IJCRR - 10(1), January, 2018
Pages: 13-17
Date of Publication: 10-Jan-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A Comparative Study of Isolation of Obligate Anaerobes and Facultative Anaerobes in Microbial Flora of Non- Vital Teeth in Diabetic (Type II) and Non-Diabetic Patients
Author: Pradeep Shetty, Monika Chawla, Sanjyot Mulay, Karan Bhargava, Tanaya Kumar, Vasudevan Vidhya
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The aim of the study was to evaluate and compare the anaerobic microflora (obligate and facultative) of the root canals of non vital teeth with periapical lesions, in diabetic (Type II) and non-diabetic patients.
Methods: Access cavity preparation and collection of necrotic pulp tissue samples was done aseptically with the help of absorbent paper points placed in the canal for 60 seconds. Samples were processed anaerobically and were subjected to microbiological analysis using culture techniques for the evaluation of microbial flora.
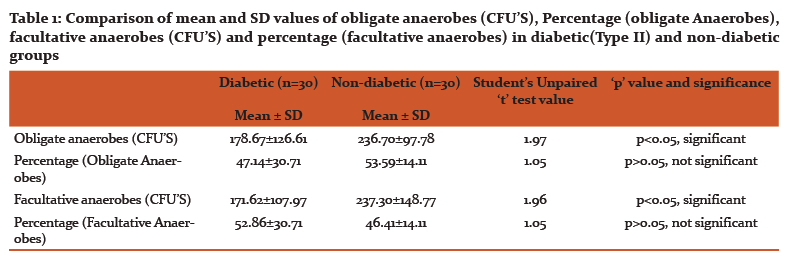
Results: There was a statistically significant difference between mean and SD values of obligate and facultative anaerobes in diabetic (Type II) and non-diabetic groups when all parameters are compared (p< 0.0001) using one-way ANOVA. Comparison of groups was done by applying Student's Unpaired 't' test. Obligate anaerobes were significantly more associated with cases of Type II diabetes mellitus, suggesting a role of these microorganisms in modulating the inflammatory and immunologic responses as well as its level in root canal infections which can have an influence on the pain threshold of patient.
Conclusion: There were significant differences in the values of microorganisms found in Diabetic (Type II) and non diabetic patients
Keywords: Necrotic pulp, Diabetic type II, Anaerobes
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1014
Full Text:
Introduction:
Around 61 million people in India are diabetic. International statistics estimate that 366 million people had diabetes mellitus in 2011; and that by 2030, this number will rise to 552 million. Around 983,000 deaths in India were caused due to diabetes in the last year.1
A group of complex multisystem metabolic disorders because of deficient insulin secretion due to dysfunction of pancreatic β-cell and/or insulin resistance in muscle as well as liver is termed as Diabetes Mellitus.2 According to findings; diabetes mellitus aggravates the risk of caries, gingivitis and periodontal disease. Increased local inflammation causes intensive increase in the level and effects of diabetes with a sharp shoot up in blood glucose level, leading to uncontrolled hyperglycemia of the patient. Thus all the causative infections concerning those of the dental pulp should be mandatorily removed.3
Literature has very well documented the complex relationship between diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. However, the association between diabetes mellitus and dental pulp and the advancement and repair of different endodontic infections has not been satisfactorily studied.3
There is an established positive, besides insignificant alliance between diabetes and presence of Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Eubacteria, Fusobacterium and Enterococcus species.5 Foregoing studies have demonstrated that in retaliation to pernicious root canal microflora particularly bacteria, the diabetic host may mature with more consequential infections.4 When the diabetic and non-diabetic population is compared, patients with diabetes mellitus and periapical lesion have shown notably diminished healing succeeding endodontic therapy.6
Hence, this study aims to isolate obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes from root canal of non-vital teeth in diabetic (Type II) and non-diabetic patients.
