IJCRR - 9(7), April, 2017
Pages: 28-32
Date of Publication: 11-Apr-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Microbiota of Chronic Periodontitis and their Association with Severity of the Disease
Author: Mohammad Mukhit Kazi, Renu Bharadwaj
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: To know the role of these microorganisms as etiological agents in chronic periodontitis and their role in the severity of the disease.
Material and Method: A total of 300 patients with chronic periodontitis and 300 age and sex matched controls were enrolled with prior informed consent. Sub gingival plaque specimens was collected and processed for bacterial and yeast etiology. The data was analyzed by using SPSS software and Chi square test with p-value of < 0.0001 was applied.
Results: The most common age group affected were 31 to 40 years and male were outnumbered the female patients but the difference was not statistically significant. Overall detection rate of aerobes, anaerobes and yeasts were 47.3%, 78.3% and 4.6% respectively. The most common etiological agents significantly associated belong to anaerobes and yeasts. Anaerobes were found to be associated significantlywith severity of disease.
Conclusion: Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, Veillonella parvula and Porphyromonas gingivaliswere predominant etiological agents implicated as etiological agents in chronic periodontitis. Aerobes were significantly associated with mild chronic periodontitis while anaerobes found to be significantly associated with severe chronic periodontitis.
Keywords: Chronic periodontitis, Microbiota, Anaerobes, Aerobes, Yeasts, Severity
Full Text:
Introduction:
Chronic periodontitis is the most common oral disease affecting worldwide especially in India which leads to tooth loss if kept untreated for long (1). It is initiated by plaque which consists of bacteria that are responsible for initiation and further progression of the disease(2). Aerobes, anaerobes and possibly yeasts could play a crucial role in the initiation of chronic periodontitis (3). The present study has evaluated the role of microorganisms in chronic periodontitis and in the severity of the disease.
Material and Methods:
The present study was a prospective case control study. The ethical approval was taken from Ethical Committee (D-1210169-71) and the study period was from June 2011 to December 2014. A total of 300 patients with chronic periodontitis (100 each from mild, moderate and severe) as per classification of American Association of Periodontologist(4) and 300 age and sex matched controls were enrolled with prior informed consent. An inclusion and exclusion criterion was applied before obtaining specimens from patients as well as healthy controls.Subgingival plaque specimen was collected and transferred to brain heart infusion (BHI) broth and Robertson cocker meat (RCM) medium and processed for cultivation of aerobes and anaerobes by standard methods (5). The data was analyzed with the help of SPSS software v17.0 and Chi square test with p-value of <0.0001 was used to find out any significant associations.
Results:
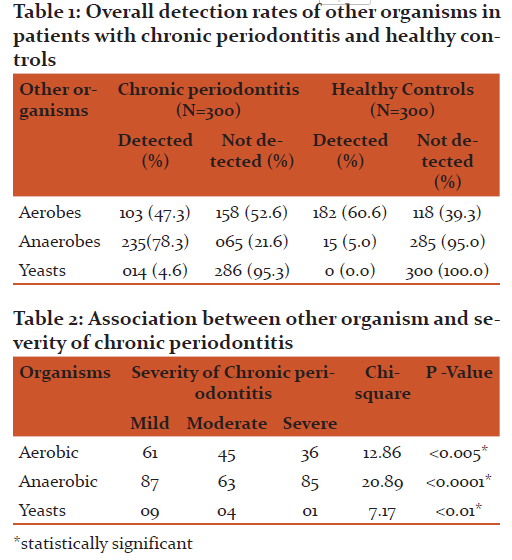
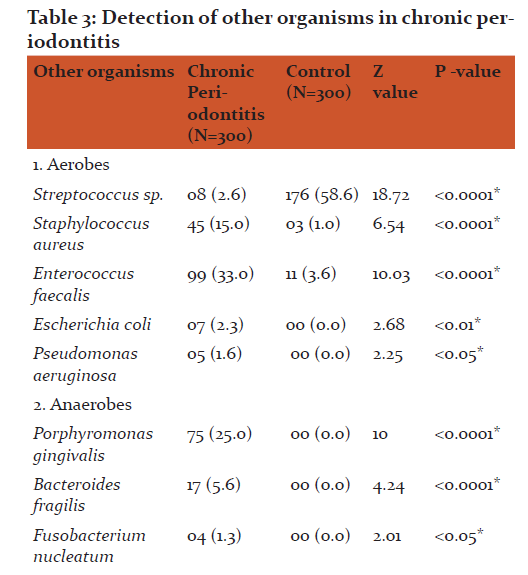
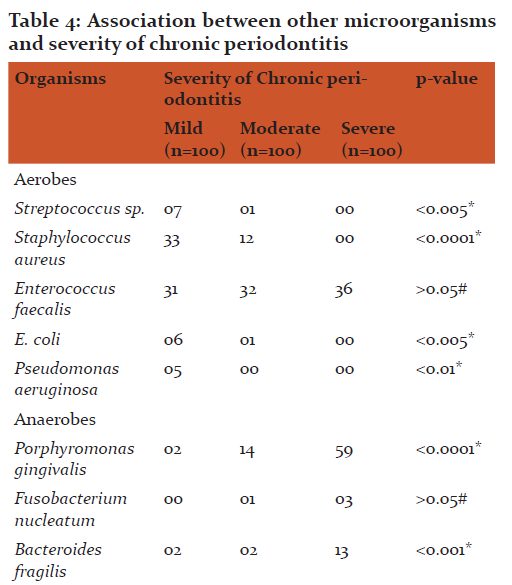
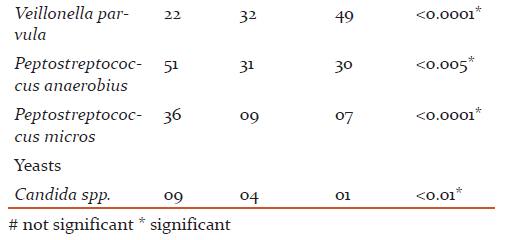
