IJCRR - 7(15), August, 2015
Pages: 56-61
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
ANALYSIS OF FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH PERITONITIS IN HOLLOW VISCUS PERFORATION
Author: Atif Abdullah C., Ganesh Babu C.P., Raghuram K., Tirou Aroul T.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Peritonitis due to hollow viscus perforation is one of the causes of acute abdomen warranting emergency laparotomy. The causes for gastro-intestinal perforation vary between the western countries and Asian countries like India. Though
there are many studies in this regard, very limited studies are available pertaining to southern parts of India. Therefore this study
was carried out to assess the common cause, factors associated and patient outcome in peritonitis due to gastro-intestinal perforation.
Methods: This study was conducted in tertiary care hospital, Pondicherry between July 2012 and July 2014. Fifty five patients who underwent exploratory laparotomy for gastro-intestinal perforation were included in the study and assessed. Appropriate surgeries were performed for the site and cause of the perforation. Patient's history, clinical examination findings, investigations, intra-operative findings, operative procedure and post-operative complications were recorded and assessed. Results: In this study, 21.8% patients were in the age group of 51-60 years. Male to female ratio was found to be 6.8:1. The most common symptom was abdominal pain which was present in all the patients. Among patients with peptic ulcer perforation, 73.3% of the patients were smokers and 42.4% of the patients gave history of NSAID intake. Peptic ulcer perforation was found in 60% of the patients. Post-operative complications occurred in 34.5% of the patients. Mortality rate was 7.3% in this study. Conclusion: Even in the Era of good drugs Peptic ulcer perforation was the commonest cause for perforation. Peptic ulcer perforation was significantly associated with smoking in this study. Alcohol consumption, prior NSAID abuse didn't significantly affect the outcome of the patients.
Keywords: Perforation, Factors associated, Peritonitis
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Peritonitis due hollow viscus perforation is one of the commonest emergencies faced by general surgeons. Perforation causes exposure of the peritoneum to the gastro-intestinal contents which results in peritonitis. Gastro-intestinal perforation can occur due to various causes but common causes in India is Duodenal ulcer perforation, Typhoid ileal perforation, Perforation due to trauma, Perforation due to malignancy, etc. in the order of frequency1 . However the scenario is different in western countries were distal perforations are more common2 . Emergency surgical intervention is required in most of the patients except few, in whom perforation is contained. Various studies have been conducted to analyze the factors associated with hollow viscus perforation and their outcome. Rajender Singh Jhobta et al in their study concluded that majority of perforation peritonitis in India involve Upper Gastro-Intestinal tract3 . Similar study conducted in Pakistan by Afridi et al found that duodenal ulcer perforation was the commonest cause of perforation followed by Tuberculous perforation of small bowel in their locality4 . Bali et al in their study conducted in Delhi found that 15% of patients gave history for NSAID intake5 . Common cause of peritonitis in their study was peptic ulcer perforation followed by appendicular perforation. Appendicular perforation usually causes localized peritonitis in contrast to perforation at any other site of gastro-intestinal tract. For this reason appendicular perforation was not included in our study. Though there are various studies focused on factors associated with hollow viscus perforation in India, studies pertaining to southern parts of India is limited. Factors contributing to perforation peritonitis in South India can be different from that of North India because of different culture, food habits, health care facilities and awareness. Chatterjee et al conducted a study on ileal perforations in Pondicherry6 , but this study didn’t analyze perforation in other parts of gastro-intestinal tract and this study didn’t include ileal perforation due to typhoid. Hence in order to analyze the factor associated with perforation peritonitis in this part of the world, this study was carried out with the principal aim of calculating the incidence of different types of perforation, assessing the various factors associated with hollow viscus perforation and recording the morbidity and mortality of patients with different types of perforation.