Material and Methodology:
Patient Selection
Patients presenting to the Department of Endodontics and Conservative Dentistry, Dr. D Y Patil Dental College were screened for the study. Comprehensive medical and dental histories were obtained from each patient. Inclusion criteria for the study were teeth with pulpal disease and periapical lesions which could be treated with endodontic therapy, patients with a history of controlled diabetes (Type II), patients either taking oral medication or insulin for the disease, patients in the age range of 45-65 years were selected. Written consent was obtained from all participating patients. Patients who met the inclusion criteria were subjected to electric pulp testing and pre-operative radiograph to investigate the presence of periapical lesion.
Group 1: 30 patients with type II diabetes mellitus were subjected to HbA1C test to determine the degree of their glycemic control. [≥7mmol(≥126mg/dl)]
Group 2: 30 patients with no history of diabetes were selected. HbA1C test was carried out on patients with no history of diabetes to confirm their non-diabetic status. [<6.1mmol(<110mg/dl)]
Microbial Sampling
Strict asepsis was followed during sample collection. To isolate the operating field, rubber dam, cotton rolls and saliva ejector were used. The isolated tooth was then washed to disinfect the crown of the tooth. The pulp chamber was then accessed with a sterile round bur. The orifices were identified and a sterile no. 15 K file was introduced in the canal upto 1mm short of the apex as assessed by the electronic apex locator and the canals were instrumented and irrigated with 1 ml sterile normal saline each. The necrotic pulp tissue samples were collected using sterile absorbent paper points placed in the canals for 60 seconds. The absorbent paper points were immediately kept in sterile Eppendorf tubes containing mineral salt solution as the storage medium. The Eppendorf tubes were then immediately transferred to department of Microbiology for analysis.
Bacterial culture
Samples were processed anaerobically. The root canal samples were diluted with sterile saline solution and then thoroughly shaken. After that 1ml of sample was carried with micropipette and plated onto nutrient blood agar media for identifying facultative anaerobes and onto RCM media for identifying obligate anaerobes. Then the blood agar plates were kept in universal incubator for 24-48 hours at 370C and the RCM media plates were kept in carbon dioxide (CO2) incubator at 270C with 5% CO2 gas for 72 hours. Then the colony forming units (CFUs) were calculated and identification of bacteria was carried out. The plates were then biochemically analyzed for growth and identification of bacteria using the colony morphology and gram staining.
 METHOD OF DATA ANALYSIS:
METHOD OF DATA ANALYSIS:
Statistical analysis was done by descriptive statistics as mean, SD, etc. Comparison of groups was done by applying Student's Unpaired 't' test. One way ANOVA test (Tukey-Kramer multiple comparison test) was applied for all the groups compared together with all parameters. All tests are applied at 5% and 1% level of significance. Statistical analysis software namely SYSTAT version 12 was applied.
RESULTS:
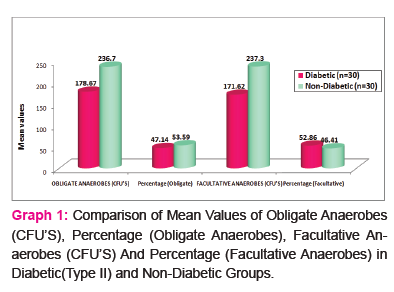
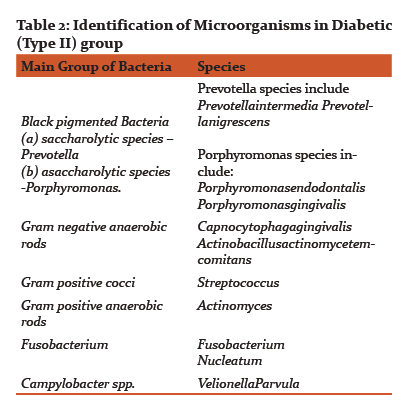
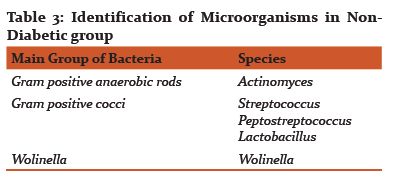
Results of CFUs of isolated obligate anaerobes and facultative anaerobes are listed in Table 1. Table 2 and 3 shows the identified colonies of obligate and facultative anaerobes.