The most common age group affected were 31 to 40 years(43.49+8.48) and male patients outnumbered female patients (p>0.05). The overall detection rate of aerobes, anaerobes and yeasts was 47.3, 78.3 and 4.6 % respectively (Table 1). The aerobes were significantly associated with mild while anaerobes were significantly associated with severe chronic periodontitis (Table 2). The common etiological agents include Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (37.3 %), Veillonella parvula (34.3 %), Enterococcus faecalis (33.0 %) and Porphyromonas gingivalis (25 %) (Table 3). Anaerobes (P. gingivalis, B. fragilis, F. nucleatum, V. parvula) were found to be associated significantly with increasing severity of the disease (Table 4).
Discussion:
In adult patients there is a complex interplay of the mixed polymicrobial infection and host response. The present study has evaluated the role of these microorganisms as etiological agents in chronic periodontitis and their association with severity of the disease.Anaerobic bacteria (78.3 %) were the commonest bacterial pathogen detected from patients with chronic periodontitis (Table 1). Various studies have reported anaerobes in periodontitis with isolation rates ranging from 57.0 % to 93.0 % (6-11). The anaerobic flora plays an important role in the progression of chronic periodontitis. This could be due to the fact that the more the pocket depth and attachment loss an anaerobic environment is created, which is ultimately favorable to the growth of anaerobic pathogens. They establish in the depth of the oral pockets and cause tissue destruction.
The anaerobes were significantly associated with the severity (p <0.0001) of chronic periodontitis (Table 2). Various studies have reported anaerobes from severe chronic periodontitis than mild periodontitis (10, 12, 13, 14). Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (37.3 %), Veillonella parvula (34.3 %) and Porphyromonas gingivalis (25.0 %) were predominantly detected from patients with chronic periodontitis and found to be associated significantly with the disease (p <0.0001) (Table 3).
Peptostreptococcus anaerobius:
P. anaerobius is found to be associated with adult periodontitis. They possesses capsule which is an important virulence factor and can produce abscesses. P. anaerobius was the commonest anaerobe (37.3 %) detected in the present study (Table 3). Younis et al (15) and Sixou et al (16,17) have reported P. anaerobius in 2.7%, 5.8% and 14.2 % from patients with periodontitis. However, Koll-Klais et al (18) have reported Peptostreptococcus spp. in 90.0 % from patients with periodontitis. They did not speciate the Peptostreptococcus spp. isolated in their study.From the findings of the current study, P. anaerobius is reflected to be a major pathogen in the etiology of chronic periodontitis. P. anaerobius was found to be associated significantly with mild chronic periodontitis. In mild chronic periodontitis, the anaerobic environment is limited, because of which P. anaerobius have been detected predominantly in the present study. This also suggests that they come first in the initiation of the disease.
Peptostreptococcus micros:
Peptostreptococcus micros were detected from 17.3 % from patients with chronic periodontitis in the present study (Table 3). Mane et al (19) have reported Peptostreptococcus micros in 23.0 % from patients with chronic periodontitis. P. micros were also found to be associated significantly with mild chronic periodontitis.
