IJCRR - 8(6), March, 2016
Pages: 22-29
Date of Publication: 22-Mar-2016
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
BIOCHEMICAL ASSESSMENT OF HOMOCYSTEINE AND LIPID PROFILE IN PEDIATRIC STROKE: AN EGYPTIAN STUDY
Author: Tahia H. Saleem, Mohammed H. Hassan, Ahmed El-Abd Ahmed, Abdallah M. A.A. El-Ebidi, Heba M. Qubaisy, Omayma A. Hasan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Stroke and cerebrovascular disorders are already amongst the top 10 causes of childhood death. Patients with homocysteinemia may present with vascular thrombotic events, with or without the traditional risk factors for a stroke. Objectives: The aim of this study was to measure plasma homocysteine levels and lipid profile (serum cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL and calculation of LDL) in pediatric patients with ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. Assess the role of homocysteinemia as an associated risk factor in pediatric ischemic stroke. Correlate the results with the clinical data of the patients. Materials and Methods: Across-sectional case control study was carried out on 60 pediatric patients, divided into two groups: group A contained 30 pediatric patients with ischemic stroke and group B contained 30 pediatric patients with hemorrhagic stroke, they were recruited from outpatient clinics or admitted to PICU (pediatric intensive care unit) in Assiut university children hospital and Qena university hospital, Upper Egypt, after approval of the university hospital ethical committee. The control group \"group C\" contained 30 healthy age and sex matched subjects. Biochemical assay of plasma homocysteine and lipid profile among the previously mentioned groups were done. Results: The plasma homocysteine level showed statistically significantly higher levels among group A when compared with group B and group C (P-Value 0.0001). There was no significant difference in plasma homocysteine among group B when compared with group C (P-Value 0.9). Regarding the lipid profile assay in the studied groups, serum triglyceride level, cholesterol and low density lipoprotein (LDL) were significantly high among group A in comparison with group B and group C (P-Value< 0.0001), while high density lipoprotein (HDL) level was significantly low among group A in comparison with group B and group C( PValue< 0.0001). There was a positive correlation between plasma homocysteine level and both LDL and triglyceride levels while a negative correlation between plasma homocysteine level and HDL level. Conclusion: Elevated plasma homocysteine can be considered as an associated risk factor among pediatric patients with ischemic stroke that could be explained by its atherogenic and thrombotic effects. This was associated with hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: Homocysteine, Lipid profile, Pediatric stroke, Egyptian study
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION Stroke and cerebrovascular disorders are already amongst the top 10 causes of childhood death 1 . Considering the onset of impairment during childhood and the effect on quality of life for the child and family, the economic and emotional costs to society are amplified 2. There are two main types of stroke. Ischemic strokes are caused by a blockage in the blood supply to the brain. Hemorrhagic strokes occur when blood leaks from a burst blood vessel into the brain3 . The majority of signs and symptoms of stroke are nonspecific, and can be easily attributed to other causes. One way to avoid delays or misdiagnoses would be to identify risk factors for stroke that would prompt more aggressive and timely inves tigation. Multiple risk factors are often present in as many as 25% of children with stroke, which means further investigations are warranted even when one risk factor has been identified 4. Homocysteine (Hcy) is a sulfur containing amino acid. Hcy is formed through demethylation of methionine, which donates a methyl group in many biochemical reactions. It is metabolized through two enzymatic pathways; trans-sulfuration and remethylation, but not in all tissues. Vitamin B6 is important in Hcy trans-sulfuration, whereas folate and vitamin B12 play significant role in Hcy re-methylation5 .
Patients with homocysteinemia could be presented with vascular thrombotic events, in presence or absence of the traditional risk factors for the occurrence of a stroke. This group of patients may already have a history of strokes and myocardial infarctions in the third or fourth decade of life 6 . From a pathophysiologic point of view, homocysteinaemia is associated with atherogenesis and increased thrombogenicity 7 . Transient and chronic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress elicited by homocysteine has been shown to adversely affect several cellular functions involved in the development and progression of atherosclerosis, including lipid dysregulation, programmed cell death and inflammation8 . Both in animal models and humans, homocysteinaemia is characterized by platelet aggregation and formation of thrombi rich in platelets at the sites of injured endothelium. The increased risk of vascular thrombosis may be derived from the vascular oxidative injury and the modification of physiological antithrombotic mechanisms7 .