METHODOLOGY
This was a Prospective observational study, which was conducted at the tertiary care hospital, Pondicherry over Two year period. From July 2012 until July 2014 we enrolled patients who were diagnosed with peritonitis due to hollow viscus perforation and underwent Exploratory laparotomy. We excluded all patients who were managed conservatively without exploratory laparotomy. Fifty five patients, who had fulfilled the inclusion criteria, were studied. Preoperative detailed history was noted. Thorough examinations were done to arrive at a preoperative diagnosis. After admission, patients were investigated and resuscitated. Patients were taken for exploratory laparotomy. Intra-operative findings were noted and depending on the type of perforation appropriate surgery was performed. Perforated duodenal ulcers were repaired by simple closure with an Omental Onlay reinforcement or patch. Primary closure, bowel resection and end to end anastomosis or entero-cutaneous stoma was done for perforation due to trauma, perforation due to typhoid etc. Post-operatively patients were followed up for 30 days and complications like surgical site infection, wound dehiscence, anastomotic leak and death were watched evaluated.
RESULTS
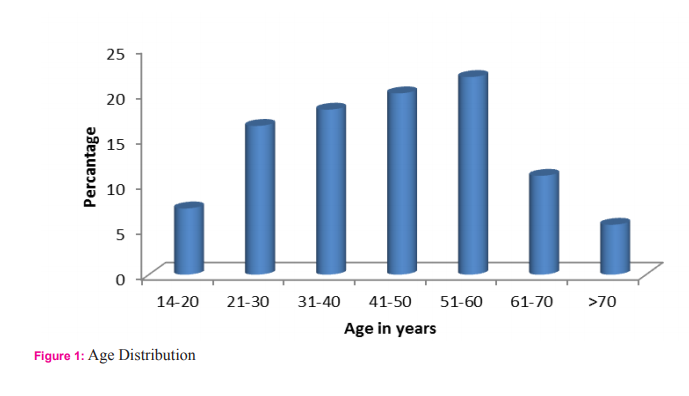
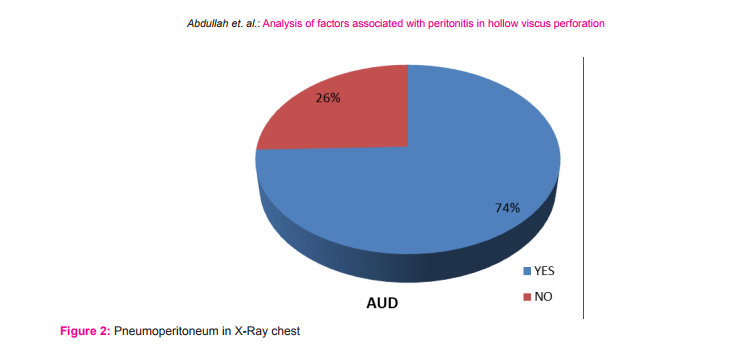
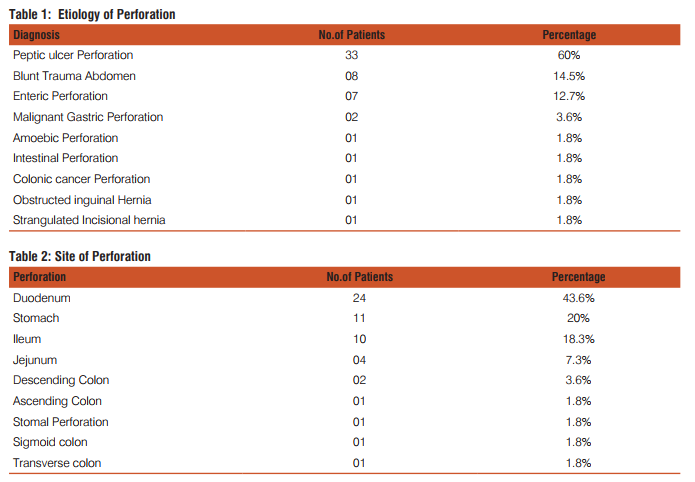
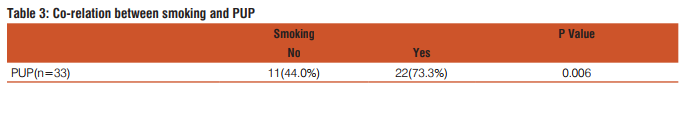
This study included fifty five patients. The aim was to calculate the incidence of different types of perforation, assess the various factors associated with hollow viscus perforation and record the morbidity and mortality of different types of perforation. In this study most of the patients with gastrointestinal perforation were in the age group of 51-60 years (21.8%) followed by age group of 41-50 years (20%).(Fig1) The youngest patient in this study was 14 years, who had ileal perforation and the oldest patient was 80 years, who had duodenal ulcer perforation. Perforation peritonitis was found in 48 (87.3%) males and 7 (12.7%) females, in this study. The most common symptom was abdominal pain, which was present in all the patients. Vomiting was second most common symptom and was present in 29 patients (52.7%). Fever was present in 14 patients (25.5%) and was the third most common symptom. Eight patients (14.5%) complained of abdominal distension. Constipation was present in 6 patients (10.9%) and 2 patients (3.6%) had history of malena. Pneumo-peritoneum in chest X-ray of the patients studied was present in 41 (74.5%) patients. Five patients who had enteric