Veillonella parvula:
V. parvula has been reported to play an essential role as early colonizers in the biofilm formation and thereby facilitate succession in development of oral biofilms which helps other microbiota to establish them. V. parvula was detected in 34.3 % of cases of chronic periodontitis in the present study (Table 3). The detection rates of the organism were seen from 9.0 % to 81.0 % in various studies(18, 20). In the present study, V. parvula was found to be associated with the increased severity of chronic periodontitis. They were detected in 49.0 % from severe chronic periodontitis as compared to mild and moderate(Table 4)suggestingtheir role too in the increased severity of the disease.
Porphyromonas gingivalis:
P. gingivalis is an important etiological agent which is postulated to play a major role in chronic periodontitis by different mechanisms. They produces many pathogenic virulence factors such as lipopolysaccharides and H2S, which can induce the host to release interleukin, tumour necrosis factors which precipitated the host’s immune response leading to bone resorption and prevent the repairing of osteal tissue. They produce proteases, collagenases which are important in the process of tissue breakdown. They possess fimbriae which are helpful in attachment to host epithelial cells and damage soft tissue directly. P. gingivalis was detected in 25.0 % of cases of chronic periodontitis in the present study (Table 3). Different studies have reported different rates ranging from 21.9 to 78.0 % from patients with chronic periodontitis (11, 18, 21, 19, 22).
The most common species associated with severe chronic periodontitis was Porphyromonas gingivalis in the present study. They were detected from 59.0 % of severe chronic periodontitis cases suggesting their strong association with the increased severity of the disease (Table 4). Different studies have reported association between P. gingivalis detection and severity of chronic periodontitis (23, 24, 25).
The other anaerobes detected were Bacteroides fragilis (5.6%) and Fusobacterium nucleatum (1.3%) from patients with chronic periodontitis suggesting their association with the disease in the present study (Table 3). Their association was found to be statistically significant. Various authors have detected various other anaerobes in their respective studies (11, 19, 23). All the above studies and the currents study have highlighted the role of Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, Veillonella parvula and Porphyromonas gingivalis as an important etiological agent of chronic periodontitis.
Aerobes establish themselves in supragingival plaque and participate in the disease initiation by deleterious effect during their interactions with the host. Aerobes were detected in 47.3 % of the patients with chronic periodontitis in the present study (Table 1). Other studies have reported aerobes as a causative agent in patients with chronic periodontitis ranging from 7.4 % to 62.3 % (8, 10, 19, 26). In the present study aerobes were detected from cases of chronic periodontitis suggesting their role too as etiological agent in chronic periodontitis.
Enterococcus faecalis:
E. faecalis possesses numerous virulence factors which may add to periodontal inflammation and tissue destruction. Enterococcus faecalis was the most common (33.0 %) aerobe detected from patient with chronic periodontitis in the present study (Table 3). Different studies have reported different detection rates ranging from 12.0 to 51.8 % in their studies(18, 27, 28). All the above studies and the present study have displayed that Enterococcus faecalis plays an important role in the causation of chronic periodontitis. E. faecalis were detected from all grades of chronic periodontitis equally. There was no statistical difference found in severity of the disease and detection of E. faecalis. The reason might be their facultative nature which allows them to grow in any adverse conditions.
Staphylococcus aureus:
The presence of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with chronic periodontitis is usually seen in mild and moderate infections. However, they can act as an opportunistic pathogen and their presence must be considered when planning antibiotic therapy. Staphylococcus aureus was the second highest (15.0 %) aerobe which was detected from cases of chronic periodontitis (Table 3). Different studies have reported different detection rates ranging from 4.5 % to 42.8 % in their respective studies (29, 30, 18, 8, 6). In the present study, S. aureusshown to be associated significantly with mild chronic periodontitis as compared to the severe chronic periodontitis suggesting their initial role in the disease(Table 4).
Other aerobes:
The other aerobes detected in the present study were Streptococcus spp. (2.6 %), E. coli (2.3 %) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1.6 %) from patients with chronic periodontitis (Table 3). Other studies have also reported these aerobes in their respective studies (9, 6) from periodontitis patients. Aerobes in subgingival samples indicate that they play a role in initiation of chronic periodontitis and create a suitable environment for invasion by other microbes i.e. anaerobes or Herpes viruses resulting in increase in severity.
The Candida spp. has various virulence factors that can make it possible for them to colonize and propagate in the oral mucosa especially the periodontal pockets. Candida spp. is a major component of oral microflora and could play a role in the initiation of periodontitis. The prevalence of Candida spp. in the present study was 4.6 % from patients with chronic periodontitis (Table 1). The other studies have reported detection of Candida spp.in chronic periodontitis which ranges from 0 to 53.5 % from patients with chronic periodontitis (9, 18, 26, 31-35).