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study design: This study is across-sectional case control study and it was carried out on 60 children with CNS stroke (38 males and 22 females). This is in addition to 30 apparently healthy age and sex matched children. The study was carried out during the period from May 2014 to July 2015.Prior to initiation of the study; every subject was informed about the aim of the study and gave a written consent. They were recruited from outpatient clinics or admitted to PICU (Pediatric intensive care unit) in Assiut university children hospital and Qena university hospital, Upper Egypt, after approval of the university hospital ethical committee and according to the inclusion criteria that x old who presented with clinical history and signs suggestive of stroke and documented by brain C.T or M.R.I, the clinical signs included (neurological deficit e.g. hemiparesis, seizures, ataxia or altered levels of consciousness, manifestations of increased intracranial tension e.g. headache, projectile vomiting and blurred vision, signs of meningeal irritation e.g. neck rigidity, spinal rigidity, photophobia, headache, and positive Kernig’s sign and Brudzinski’s sign, cranial nerve affection e.g. ptosis (cranial nerve III affection), facial palsy(cranial nerve VII affection), or bulbar palsy (cranial nerve IX, X, XI, XII affection).The study was carried out during the period from May 2014 to July 2015. Prior to initiation of the study; every subject was informed about the aim of the study and gave a written consent.
Data collections: History taking for all included pediatric patients, including: Personal history/ Family History: age, sex, residence, history of consanguineous marriage among the patients’ parents. History of associated risk factors e.g. infection, diabetes mellitus, rheumatic heart disease, receiving certain drugs e.g. anticoagulant therapy, history of recurrence (recurrent stroke), history of having any metabolic disorders or collagen disease, epilepsy, history suggestive of disseminated intravascular coagulation “DIC”, history of vaso-occlussive crisis. Family history of early coronary heart disease. Thorough Clinical examination for: vital signs. Anthropometric measurement. Skin examination: purpuric eruptions, echemotic patches or abnormal rash. Cardiac examination: murmurs, arrhythmias, cardiomegaly. Neurological examination: level of consciousness assessed by Glasco coma scale (GCS), motor and sensory system examination, and cranial nerves examination. Radiological evaluation including Computed tomography (CT) was done to every patient.
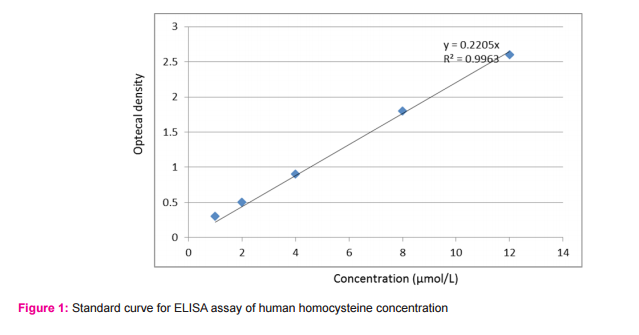
Methodology: Two milliliters venous blood was drawn which were divided into: 1 ml on EDTA for assay of plasma homocysteine, 1 ml on plain tube for lipid profile assay, among the previously mentioned groups. Samples were centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 minutes. Serum and plasma were transferred into 1 ml cryotubes and stored at -20 0C for later analysis. Plasma homocysteine levels were measured according to the manufacture protocol using an enzyme-linked immune-sorbent (ELISA) assay kit, provided by Chongqing Biospes Co., Ltd. Paradise Walk, Jiangbei District, Chongqing, 400020, China. Standard curve for homocysteine was done (Figure 1). Serum lipids (HDL, triglycerides and total cholesterol) were measured according to the manufacture protocol using a spectrophotometric assay kit provided by BIOLABO SAS, Les Hautes Rives 02160, Maizy, France. The serum level of LDL cholesterol was determined by the Friedewald formula (9). Triglycerides
LDLc (mg/dl) = Total cholesterol - (------------------ + HDL).
Statistical analysis: Values are given as means ± SD, range, or as the number of patients and proportions. The chi square test was used to compare proportions. Correlation coefficients were used to describe associations between variables. P < 0.05 was considered significant. Analyses were performed using the SPSS software package (SPSS V 17 for Windows).