perforation of the ileum didn’t have pneumo-peritoneum in the chest X-ray. Four patients who had peptic ulcer perforation of the duodenum and one patient who had peptic ulcer perforation of the stomach didn’t show pneumo-peritoneum. Two patients who had gastrointestinal perforation due blunt trauma abdomen didn’t show pneumo-peritoneum. Out of two patients, one had sigmoid perforation and the other had ileal perforation. One patient who had colonic carcinoma with perforation peritonitis didn’t show pneumo-peritoneum in X-ray. Those patients who didn’t have pneumo-peritoneum in chest X-ray underwent exploratory laparotomy as they had clinical signs strongly suspicious of peritonitis requiring laparotomy. Peptic ulcer disease was the commonest etiology for perforation. It was found in 33 patients (60%). Duodenal ulcer perforation was found in 24 patients and eight patients had gastric ulcer perforation. One patient had stomal ulcer perforation, who had previously undergone truncalvagotomy and gastrojejunostomy (TVGJ). Blunt trauma to abdomen was the cause for gastrointestinal perforation in eight patients (14.5%). Three of the perforation due to blunt trauma to abdomen was in ileum, three were in jejunum, one was in stomach and one was in sigmoid colon. Typhoid enteritis was the cause for perforation in seven patients (12.7.5%). Malignant gastric perforation was found in 2 patients (3.6%). One patient (1.8%) had amoebic perforation of the descending colon. One patient (1.8%) had abdominal tuberculosis with perforation of the ileum.(Table 1) Duodenum(43.6%) was the commonest site for perforation. Other sites in the order of frequency were stomach(20%), ileum(18.2%), jejunum(7.3%), descending colon(1.8%), ascending colon, stomal perforation, sigmoid perforation and transverse perforation.(Table 2) Nineteen patients (34.5%) had post-operative complications. Four patients (7.3%) succumbed to the disease. Superficial surgical site infection was most common complication and was present in 11 patients (20%). Four patients (7.3%) developed burst abdomen out of which two were associated with leak (3.6%). Age, gender and duration of the symptom didn’t affect the outcome of the patient significantly. Twenty patients (66.7%) who had peptic ulcer perforation were alcoholic. Twenty two patients (73.3%) with peptic ulcer perforation were smokers. Smoking was significantly associated with peptic ulcer peforation (P value 0.006).(Table3) Fourteen patients (42.4%) out of 33 patients who had peptic ulcer perforation gave history of NSAID intake. (P value 0.2187).
