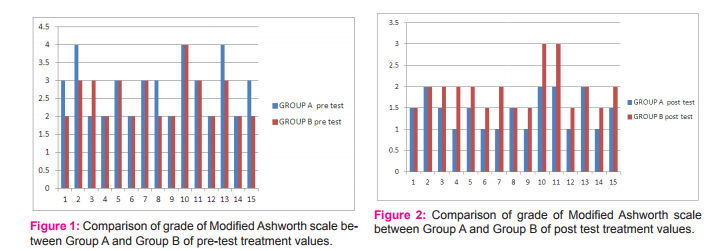
Table 1 and Table 2 details the results of present study. Within group analysis revealed significant improvement of pre treatment values of first days and post treatment values of last days of treatment sessions of both the groups. When the mean values 2.80 of group A pre-treatment was compared with mean value 1.43 post treatment of same group than P value was found to be 0.0001 which was less than 0.05. It shows that result was significant. Similarly when mean value 2.53 of group B was compared with mean value 1.93 of same group , then p value was found to be 0.007 which was less than 0.05 , that it shows result was significant. When the mean value 2.80 of Group A pre-treatment was compared to the mean value 2.53 of Group B pretreatment then the P value found out to be 0.31 which was greater than 0.05. It shown that result was not significant. Similarly when mean value 1.43 of Group A post treatment was compared to the mean value 1.93 of Group B post treatment then the P value found to be 0.0057 which was less than 0.05. It shown that result was statically significant.Above result showed that on last day of treatment regimen reduction of spasticity (pre treatment values and post treatment values on modified aswarth scale) was better in group A as compared to group B.
DISCUSSION
The results of our study found significant differences between the two groups that is Group A (electrical stimulation with passive stretching) and Group B (alone passive stretching). Result of our study shown that (Group A) when electrical stimulation was added to passive stretching, it helps in better reduction in spasticity than (Group B) alone passive stretching. Modified Ashworth Scale was used to assess and evaluate the patient response to treatment. This study was designed to compare the effect of electrical stimulation with passive stretching and alone passive stretching of diplegic cerebral palsy children patients. The mean value of Modified Ashworth Scale in Group A pre-treatment was 2.80 which was decreased to 1.43 in the post treatment of Group A. This reflected a marked decrease in the percentage outcome of 32% in the mean score. However the mean value of Modified Ashworth Scale of Group B pre-treatment was 2.53 which was decreased to 1.93 in the post treatment of Group B. This reflected a marked decrease in the percentage outcome of 13.4% in the mean score. It was therefore being concluded from the research that electrical stimulation when added to passive stretching reduce spasticity. There are numerous reasons that the patients who were given electrical stimulation in combination with passive stretching showed benefit. The results of our study support the previous work done by Khalli MA et al7 . They performed a study on the bilateral knee flexors spasticity patients and concluded that electrical stimulation when given combination with passive stretching reduces spasticity and contracture more than alone passive stretching. That means those subjects in the electrical stimulation with passive stretching has greatly reduces the spasticity than compared with alone passive stretching. Electrical stimulation may have a direct effect which leads to increase muscle strength, decrease muscle tone, improve motor control and reduces upper limb disability. It has been claimed that improvement in the muscle strength after application of electrical stimulation may be due to the reduction of the muscle tone.23 Electrical stimulation is a simple, convenient method of repetitive contraction and stretching the antagonistic muscles.13Electrical stimulation has a direct effect as well as via mechanical changes of tension in the muscles on spasticity. Stimulation of the antagonist muscle of the spastic muscle will result in the mechanism of reciprocal inhibition as the Ia afferents nerve passes from the muscle spindle to the spinal cord and excite the inhibitory inter neurons, reducing activity of spastic muscle. Electrical stimulation to the antagonist of the spastic muscle for an extended period of time will result in strengthening of the synaptic connections and reduction in spasticity.35According to result and above discussion showed that an electrical stimulation with passive stretching led to a decrease in elbow flexor spasticity with Grade between 2-4 in Modified Ashworth Scale .of diplegic cerebral palsy children patient.
Future Research
Science is dynamic and there is always a scope of improvement and change in time to come ahead. With the progressive aim to move ahead we aspire to achieve highly accurate and reliable results. Thus, every study leaves back scopes for other researcher to do something more advanced and varied in order to touch the height of perfection. This study examined only 30 subjects in total and data collection was confined to closed setup with minimum distractible conditions. Thus future researchers can expand the study by including more number of subjects so as to make generalization of results and practice such experiments in variable environmental setups such as open environment. Thus it could be applied to real life situation. In this study the protocol used included electrical stimulation and passive stretching. But future researchers can progress the study by modifying the protocol like incorporating positions and cryotherapy in the protocol given, protocol related to the real life situations could be used, such as using advanced different types of neuromuscular electrical stimulation. The scope of study can be expanded to different grade of spasticity and other neurological conditions.