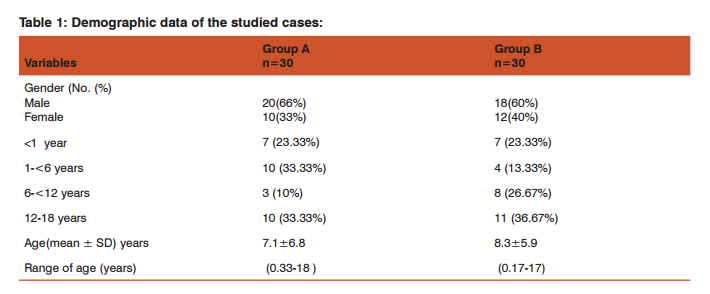
RESULTS Table 1 presents the demographic data of the studied cases: As regard sex, the ?/? ratio was 2:1 in group A, and 3:2 in group B. Age range for group A was 0.33-18 years (mean age 7.1±6.8 SD years), and for group B age range was 0.17-17 years (mean age 8.3±5.9 SD years). According to the age at presentation, we divided the patients included in the study into 4 groups. Regarding group A, the highest age groups were (above 12 years age group, and 1-<6 years age group, 33.33% for each) followed by (<1 year age group, 23.33%) and (6-<12 age group, 10%).
Regarding group B, the highest age group was (above 12 years age group, 36.67%) followed by (6-<12 age group, 26.67%), (<1 year age group, 23.33%) and (1-<6 years age group, 13.33%). The frequency distribution of the associated risk factors among patients of group A and group B are shown in table 2; among patients of group A, infection was the most common risk factor (36%), followed by dehydration (23%), history of recurrence (20%), rheumatic heart disease (13%), and diabetes mellitus (3%). Among patients of group B, infection was the most common risk factor (30%), followed by cerebral aneurysm (13%), thrombocytopenia (10%), and anticoagulant therapy (3%). Table 3 presents the frequency distribution of the main clinical findings of the studied cases; in group A, the most frequent presentation was hemiparesis which was present in (60%) of cases, followed by both convulsions and disturbed conscious level (40% each ), (27%), increased intracranial tension (17%), cranial nerve affection (7%), loss of vision (1%), and ataxia (1%). In group B, the most frequent presentation was disturbed conscious level which was present in (50%) of cases, followed by convulsions (47%), increased intracranial tension (40%), hemiparesis (33%), fever (23%), and meningeal signs (17%).
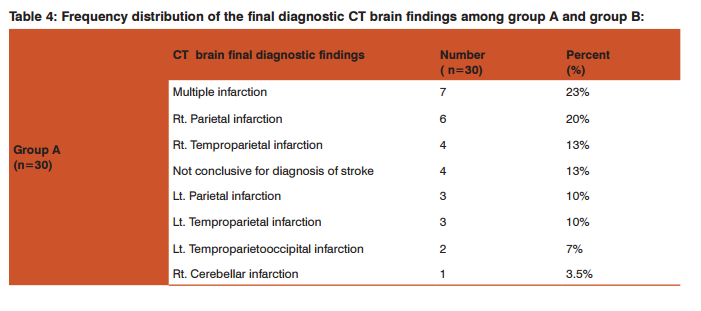
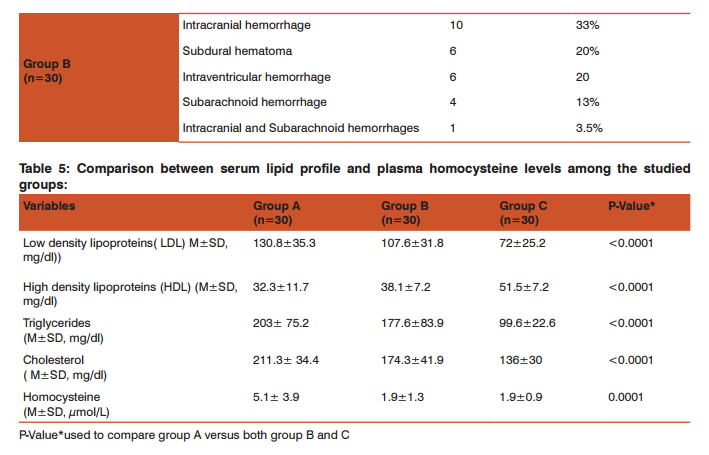
Table 4 showed frequency distribution of the final diagnostic CT brain findings; among group A: multiple infarctions was the most common diagnosis (23%), followed by right parietal infarction (20%), right temproparietal infarction (13%),parietal infarction and left temproparietal infarction (10% for each), left temproparietooccipital infarction ( 7%), right cerebellar infarction(3.5%), and the CT was not conclusive for diagnosis of stroke in 13% of patients and group B: intracranial hemorrhage was the most common diagnosis (33%), followed by subdural haematoma and intraventricular hemorrhage(20% for each), subarachnoid haemorrhage (13%), intracranial and intraventricular hemorrhages (7%), intracranial and subarachnoid hemorrhages (3.5%) and intraventricular and subarachnoid haemorrhages (3.5%).