DISCUSSION
Peritonitis due gastrointestinal perforation is common in developing countries like India. As there are limited studies in this regard pertaining to this part of the world, this study was carried out to assess the factors associated with peritonitis. The commonest age group in this study was 51-60(21.8%) years followed by 41-50(20%) years. Mean age was 44.8 years (range from 14 to 80 years). Afridi et al who conducted similar study found that the mean age of patients with peritonitis due gastrointestinal perforation was 40.5 years4 . Out of 55 patients, 48(87.3%) were males and 7(12.7%) were females with sex of 6.8:1. Bhupender Kumar Jain et al in his study found that sex ratio was 5:17 . However various authors have found varying sex ratio in their study. Abdominal pain was most common symptom and was found in all the patients followed by vomiting which was present in 29 patients (52.7%), fever was present in 14 patients (25.5%) and 8 patients (14.5%) had abdominal distension. Bali et al in their study found that abdominal pain was present in 98% of the patients, 41.5% of the patients had vomiting and 28% of the patients had abdominal distension5 . Thirty eight patients (69.1%) had presented within 1-2 days of onset of the symptoms10 patients (18.2%) had presented between 3-5 days, 6 patients (10.9%) had presented between 6-10 days and 1 patient (1.8%) presented on the 11th day from the onset of the symptom. However, duration of the presentation didn’t significantly affect the outcome of the patient in this study. Thirty patients (54.5%) were smokers. Fourteen patients (42.4%) who had peptic ulcer perforation were smokers and smoking was significantly associated with peptic ulcer perforation in this study. Twenty patients (66.7%) who had peptic ulcer perforation were alcoholic. Fourteen patients (42.4%) who had peptic ulcer perforation had history of NSAID intake. Various studies have shown association between peptic ulcer disease and NSAID. Ohene –yeboah et al in their study they found 47% of patients had history of NSAID intake8 . However in this study NSAID intake was not significantly associated with peptic ulcer perforation. Pneumoperitoneum in X-ray was found in 41 patients (74.5%) and 14 patients (25.5%) didn’t have air under diaphragm. In contrast to this study, Rajender Singh Jhobta et al in their study found only 50% of the patients had air under diaphragm in X-ray. Peptic ulcer disease was the commonest cause of gastrointestinal perforation in contrast to western population where distal gastrointestinal perforations are common9 . The common causes for peptic ulcer disease are H. pylori infection, NSAID abuse and smoking. In the recent times with frequent use of proton pump inhibitors, frequency of surgery for peptic ulcer disease had markedly decreased but emergency surgery for peptic ulcer complications like perforation and bleeding has remained constant. In this study, peptic ulcer disease was the cause of perforation in 33 patients (60%). Duodenal ulcer perforation was present 72.7%, gastric ulcer perforation was found in 24.2% and one patient (3.03%) had stomal ulcer perforation from gastro-jejunostomy site. Dokubo et al in their study found that 88% of the peptic ulcer perforations were found in duodenum and 12% were found in stomach10. Graham’s omental patch repair was the performed in all the patients. Leeman et al in their study 91% of gastric ulcer was treated with graham’s omental patch and large perforations more than 2cm was treated either by simple closure (4.5%) or distal gastrectomy (4.5%)11. Chaudary et al in their study concluded that gastrointestinal ulcer larger than 2 cm can be treated with jejunal loop as serosal patch12. However, in this current study large perforations were not encountered. Three patients (9%) had succumbed to the disease and cause of death in all the three patients was septicemia with multi organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Naguiero et al in their study found similar results, 10% of the patients had died because of peptic ulcer perforation13. Blunt trauma abdomen was the second common cause of gastro-intestinal perforation in this study. Eight patients (14.5%) had perforation peritonitis due blunt trauma abdomen. Jhobta et al in their study found 6% patients had gastrointestinal perforation due to blunt trauma abdomen3 . Out of 8 patients, 3 patients (43%) had ileal perforation, 3 patients (28.5%) had jejunal perforation, 1 patient (14.2%) had sigmoid colon perforation, 1 patient (14.2%) has gastric perforation and 1 patient (14.2%) had rectal perforation which was associated with ileal perforation. Sule et al in their study on perforation peritonitis following blunt trauma abdomen found that the site of perforation in the order of frequency was jejunum (16.07%), ileum (14.2%), stomach (3.5%) and colon (3.5%)14. Salmonella typhi causes typhoid or enteric fever and commonly reside in the lymphoid tissue (Peyer’s patch) of small intestine. They cause oval shaped ulcer in the mucosa of the small intestine and perforation usually occurs after two weeks of typhoid fever. In