Discussion:
In this study diabetic (Type II) patients were selected because there is little knowledge available regarding pathogenesis, progression and healing of periradicular and pulpal diseases. Anaerobic infection is also increased by vascular problems associated with diabetes, which may be associated to shortened oxygen diffusion over the capillary wall. Because of neutrophil microbicidal suppression, synergism of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, infection becomes more severe and it also lasts longer due to anoxia.3
In teeth with pulp necrosis and aerobe bacterial culture techniques were predominantly used from the 19th century to the middle of the 20th century, to isolate the microbial species from root canal. The techniques have very minimal scope and they are confined to the culture and identification of organisms which are strictly anaerobic in nature.14 Hence pulpally necrosed teeth demonstrated more of facultative anaerobes and aerobic microorganisms.15,16,17 Some early studies were unable to report the existence of obligate anaerobes.18
The present study revealed that that the difference between mean values of colony forming units in all two groups under comparison (p<0.05) was significant. No significant difference was found in percentage values of all two study groups under comparison (p>0.05).
In teeth infected with pulp necrosis, success of endodontic treatment is ensured by complete control of the endodontic infection and removal of the etiological agents. When infectious process starts within dental pulp, the majority of the endodontic microflora comprises gram- positive organisms with majority being facultative aerobes, with cocci dominating bacilli and filamentous microorganisms.19Of late, major advances have occurred in the field of bacterial culture and identification techniques, due to which predominantly obligate anaerobes have been found in non-vital teeth and teeth with a definite periapical lesion,19,20 particularly gram-negative endodontic microflora.21The advancements in anaerobic culture techniques lead to recovery of obligate anaerobes recovered from necrosed pulp,22 and other studies illustrated the prevalence of endodontic infection occurring due to anaerobes to be above 90%.23,24 It is worth visualizing, that isolated microorganisms are not same in each case but differ from one individual to other, i.e., Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Peptostreptococcus, Peptococcus and Eubacterium and these bacteria have been found out to be the main causative agent of endodontic infection.25
Studies have shown that black-pigmented bacteria are highly prevalent in cases of acute periradicular abscesses. In a cultural study Van Winkelhoff et al. isolated Prevotella intermedia from 63%, Porphyromonas endodontalis from 53%, and Porphyromonas gingivalis from 12% of the examined periradicular abscesses.26 Sundqvist et al. found P. intermedia in 10 of 17 cases of endodontic abscesses. P. gingivalis and P. endodontalis were isolated from 1 and 4 cases, respectively.27Scientific evidences suggest that black-pigmented anaerobic rods may be implicated in the etiology of periradicular pathosis.28
The obligate anaerobes found in diabetic and non-diabetic group in this study were black pigmented bacteria i.e. Prevotella and porphyromonas species, Fusobacterium, Actinomyces, Campylobacter, Peptostreptococcus. The facultative anaerobes that were isolated in diabetic (type II) and non-diabetic group were Capnocytophaga Gingivalis, Actinobacillus Actinomycetemcomitans, Streptococcus, Lactobacillus and Wolinella.
Concerning obligate anaerobes, black-pigmented bacilli (Porphyromonas sp. and Prevotella sp.) are associated with various signs as well as symptoms of endodontic nature, such as: tenderness and pain on percussion, severe pain with affected teeth, pain on palpation, generalized or localized swelling, and persisting exudate.20 The results in this research study have shown the presence of different bacteria and their co-relation with preoperative and postoperative pain. Still pertaining to the cases with acute symptoms, the commonly causing microorganism was found to be Fusobacterium nucleatum.
