IJCRR - 10(1), January, 2018
Pages: 01-06
Date of Publication: 10-Jan-2018
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Stratosphere-mesosphere Coupling Through Vertically Propagating Gravity Waves During Mesospheric Temperature Inversion (MTI): An Evidence
Author: G. Venkata Chalapathi, S. Eswaraiah, M. Venkat Ratnam, K. Niranjan Kumar, P. Vishnu Prasanth, Jaewook Lee, Yong Ha Kim, S.V.B. Rao
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Objective: It is theoretically observed that atmospheric gravity waves play a key role in vertical coupling during the Mesosphere Temperature Inversion (MTI). Therefore, the present paper describes the observational evidence for vertical coupling between the stratosphere and mesosphere through the short-period gravity waves (GWs), during the Mesosphere Temperature Inversion (MTI) over a tropical region, Gadanki (13.5oN, 79.2oE), India.
Method: The combined observations of Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere (MST) Radar and Rayleigh LIDAR located at Gadanki is utilized to study the vertical coupling. We used a unique experimental design from the two ground-based instruments that scan the lower and middle atmosphere simultaneously during the observational campaign. This kind of combined instruments are very sparsely located on the same site to make the observations unique to understand the vertical coupling processes of GWs.
Result: The vertical flux of the horizontal momentum of GWs of periods in the range 20 min. to 2h is investigated in the mesosphere using the MST Radar winds. The emphasis is made on the variability of zonal and meridional momentum fluxes in the mesosphere and possible reasons for the variability of fluxes during MTI. It is observed that raise in momentum fluxes of ~7 m2/ s2 in the eastward flux and ~10 m2/s2 in southward flux at mesospheric altitudes during the MTI.
Conclusion: The gravity wave (GW) analysis using the LIDAR temperature profiles indicate the connection between GW breaking at mesosphere altitudes and temperature inversion and thus the turbulence caused mesospheric echoes. The study suggests the prospect of coupling between stratosphere and mesosphere during the MTI.
Keywords: Gravity wave coupling, Mesospheric Temperature Inversion (MTI), MST Radar, Rayleigh LIDAR
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2018.1011
Full Text:
Introduction
The role of atmospheric gravity waves (GWs) in modulating the energy budget of the Mesosphere-Lower thermosphere (MLT) has been well recognized (Fritts and Alexander, 2003). The short-period GWs are playing a key role in vertical coupling of the different regions of the atmosphere (Sato, 1993;Fritts and Alexander, 2003). The tropical region is found to be a fountain of generating short-period GWs (Fritts and Alexander, 2003), and their generation and propagation studies are well established in the lower atmosphere over the Indian tropical region (Dhaka et al., 2002; Debashis Nath et al.,2009 and references therein). However, its effects on the MLT is sparsely studied over this region.
Earlier studies highlighted the importance of GWs in changing the MLT thermal structure (Fritts and Alexander, 2003). It was understood that vertically propagating GWs begins to break at the level where there is a sudden change in the temperature lapse rate or at the critical level(Meriwetherand Gerrard, 2004), and deposit large amount of energy and momentum (Fritts and Nastrom, 1992; Gardner and Yang, 1998; Ramesh and Sridharan, 2012). The studies on GW effects on the mesosphere temperature and the Mesosphere Temperature Inversion (MTI) are well existed (Garcia and Solomon, 1985; Hauchecorne et al., 1987; Venkat Ratnam et al., 2003; Ramesh and Sridharan, 2012). The occurrence mechanism of MTI or “mesospheric inversion layer” (MIL) is clearly discussed by Meriwether and Gerrard (2004). The occurrence of MIL and its characteristics are well studied using LIDAR’s, Radars, Rocket Sonde, and Satellites over different geographic locations (Ramesh et al., 2014 and references therein). Thus the earlier studies described the relation between MTI and GW breaking, however, the relation between the mesospheric radar echoes and MTI and GWs breaking studies sparsely exist over the tropical region. Further, the simultaneous ground-based observations both in the stratosphere and mesosphere and the quantification of GW breaking at mesosphere altitudes is still incomplete. In the present study, we made an attempt to unclear this issue and presented the vertical coupling using the unique data set over a tropical region Gadanki.