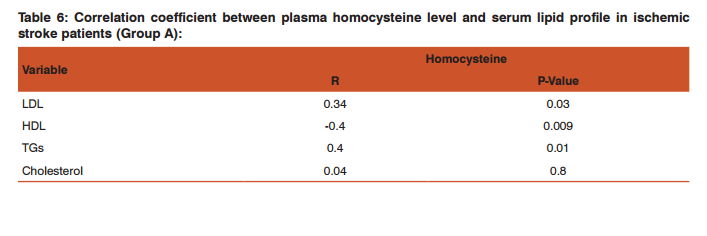
Comparison between serum lipid profile and plasma homocysteine levels among the studied groups was done which revealed that; the plasma homocysteine level showed statistically significant higher levels among group A when compared with group B and group C (P-Value 0.0001). Regarding the lipid profile assay in the studied groups, serum triglyceride level, cholesterol and low density lipoprotein (LDL) were significantly high among group A in comparison with group B and group C (P-Value<0.0001), while high density lipoprotein (HDL) level was significantly low among group A in comparison with group B and group C (P-Value<0.0001) (Table 5). The correlation coefficient between plasma homocysteine level and serum lipid profile in ischemic stroke patients (Group A): There was a positive correlation between plasma homocysteine level and both LDL (r=0.34, p=0.03) and triglyceride levels(r=0. 4, p=0.01) while a negative correlation between plasma homocysteine level and HDL level (r= -0. 4, p=0.009) (Table 6). Figure 1 showed Standard curve for ELISA assay of human homocysteine concentration (y= 0. 2, R2 =0.9).
DISCUSSION Stroke is a neurological injury caused by the occlusion or rupture of cerebral blood vessels. Stroke can be ischemic, hemorrhagic, or both (10). In the present study, according to the age at presentation, regarding group A, the highest age group was above 12 years age group, and 1-<6 years age group, (33.33% for each). Regarding group B, the highest age group was (above 12 years age group, 36.67%) followed by (6-<12 age group, 26.67%) as shown in table-1.These findings were in agreement with Ogeng’o et al 11, Chung and Wong12 and Salih et al13. Regarding the frequency of the associated risk factors among patients of group A, infection was the most common risk factor (36%), followed by dehydration (23%). history of recurrent ischemic stroke (20%), rheumatic heart disease (13%), and diabetes mellitus (3%) as shown in table -2.While among patients of group B, infection was the most common risk factor (30%), followed by cerebral aneurysm (13%), thrombocytopenia (10%), and anticoagulant therapy (3%) as shown in table -2.
This is in agreement with Kalita et al 14 and Saima et al 15.As regard the main clinical findings of the studied cases, , the most frequent presentation among group A was hemiparesis which was present in (60%) of cases, followed by both convulsions and disturbed conscious level (40% for each), fever (27%), increased intracranial tension (17%), cranial nerve affection (7%), loss of vision (1%), and finally ataxia (1%). While the most frequent presentation among group B was disturbed conscious level which was present in (50%) of cases, followed by convulsions (47%), increased intracranial tension (40%), hemiparesis (33%), followed by fever (23%), and finally signs of meningeal irritation (17%) as shown in table-3. In agreement with these results, a study done by Salih et al 13 on Saudian children with stroke showed that hemiparesis/ hemiplegia was the most common presenting symptom. Another study was done by Parakh et al16 who evaluated the clinical profile of pediatric stroke in Western Rajasthan and found that disturbed conscious level and convulsions were most common presentations among pediatric patients with hemorrhagic stroke.