Although a large number of anaerobes have been isolated by our study, still even with all the caution during execution of the research, there are chances that some species extremely sensitive to the presence of oxygen may have left out and could not be detected. The inoculation of the samples was done in proper and effective transport media which were thoroughly nutritive, processed under effective anaerobic conditions and the time period for which the microorganisms were inoculated was enough and according to the recommendations of the microbiologist. This ensured the growth of all possible microorganisms. Although Enterococcus faecalis could not be isolated by us, these bacteria holds an important place in endodontic infections great due to their relationship with chronic periradicular diseases and persistent endodontic infections; additionally, they show high resistance to harsh and unfavorable environmental conditions ultimately rendering them difficult to eliminate from the root canals and.25
The gold standard techniques used for the isolation and identification of the endodontic microflora related to different infectious diseases is the microbiological culturing techniques.25Other traditional techniques employed in identification and quantification of microorganisms is microscopy, immunological methods. PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is the most extensively accepted technique in molecular technology. Since its invention, different varieties and types of PCR techniques have been developed. The widely used PCR-derived assays being Reverse Transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR), nested PCR, Multiplex PCR, PCR-based microbial typing, Real-Time PCR, broad-range PCR. Other molecular diagnostic techniques are denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis, terminal-RFLP, DNA-DNA hybridization, DNA microarrays, fluorescence in situ hybridization.29
In this research study we strictly pertained to microbial culturing technique for the determination of the anaerobes (facultative and obligate) since it was the only method for identifying the viable microflora exclusively. Various other authors have also employed this technique to evaluate and identify the endodontic microflora.20,30,31,32
Conclusion:
Thus the present study has highlighted the polymicrobial nature of root canal infections and the importance of obligate anaerobes and facultative microorganisms in non-vital teeth of diabetic (type II) and non-diabetic patients. Obligate anaerobes were significantly more associated with cases of type II diabetes mellitus, suggesting a role of these microorganisms in modulating the inflammatory and immunologic responses as well as its level in root canal infections which can have an influence on the pain threshold of patient. However, further research using a broad range molecular microbiological method for identifying more number of endodontic pathogens may be necessary to demonstrate a significant association between diabetes mellitus and endodontic infections and the differences in microflora of non-vital teeth in diabetic (Type II) and Non-Diabetic patients.
There are no conflicts of interests related to this study.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The Author are also grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers/ of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
-
http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-12-14/india/30515422 1 diabetic- patients- high- blood- sugar-level (14th December 2011).
-
Juan J Segura-Egea 1, Lizett Castellanos-Cosano 1, Guillermo Machuca et al. Diabetes mellitus, periapical inflammation and endodontic treatment outcome. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012 Mar 1;17 (2):356-61.
-
IB. Bender and A. B. Bender. Diabetes Mellitus and the Dental Pulp. J Endod2003;29(6):383–9.
-
K V Ramana. Clinical Microbiology: Reemphasizing the Role of Anaerobic Bacteria in Human Infections. J Med Microb Diagn 2012, 1:4.
-
Ashraf F. Fouad. Diabetes Mellitus as a Modulating Factor of Endodontic Infections. J Dent Educ 2003;67(4):459-467.
-
Ashraf F. Fouad, Jody Barry, Melissa Caimano et al. PCR-Based Identification of Bacteria Associated with Endodontic Infections.J. Clin. Microbiol 2002;40(9):3223-31.
-
Bissada NF, Sharawy AM. Histologic study of gingival and pulpal vascular change in human diabetics. Egypt Dent J 1970;16:283-96.
-
Bennett C.M, Guo M, Dharmage S.C. HbA1c as a screening tool for detection of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diab Med 2007; 24: 333–343
-
-
-
Pishipati Vinayak Kalyan Chakravarthy. Diabetes mellitus: An endodontic perspective. Eur J Dent 2013;2(3).
-
Falk H, Hugoson A, Thorstensson H, Number of teeth, prevalence of caries and periapical lesions in insulin dependent diabetes. Scand J Den Res 1989; 97: 198-206
-
Lamster IB, Borgnakke WS, Taylor GW. The relationship between oral health and Diabetes mellitus. JADA 2008; 139: 19s-24s
-
Nayak Moksha, et al. Diabetes mellitus and apical periodontitis. Endodontology (2013): 103-108.