To this end, up to our knowledge concerned, this is the first report on the mesospheric echo phenomenon and their relation to GW breaking and thus the MTI. The details of the data used and methodology followed for the current study is briefly given in section 2, the results and discussions are provided in section 3, comprehensive summary, and key findingsare emphasized in section 4.
Data
In the present study, the unique data set of Mesosphere-Stratosphere-Troposphere (MST) Radar and Rayleigh LIDAR located in a tropical region, Gadanki(13.5oN, 79.2oE), India is utilized. Short-period (20 min.-2 h) GW momentum fluxes are estimated in the mesosphere using the MST Radar wind data, and LIDAR temperature profiles are used to represent the MTI and GW characteristics both at the stratosphere and mesosphere altitudes.
Methodology
MST radar
The Gadanki MST Radar is high power VHF radar with a peak transmitter power of2.5 MW and operates at 53 MHz. The MST Radar provides winds from surface to 22 km and 65-85 km. More details of MST Radar can be found in Rao et al. (1995). As mesospheric echoes from the MST Radar are mainly due to ?uctuations in electron density gradients and irregularities, they are con?ned to day-time and hence the availability of data is restricted to ∼10:00 to 17:00h Indian Standard Time (IST) (IST=UT+05:30 h).The structure and characteristics of MST Radar mesospheric echoes and mesospheric wind estimation are discussed in Kumar et al. (2007) and Eswaraiah et al. (2011). For the present study, a clear analysis of radar radial velocity profiles of individual days and defined percentage occurrence (PO) of echoes are performed for reliable wind estimation; the detailed procedure is given in Eswaraiah et al (2013). The reliable estimates of GW momentum flux can be obtained using a threshold of 20% of PO. Thus, the echoes in the range bins with PO less than 20% are omitted. For the flux estimation, the symmetric beam radar method of Vincent and Reid (1983) is utilized and the procedure has been discussed in Eswaraiah et al. (2013).
The momentum fluxes of horizontal winds have been estimated using the following equations
Momentum flux for the E-W beam: 
moreover, for the N-S beam: 
Where 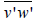 is zonal momentum flux,
is zonal momentum flux, 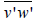 is meridional momentum flux and
is meridional momentum flux and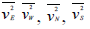 are square of radial wind perturbation in east, west, north and south directions, respectively, and θ is the anglebetween the radar beam to the zenith. Two consecutive radar beams make an angle θ, each beam being at zenith. In the present case, it is 10o.
are square of radial wind perturbation in east, west, north and south directions, respectively, and θ is the anglebetween the radar beam to the zenith. Two consecutive radar beams make an angle θ, each beam being at zenith. In the present case, it is 10o.
Rayleigh Lidar
The Gadanki Rayleigh LIDAR data is used to observe the MTI and GWs in the stratosphere and mesosphere, but not for GW momentum flux estimation. The LIDAR employs the second harmonic of Nd: YAG pulsed laser at 532 nm with a pulse energy of ~ 550 mJ and Rayleigh receiver is used, which employs a Newtonian telescope. The LIDAR provides photon count profiles with an altitude resolution of 300m and time resolution of 250s (5000 laser shots were integrated for one profile). Although the temperature can be derived up to 85 km, due to low SNR at higher altitudes, the altitude range considered for the present study is from 35 to 75 km. The basic method of deriving the temperature profile from the measured photon count is similar to the procedure given by Hauchecorne and Chanin (1980). Usually, the random errors occur while deriving the temperature and they vary from 2 K at 30 km to 4 K at 75 km (Parameswaran et al., 2000). The total vertical flux of horizontal momentum using LIDAR temperature profiles is discussed in Eswaraiah et al., (2013).More details of this instrument and method of analysis can be found from Bhavani Kumar et al. (2001), Siva Kumar et al. (2001) and Ratnam et al. (2002).