this study, enteric perforation was found in 7 patients (12.7%). Bali et al in their study found that enteric perforation occurred in 12% of the patients and was comparable to the present study5 . Out of 7 patients with enteric perforation, 3 patients were treated with ileostomy, 3 patients were treated with primary closure and 1 patient was treated with resection and end to end anastomosis. In this study all patients with enteric perforation survived. Similar results were obtained by Anupam Pujar et al in their study15. Whereas Edino et al in their study conducted in Nigeria found 15% mortality16. This difference in mortality rate can be variation in severity of the disease in that part of the world. Malignant gastric perforation was found in 2 patients (3.6%). Both patients had malignant growth in the pylorus and perforation was found in the anterior aspect. Both patients under went graham’s omental patch repair and feeding jejunostomy. Definitive procedure was deferred due to poor general condition. Both patients were found to have adenocarcinoma of stomach following histopathological examination of the biopsy from edge of the perforation. Kotan et al in their study found that the incidence of malignant gastric perforation was 4.2% which was similar to this current study17. Intestinal tuberculosis was cause of gastrointestinal perforation in 1 patient (1.8%). Patient had perforation in the ileum and there were multiple tubercles in the ileum which was suggestive of tuberculosis and biopsy from the tubercle was consistent with tuberculosis. Ileostomy was done and closed after 4 weeks. Patient was started on anti-tubercular treatment. Abro et al in their study conducted in Pakistan found that perforation of ileum in intestinal tuberculosis was present in 10% of the patients18. In this study 1 patient (1.8%) had amoebic perforation of the descending colon. Intra-operatively, multiple perforations were present in the descending colon. It was treated with primary closure of the perforation and a diversion ileostomy. Patient expired on the post-operative day 10 due to septicemia and multi organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). Jain et al in their study 186 patients who underwent exploratory laparotomy 15 patients (8%) had amoebic colonic perforation and also found that mortality was 40% in patients with amoebic perforation of the colon19. In this study colonic cancer perforation was found in 1 patient (1.8%). Intra-operatively patient had malignant growth in the descending colon with perforation of size 5mm. Patient also had liver metastases. Limited resection of the colon with transverse end colostomy and descending colon mucous fistula was done. Afridi et al in their study found colonic cancer perforation was found in 2% of the patients4 . One patient (1.8%) had obstructed left inguinal hernia with perforation of ascending colon. Patient was treated with herniorraphyand primary closure of the perforation of the ascending colon and diversion ileostomy. One patient (1.8%) in this study had strangulated incisional hernia with perforation of the transverse colon. Rajender Jhobta et al in their study found that strangulation of bowel leading to perforation peritonitis was found in 5% of the patients3 . Nineteen patients (34.5%) developed post-operative complications. Eleven patients (20%) developed superficial surgical site infection. Four patients (7.3%) developed burst abdomen and 2 of the patients (3.6%) with burst abdomen had leak from the perforation closure site. Four patients (7.3%) succumbed to the disease. Sharma et al who had conducted similar study in Delhi found similar mortality rate (8%)20. Agarwal et al in his study found burst abdomen in 11% and leak 5 % which was comparable with the present study15. (Table 2) Alcohol consumption and NSAID were not found to be significantly associated with the peptic ulcer perforation. Twenty two patients (73.3%) with peptic ulcer perforation were smokers. Smoking was significantly associated with peptic ulcer peforation (P value 0.006). (Table3) Strength of this study is that, it is one of the few prospective studies which analyzed the factors for gastro-intestinal perforation in this part of the world. Limitation of the study was sample size. The study included only 55 patients.
CONCLUSION
To conclude, peptic ulcer disease was found to be the most common cause of perforation peritonitis followed by blunt trauma abdomen and enteric perforation in contrast to western world where perforation due inflammatory disease and malignancy is common. Gastro-intestinal perforation due to malignancy and obstructed hernia were the least common cause in this study. Surgical site infection was the commonest complication. Smoking was significantly associated with peptic ulcer perforation. Alcohol consumption, prior NSAID abuse and duration of symptoms didn’t significantly affect the outcome of the patient. Morbidity rate was found to be 34% and mortality was 7.3%.
References:
1. Yadav D, Garg PK. Spectrum of Perforation Peritonitis in Delhi: 77 Cases Experience. Indian J Surg. 2013 Apr;75(2):133–7.