-
Möller AJ, Fabricius L, Dahlen G. Influence on periapical tissues of indigenous oral bacteria and necrotic pulp tissue in monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1981;89(6):475-84.
-
Alencar AH, Pimenta FC, Ito IY, Bruno KF, Leonardo MR. Determinação dos microrganismos no canal radicular, antes do preparobiomecânico e após a utilização da medicaçãointracanal, emdentes com necrosepulpar e reaçãoperiapicalcrônica. ArqOdontol.2005;41(2):105-92.
-
Brown Jr. LR, Rudolph Jr. CE. Isolation and identification of microorganisms from unexposed canals of pulp-involved teeth. OralSurg. Oral Surg. 1957;10(10):1094-9
-
Socranscky SS, Mcdonald JB, Sawyer S. The cultivation of Treponemamicrodentium as surface colonies. Arch Oral Biol. 1959;1(2):171-2
-
Winkler KC, Van Amerongen J. Bacteriologic results from 4.000 root canal cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1959;12(7):857-75
-
Drucker, D. B. and Natsiou, I. Microbial ecology of the dental root canal. Microb Ecol Health Dis 2000 12, 160–169
-
Fabricius L, Dahlén G, Holm SE, Möller AJR. Influence of combinations of oral bacteria on periapical tissue of monkeys. Scand J Dent. 1982;90(3):200-6.
-
Gomes BP, Lilley JD, Drucker DB. Associations of endodontic symptoms and signs with particular combinations of specific bacteria. Int Endod J. 1996;29(2):69-75.
-
Assed S, Ito IY, Leonardo MR, Silva LAB, Lopatin D. Anaerobic microorganisms in root canals of human teeth with chronic apical periodontitis detected by indirect immunofluorescence. Endo Dent Traumatol. 1996;12(2):66-9
-
Morse DR. Endodontic microbiology in the 1970s. Int Endod J. 1981;14(2):69-79.
-
Ferreira CM, Bonifácio KC, Fröner IC, Ito IY. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of three irrigating solutions in teeth with pulpal necrosis. Braz Dent J. 1999;10(1):15-21
-
Haapasalo M. Bacteroidesspp in dental root canal infections. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1989;5(1):1-10.
-
de Lima Guimarães, Soares NL, Otoch, Machado H, de Andrade, Cavalcante L. Microbiological evaluation of infected root canals and their correlation with pain. Rev Sul-Bras de Odontol 2012;9:31
-
Van Winkelhoff AJ, Carlee AW, de Graaff J. Bacteroidesendodontalis and other black-pigmented Bacteroides species in odontogenic abscesses. Infect Immun 1985;49:494–8.
-
Sundqvist G, Johansson E, Sjo¨gren U. Prevalence of black-pigmented Bacteroides species in root canal infections. J Endodon 1989;15:13–9.
-
Sundqvist GK, Eckerbom MI, Larsson AP, Sjo¨gren UF. Capacity of anaerobic bacteria from necrotic dental pulps to induce purulent infections. Infect Immun 1979;25:685–93.
-
Siqueira JF Jr, Rôças IN. Exploiting molecular methods to explore endodontic infections: Part 1—current molecular technologies for microbiological diagnosis. J Endod. 2005 Jun;31(6):411-23.
-
Ferrari PHP, Cai S, Bombana AC. Effectof Effect of endodontic procedures on enterococci, enteric bacteria and yeasts in primary endodontic infections. IntEndodJ.2005;38(6):372-80 Int Endod J. 2005;38(6):372-80.
-
Dougherty WJ, Bae KS, Watkins BJ, Baumgartner JC. Black-pigmented bacteria in coronal and apical segments of infected root canals. J Endod. 1998;24(5):356-8.
-
Drucker DB, Gomes BPFA, Lilley JD. Role of anaerobic species in endodontic infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25(2):220-1.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License