As regard the CT brain final diagnostic findings among group A patients involved in this study: multiple infarctions was the most common diagnosis (23%), followed by right parietal infarction (20%) as shown in table-4 and the CT was not conclusive for diagnosis in 4 patients (13%), for whom MRI brain was done and revealed that 3 patients (10%) had cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), and 1 patient (3.33%) had brain stem and cerebellar infarctions. While the CT brain final diagnostic findings among group B patients involved in this study: intracranial hemorrhage was the most common diagnosis (33%), followed by Subdural haematoma and intraventricular hemorrhage(20% for each) as shown in table -4. In agreement with these findings a study done by Ogeng’o et al 11 who found that more than half of cases had cortical lesions, distributed fronto-parietal (most common), followed by parietal, temporal, occipital and one frontal lesions. In the present study, the plasma homocysteine level showed a statistically significantly higher levels among group A (mean 5.1± 3.9 SD, μmol/L) when compared with group B (mean 1.9±1.3 SD, μmol/L) and group C (mean 1.9±0.9 SD, μmol/L), P-Value0.0001 as shown in table-5.
In agreement with these results, Vijaya et al 17, Ashjazadeh et al 18 and Naranget al 19, all of they found that levels of serum homocysteine were significantly higher in the cases with ischemic stroke than in the control group. Regarding the lipid profile in the studied groups, the present study showed that low density lipoprotein ( LDL) level was significantly high among group A (mean130.8±35.3 SD mg/dl) in comparison with group B (mean 107.6±31.8 SD, mg/dl) and group C (mean72±25.2 SD, mg/dl), PValue<0.0001. High density lipoprotein (HDL) level was significantly low among group A (mean 32.3±11.7 SD, mg/ dl) in comparison with group B (mean 38.1±7.2 SD, mg/dl) and group C (mean51.5±7.2 SD, mg/dl), P-Value<0.0001. Serum triglyceride level was significantly high among group A (mean 203± 75.2SD, mg/dl) in comparison with group B (mean 177.6±83.9 SD, mg/dl) and group C (mean 99.6±22.6 SD, mg/dl), P-Value<0.0001. Serum cholesterol level was significantly high among group A (mean 211.3± 34.4SD, mg/ dl) in comparison with group B (mean 174.3±41.9 SD, mg/ dl) and group C (mean 136±30 SD, mg/dl), P-Value<0.0001 as shown in table -5.
In agreement with these findings, a study done by Vijaya et al 17 who found that LDL level was significantly higher among ischemic stroke patients than controls. High density lipoprotein (HDL) level was significantly lower among ischemic stroke patients than controls. Serum triglyceride level was significantly higher among ischemic stroke patients than controls. Serum cholesterol level was significantly higher among ischemic stroke patients than controls. Another study done by García et al 20 who found that patients with ischemic stroke had significantly higher total cholesterol levels, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglycerides than those in the control group. In the present study, among the ischemic stroke pediatric patients (group A), there was a positive correlation between plasma homocysteine level and LDL level, r was 0.34, and P-value was 0.03. Also, there was a positive correlation between plasma homocysteine level and triglyceride level, r was 0.4 and P-value was 0.01.But there was a negative correlation between plasma homocysteine level and HDL level, r was -0.4 and P-value was 0.009. There was no significant correlation between plasma homocysteine level and serum cholesterol level as shown in table -6. In agreement with these findings: A study done by Xiao et al 21 who found a negative correlation between homocysteine level and HDL and also in that there was no significant relation between homocysteine level and serum cholesterol level, but he found that there was no significant relation between homocysteine level and each of LDL level and triglyceride level. Also another study done by Elshorbagy et al 22 who found that there was a negative relation between homocysteine level and HDL, and a positive correlation between homocysteine level and serum cholesterol level. Also another study done by Elkhairy et al 23 who found that there was a positive correlation between homocysteine level and each of LDL, triglyceride level and serum cholesterol level.
CONCLUSION Elevated plasma homocysteine proved to be an associated risk factor among pediatric patients with ischemic stroke and this may explain the associated hyperlipidemia due to the atherogenic and thrombotic effect of high plasma homocysteine, so, plasma homocysteine assay should be routinely.done to any pediatric patients with ischemic stroke and folic acid, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 therapy to those patients may have a beneficial effects, as they enhance the metabolism of homocysteine leading to lowering of its plasma level.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Authors would like to acknowledge the team work of the Metabolic and Genetic Disorders Unit- Faculty of MedicineAssiut University, where the laboratory work of this study has been done. Also, authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this research article. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Ethical approval: The Research Committee at Qena Faculty of Medicine, South Valley University approved this study (R. Nr. 10/01/015). Funding: This research was funded by Qena faculty of Medicine- South Valley University. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.