In the present study, Candida spp. was detected mainly from patients with mild chronic periodontitis (9.0 %) suggesting their association in the initial stage of the disease (Table 4). Canabaro et al (34) and Jarvensivuet al (32) have reported association of Candida spp. with deep pockets suggesting their role in severity of the disease. However, in the present study, Candida spp. has been detected more significantly in the mild chronic periodontitis suggesting their role in the initial phase of the disease.
Conclusion:
Chronic periodontitis is a multi-etiologic oral disease affecting wide range of population. It is mainly initiated by aerobic flora and yeasts which is then followed by anaerobes. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius, Veillonella parvula and Porphyromonas gingivalis were the most predominant etiological agents along with Staphylococcus aureus. In the severity of the disease aerobes were associated more with mild chronic periodontitis while anaerobes such as P. gingivalis were associated with severe chronic periodontitis. Thus, before initiation of any therapeutic treatment it is essential to know the stage of the disease and the etiology of the disease which help in management of the disease.
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors / publishers of all of those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The authors are also thankful to Dr. Sameer Patil, Dr. Rajeev Saxena, Dr. Daisy, Dr. Asawari and Mrs. Varsha Pendse for their support.
Conflict of Interest:
None
Financial support:
No
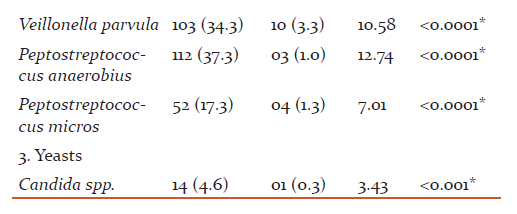
References:
- Kumar TS, Dagli RJ, Mathur A, Jain M, Balasubramanyam G, Prabhu D, et al. Oral health status and practices of dentate Bhil adult tribes of southern Rajasthan, India. Int Dent J. 2009; 59(3):133-40.
- Page RC, Schroeder HE. Pathogenesis of inflammatory periodontal disease. A summary of current work. Lab Invest.1976; 34:235–49.
- Aas JA, Barbuto SM, Alpagot T, Olsen I, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ. Subgingival plaque microbiota in HIV positive patients. J Clin Periodontol. 2007; 34 (3): 189-95.
- The American Academy of Periodontology. Proceedings of the World Workshop in Clinical Periodontics. Chicago. The American Academy of Periodontology. 1989; 1-22.
- Summanen P, Baron EJ, Citron DM, Strong C, Wexler HM, and Finegold SM. Wadsworth Anaerobic Bacteriology Manual, 5th ed. Star Publishing Co., Belmont, Calif. 1993.
- Saini A, Gupta N, Mahajan A, Arora DR. Microbial flora in orodental infections. Indian J of Medical Microbiology. 2003; 21(2):111-4.
- Mane AK, Karmarkar AP, Bharadwaj RS. Anaerobic Bacteria in Subjects with Chronic Periodontitis and in Periodontal Health. JOHCD. 2009; 3(3):49-51.
- Benachinmardi KK, Nagamoti J, Kothiwale S, Metgud SC. Microbial flora in chronic periodontitis: Study at a tertiary health care center from North Karnataka. J Lab Physicians. 2015;7:49-54.
- Daniluk T, Tokajuk G, Cylwik-Rokicka D, Rozkiewicz D, Zaremba ML, Stokowska W. Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in subgingival and supragingival plaques of adult patients with periodontal disease. Advances in Medical Sciences. 2006;51 (supl 1):81-5.
- Boyanova L, Setchanova L, Gergova G, Kostyanev T, Yordanov D, Popova C, et al. Microbiological diagnosis of the severe chronic periodontitis. Journal of IMAB – Annual proceedings (Scientific paper) 2009, book 2:89-94.
- Salari MH, Kadkhoda Z. Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis. Journal of Oral Science. 2004; 46(3):157-61.
- Edwardsson S, Bing M, Axtelius B, Lindberg B, SoÈderfeldt B, AttstroÈm R. The microbiota of periodontal pockets with different depths in therapy-resistant periodontitis. J Clin Periodontal. 1999; 26 (3): 143-52.
- Farias BC, Souza PRE, Ferreira B, Melo RSA, Machado FB, Gusmão ES, et al. Occurrence of periodontal pathogens among patients with chronic periodontitis. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 2012; 43(3): 909-16.
- Kamma JJ, Nakul M, Mant FA. Predominant microflora of severe, moderate and minimal lesions in young adults with rapidly progressive periodontitis. Periodontol Res. 1995; 30 (1): 66-72.
- Younis HM, Al- Jebouri MM. Anaerobic Microbiological study of periodontitis in Salah Al – Deen City. Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences. 2016; 4:10-5.