2. Chakma SM, Singh RL, Parmekar MV, Singh KG, Kapa B, Sharatchandra KH, et al. Spectrum of Perforation Peritonitis. J Clin Diagn Res JCDR. 2013;7(11):2518.
3. Jhobta RS, Attri AK, Kaushik R, Sharma R, Jhobta A. World Journal of Emergency Surgery. World J Emerg Surg. 2006;1:26.
4. Afridi SP, Malik F, Ur-Rahman S, Shamim S, Samo KA. World Journal of Emergency Surgery. World J Emerg Surg. 2008;3:31.
5. Bali RS, Verma S, Agarwal PN, Singh R, Talwar N. Perforation Peritonitis and the Developing World. IntSch Res Not [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2014 Aug 13];2014. Available from: http://www. hindawi.com/journals/isrn/2014/105492/abs/
6. Chatterjee H, Pai D, Jagdish S, Satish N, Jayadev D, Srikanthreddy P. Pattern of nontyphoidileal perforation over three dec- ades in Pondicherry. Trop Gastroenterol Off J Dig Dis Found. 2003 Sep;24(3):144–7.
7. Nuhu A, Kassama Y. Experience with acute perforated duodenal ulcer in a West African population. Niger J Med J Natl Assoc Resid Dr Niger. 2008 Dec;17(4):403–6.
8. Ohene-Yeboah M, Togbe B. Perforated gastric and duodenal ulcers in an urban African population. West Afr J Med. 2006 Sep;25(3):205–11.
9. Malangoni MA, Inui T. Peritonitis - the Western experience. World J Emerg Surg WJES. 2006;1.
10. Dakubo JCB, Naaeder SB, Clegg-Lamptey JN.Gastro-duodenal peptic ulcer perforation. East Afr Med J. 2009 Mar;86(3):100–9.
11. Leeman MF, Skouras C, Paterson-Brown S. The management of perforated gastric ulcers. Int J SurgLond Engl. 2013;11(4):322– 4.
12. Chaudhary A, Bose SM, Gupta NM, Wig JD, Khanna SK. Giant perforations of duodenal ulcer. Indian J Gastroenterol Off J Indian Soc Gastroenterol. 1991 Jan;10(1):14–5.
13. Noguiera C, Silva AS, Santos JN, Silva AG, Ferreira J, Matos E, et al. Perforated peptic ulcer: main factors of morbidity and mortality. World J Surg. 2003 Jul;27(7):782–7.
14. Sule AZ, Kidmas AT, Awani K, Uba F, Misauno M. Gastrointestinal perforation following blunt abdominal trauma. East Afr Med J. 2007 Sep;84(9):429–33.
15. Agarwal N, Saha S, Srivastava A, Chumber S, Dhar A, Garg S. Peritonitis: 10 years’ experience in a single surgical unit. Trop Gastroenterol Off J Dig Dis Found. 2007 Sep;28(3):117–20.
16. Edino ST, Yakubu AA, Mohammed AZ, Abubakar IS. Prognostic factors in typhoid ileal perforation: a prospective study of 53 cases. J Natl Med Assoc. 2007 Sep;99(9):1042–5.
17. Kotan C, Sumer A, Baser M, K?z?ltan R, Carparlar MA. An analysis of 13 patients with perforated gastric carcinoma: A surgeon’s nightmare? World J Emerg Surg. 2008;3(1):17.
18. Abro A, Siddiqui FG, Akhtar S, Memon AS. Spectrum of clinical presentation and surgical management of intestinal tuberculosis at tertiary care hospital. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad JAMC. 2010 Sep;22(3):96–9.
19. Jain BK, Garg PK, Kumar A, Mishra K, Mohanty D, Agrawal V. Colonic perforation with peritonitis in amoebiasis: a tropical disease with high mortality. Trop Gastroenterol Off J Dig Dis Found. 2013 Jun;34(2):83–6.
20. Sharma L, Gupta S, Soin AS, Sikora S, Kapoor V. Generalized peritonitis in India--the tropical spectrum. Jpn J Surg. 1991 May;21(3):272–7.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License