References:
1. Neil F. Pediatric Stroke: Past, Present and Future. Advances in Pediatrics 2009; 56: 271–299.
2. Sharmini R. Arterial ischemic stroke in childhood. Pediatrics and Child Health 2014; 24:462-467.
3. Timothy J, Warren L and Mark T. Towards a consensus-based classification of childhood arterial ischemic stroke. Stroke 2012; 43:371-377.
4. Jonathan H, Daniel S. Pediatric stroke: a review. Emergency Medicine International 2011:1–10.
5. Djuric D, Jakovljevic V, Rasic-Markovic1 A, Djuric A, Stanojlovic O. Homocysteine, folic acid and coronary artery Disease: Possible Impact on Prognosis and Therapy. The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases and Allied Sciences 2008; 50: 39-48.
6. Richard E, Desviat L, Ugarte M, Pérez B. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in homocystinuria patients with genetic remethylation defects. J Cell Biochem 2013; 114(1):183-91.
7. Antoniades C, Alexios S. Antonopoulos, Dimitris T, Kyriakoula M, Christodoulos S. Homocysteine and coronary atherosclerosis: from folate fortification to the recent clinical trials. European Heart Journal 2009; 30: 6–15
8. Lawrence de Koning A, Geoff H, Richard C. Hyperhomocysteinemia and its role in the development of atherosclerosis. Clinical Biochemistry 2003; 36:441–431.
9. Friedewald W, Levy R, Fredrickson D. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem 1972; 18 (6): 499-502.
10. DeVeber G. In pursuit of evidence-based treatments for pediatric stroke: the UK and Chest guidelines. The Lancet Neurology 2005; 4(7):432–436.
11. Ogeng’o J, Olabu B, Mburu A, Sinkeet S. Pediatric stroke in an African country. Journal of pediatric neurosciences 2010; 5(1): 22-24.
12. Chung B, Wong V. Pediatric stroke among Hong Kong Chinese subjects. Pediatrics 2004;114(2): 206–212.
13. Salih M, Abdel-Gader A, Al-JarallahA. Infectious and inflammatory disorders of the circulatory system as risk factors for stroke in Saudi children. Saudi Medical Journal 2006; 27(1): 41–52.
14. Kalita J, Goyal G, Misra U. Experience of pediatric stroke from a tertiary medical center in North India. Journal of the neurological sciences 2013; 325(1): 67-73.
15. Saima B, Gilani S, Shah S, Siddiqui T: Childhood strokes: epidemiology, clinical features and risk factors. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2011; 23(2): 69-71.
16. Parakh M, Arora V, Khilery B. A Prospective Study Evaluating the Clinical Profile of Pediatric Stroke in Western Rajasthan. Journal of Neurological Disorders 2014; 2 (6) :1-4.
17. Vijaya B, Vennela D, Suma P. Study of homocysteine, lipoprotein (a) and lipid profile in ischemic stroke. Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. 2014; 2(4):1247-1250.
18. Ashjazadeh N, Fathi M, ShariatA. Evaluation of homocysteine level as a risk factor among patients with ischemic stroke and its subtypes. Iranian journal of medical sciences 2013; 38(3): 233-9.
19. Narang A, Verma I, Kaur S, Narang A, Gupta S, Avasthi G . Homocysteine- Risk factor for ischemic stroke?Indian J PhysiolPharmacol 2009; 53(1): 34-8.
20. García S, Concepción O, Carriera R, Zuaznábar M. Association between Blood Lipids and Types of Stroke. MEDICC Review 2008; 10(2): 27-32.
21. Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Lv X, et al. Relationship between lipid profiles and plasma total homocysteine, cysteine and the risk of coronary artery disease in coronary angiographic subjects. Lipids in Health and Disease 2011; 10(137): 1476-511.
22. Elshorbagy A, Nurk E, Gjesdal C, Tell G, Ueland P, Nygård O, Refsum H. Homocysteine, cysteine, and body composition in the HordalandHomocysteine Study: does cysteine link amino acid and lipid metabolism?.The American journal of clinical nutrition 2008; 88(3): 738-746.
23. El-Khairy L, Ueland P, Refsum H, Graham I, Vollset S . Plasma total cysteine as a risk factor for vascular disease The European Concerted Action Project. Circulation 2001; 103(21): 2544- 2549.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License