- Sixou JL, Magaud C, Jolivet-Gougeon A, Cormier M, Bonnaure-Mallet M. Microbiology of mandibular third molar pericoronitis: Incidence of beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;95 (6):655–9.
- Sixou JL, Magaud C, Jolivet-Gougeon A, Cormier M, Bonnaure-Mallet M. Evaluation of the mandibular third molar pericoronitis flora and its susceptibility to different antibiotics prescribed in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5794–7.
- Koll-Klais P, Mandar R, LeiburE and Mikelsaar M. Oral microbial ecology in chronic periodontitis and periodontal health. Microbial Ecology in Health and Disease. 2005; 17 (3): 146-55.
- Mane AK,Karmakar AP, Bharadwaj RS, Van Winkelhoff AJ, Loss BG, Van der Reijden WA, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacteroids forsythus and other periodontal pathogens in subjects with and without periodontal destruction. J Clin Periodontal. 2002;29 (11):1023.
- Mashima I, Fujita M, NakatsukaY, Kado T, Furuichi Y, Herastuti S et al. The Distribution and Frequency of Oral Veillonella spp. Associated with Chronic Periodontitis. In J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2015; 4(3): 150-60.
- Ardila CM, Granada MI, Guzma´n IC. Antibiotic resistance of subgingival species in chronic periodontitis patients. J Periodontal Res. 2010; 45 (4): 557–63.
- Rams TR, Degener JE and van Winkelhoff AJ. Antibiotic Resistance in Human Chronic Periodontitis Microbiota. J Periodontol. 2014; 85 (1):160-9.
- Van Winkelhoff AJ, Loss BG, Van der Reijden WA, Van der Velden U. Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacteroides forsythus and other periodontal pathogens in subjects with and without periodontal destruction. J Clin Periodontol. 2002; 29 (11):1023-8.
- Kamma JJ, Nakou M and Manti FA. Predominant microflora of severe, moderate and minimal periodontal lesions in young adults with rapidly progressive periodontitis. Journal of Periodontal Research. 1995;3:66–72.
- Mombelli A, Gmur R, Frey J, Meyer J, Zee KY, Tam JO, et al. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis in young Chinese adults. Oral Microbiology and Immunology. 1998;13 (4): 231–7.
- Parekh M, Pammi V, Vardhana SB, Hinduja DM, Asnani MM, Ahmed A. Isolation and evaluation of microbial flora in patients with chronic periodontitis: A microbiological study. J Int Oral Health. 2016;8(5):619-622.
- Souto R. and Colombo APV. Prevalence of Enterococcus faecalis in subgingival biofilm and saliva of subjects with chronic periodontal infection. Archives of Oral Biology. 2008; 53 (2):155-60.
- Balaei-Gajan E, Shirmohammadi A, Abashov R, Agazadeh M, Faramarzie M. Detection of enterococcus faecalis in subgingival biofilm of patients with chronic refractory periodontitis. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010;15 (4):e667-70.
- Loberto JCS, de Paiva Martins CA, Ferreira dos Santos SS, Cortelli JR. Staphylococcus spp. in the oral cavity and periodontal pockets of chronic periodontitis patients. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 2004;35 (1-2):64-68.
- Dahlén G, Wikström M. Occurrence of enteric rods, staphylococci and Candida in subgingival samples. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1995; 10 (1):42-6.
- Dr. Joshi PS, Dr. Joshi SG, Dr. Gedam R. Isolation of Candida Albicans from Subgingival Plaque in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis- A Microbiological Study. International J of Scientific Research. 2013;2(2):286-70.
- Jarvensivu A, Hietanen J, Rautemaa R, Sorsa T, Richardson M. Candida yeasts in chronic periodontitis tissues and subgingival microbial biofilms in vivo. Oral Diseases. 2004; 10 (2): 106–12.
- Arumugam M, Seshan H, Hemanth B. A Comparative Evaluation of Subgingival Occurrence of Candida Species in Periodontal Pockets of Female Patients Using Hormonal Contraceptives and Non-users – A Clinical and Microbiological Study. OHDM. 2015;14(4):206-11.
- Canabaro A, Valle C, Farias M R, Santos F B, Lazera M, Wanke B. Association of subgingival colonization of Candida albicans and other yeasts with severity of chronic periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2013; 48 (4): 428–32.
- Cuesta AI, Jewtuchowicz V, Brusca MI, Nastri ML, Rosa AC. Prevalence of Staphylococcus spp and Candida spp in the oral cavity and periodontal pockets of periodontal disease patients. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2010; 23 (1):20-6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License