Relevance to clinical practice
The result obtained in this study suggest that electrical stimulation with passive stretching on spasticity of stroke patients is more beneficial than using alone passive stretching, so these results show that electrical stimulation with passive stretching should be used for training tasks to patients with grade 2 -4 spasticity of diplegic cerebral palsy children.
Limitations of the study
There are several limitations regarding to the study that7, 19, 23.
1. The sample size is small.
2. Modified Ashworth scale is not an optimum measure of spasticity. For a large numbers of subjects it may not be possible due to the numerous physical impairments present in the population being studied.
3. Logistics of transportation and participation over several weeks may be difficult for these patients.
4. Assignment to groups will be non-random due to matching of functional levels between the stroke survivors.
5. The final outcome measurement occurred immediately after the last intervention sessions, the within intervention differences are likely to be the result of the transient changes of the muscle extensibility.
6. The result reflects short term effects of electrical stimulation and passive stretching therefore a long term effect could be evaluated in the future study.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study support the experimental hypothesis that electrical stimulation when added to passive stretching has statistically, significantly greater effects than alone passive stretching on spasticity of spastic diplegic cerebral palsy children.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.

References:
1. A. Hussain R. Saadi et al. Maternal and foetal risk factors of cerebral palsy among Iraqi children: A case control study. 2012:2(3): 350-358.
2. Walraich, M, Droter, D et al. Developmental behavioural peditric, Evidence and practice. 2008: 14 : 483-517.
3. C. Rethelfsen SA et al. Classifiation systems in cerebral palsy.” Orthop Clin North Am. 2010 oct: 41 (4): 457–67.
4. Stanley F et al. Cerebral Palsies: Epidemiology and Causal Pathways. London, United Kingdom: MacKeith Press; 2000.
5. J. Maheshwari. Essential Orthopaedics. 4th edition: 222
. 6. Allison Brashear, Elie. P Elovic; Spasticity: Diagnosis and management; Demos medical publication.
7. Khalili, Mohammad A; Hajihassanie, Abdulhamid; Electrical simulation in addition to passive stretch has a small effect on spasticity and contracture; Journal of Physiotherapy; 2008; 54, 3; ProQuest Nursing and Allied Health Source.
8. Kuen-Horng Tsai et al. Effect of single session of Prolonged muscle stretch on Spastic muscle of stroke patients;
9. Bipin B Bhakta; Management of Spasticity in Stroke; Rheumatology and Rehabilitation; British Medical bulletin; 2000: 56: 476-485.
10. Sommerfeld DK et al.Spas ticity after stroke: Its occurrence and association with motor impairments and activity limitations. Stroke. 2004; 35: 134-140.
11. Lesley Wiart et al. Stretching with children with Cerebral Palsy, what do we know and where are we going;Pediatric PhysTher 2008; 20: 173-178.
12. Tamis Pin et al. The effectiveness of passive stretching in children with cerebral palsy; Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 2006, 48: 855-862.
13. Carolyn Kisner, Lynn Allen Colby, Therapeutic Exercise: Foundations and Techniques, Jaypee, 4th Edition.
14. Sheila Kitchen, Sarah Bazin; Clayton’s Electrotherapy; Saunders; 1996.
15. John Low and Ann Reed; Electrotherapy Explained : Principles and Practice; 3rd Edition; Elseiver; 2003.
16. Juan Nicolás Cuenca and Eric Lazar; Functional Electrical stimulation in stroke.
17. Lourenção MI et al. Analysis of results of functional electrical stimulation on hemiplegic patients’ upper extremities using the Minnesota manual dexterity test. IntRehabil Res. 2005; 28: 25-31.
18. Liberson WT et al. Functional electrotherapy: stimulation of the peroneal nerve synchronized with the swing phase of the gait of hemiplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1961; 42: 101–105.
19. Susan R O Sullivan and Thomas J Schmitz; Physical Rehabilitation: Assessment and Treatment; Jaypee Brothers; 4lh Edition, 2001.
20. C. R. W.Edwards et al. Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine; Churchill Livingstone; 18th edition ; 2000.
21. Barbara M Doucet; High vs. low electrical stimulation frequencies for motor recovery in hemiplegia; December. 2004.
22. A. Pandayan et al. Electrical stimulation of wrist extensors in post stroke hemiplegia; Stroke journal of American Heart Association 1999 : 30 :1384 – 1389.
23. S.R.A Akinbo et al. Comparison of the effect of Neuromuscular electrical stimulation and Cryotherapy on Spasticity and hand function in patients with spastic cerebral palsy; Nigeria medical practioner; 2005(6): 51: 128-132.
24. Sheila Kitchen, Sarah Bazin; Electrotherapy; Evidence based practice; 11th edition, 2002.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License