For the present study, MST Radar data on 18 November 1998 and 11 January 1999 has been used. Similarly, the Rayleigh LIDAR night time temperature measurements on 18 November 1998 and 11 January 1999 have been used. For 18/19 November 1998, the temperature measurements were made from 03:20 h IST to 05:40 h IST and for 11/12 January 1999 the observations were made between 21:29 h IST to 04:10 h IST on the next day. The simultaneous MST radar observations in the mesosphere and Lidar observations are very rarely will match, since the radar mesospheric echoes are highly sporadic and they will not every day. Though the observational data is old, the scope of the present study is sparse and it is new.
Discussions
Figures 1(a) and 1(b) depicts the radar reflectivity in terms of SNR (Signal to Noise Ratio) observed on 18 November 1998 and 11 January 1999, respectively. Corresponding late night time mean temperature profiles observed by Rayleigh LIDAR are shown in Figure 1(c) and 1(d). Temperature inversion in the mesosphere (Fig.1(c)) is seen on 18 November 1998 but not on 11 January 1999. On the temperature inversion day active radar (MST) echoes at mesospheric altitudes just below the temperature inversion layer (below 75 km) are observed, whereas on non-inversion day no radar echoes are seen in the mesosphere, indicating a close association between mesospheric radar echo occurrence and temperature inversion. Past studies on mesosphere thermal structure (Ratnam et al., 2002; Kishore Kumar et al., 2008) explained the reasons behind this phenomenon. It is observed that whenever the strong mesospheric radar echoes are noticed in the day-time, then mesospheric temperature inversion is evident in the associated night-time LIDAR temperature profiles. It is also seen that whenever there is no temperature inversion, there are no strong echoes observed in the MST Radar observations (Ratnam et al., 2002).The temperature inversion at mesospheric altitudes and turbulence generated to form mesospheric echoes can be understood by verifying the short-period GW features in both the stratosphere and mesosphere and their breaking at mesosphere altitudes. To find the existence of short-period GWs and their propagation from the lower atmosphere to mesosphere, the periodicities and propagation of GW shave been tested. The GW features and their propagation has been verified using the simultaneous observations of MST Radar and LIDAR from the troposphere to mesosphere altitudes by performing spectral analysis. Wavelet analysis has been applied for the de-trended radial velocities of radar, both at the troposphere (18 km) and mesosphere (70.8 km) altitudes and for the temperature perturbations of LIDAR at the stratosphere (45.1 km) and mesosphere (77.2 km) altitudes on 18 November 1998 and are shown in Figure 2.The magnitude of wavelet power is shown in logarithmic values. From the figure, it can be noticed that in the mesosphere at 70.8 km (Figs.2(a) and 2(b)),30 min. to 1 h and 1-2 h period waves are present between 11:30 h-12:30 h IST in east beam and again between 14:30 h-15:30 h IST in the north beam of MST Radar observations. Since the MST Radar will not give background wind information in the gap region (20-60 km), the LIDAR temperature perturbations for the wave information is taken into consideration. At 45 km (Fig.2(c)) in the stratosphere, 30 min. to 1 h period and at 77.2 km (Fig.2(d)) 30 min. to 2 h period, waves are evidenced. The similar analysis has been performed at 18 km (Figs. (2e) and (2f)) i.e., in the troposphere, and it shows that the waves with periodicities up to 1 h are significant both in east and north beams of radar radial velocities. The analysis resembles that at the troposphere altitudes waves with a wide spectrum of periodicities exist and with altitude the waves with low periods propagate to the mesosphere altitude and break when there exists temperature inversion in the background, resulting in turbulence at the mesosphere altitudes below the inversion layer (Fig.1(a)). Further, to show the difference in wave propagation on inversion and non-inversion days, the 30 min. to 1 h and 1-2 h periodicities are filtered from LIDAR temperature perturbations and shown along with daily mean temperature profiles in Figure 3. Figs.3(a), and 3(b) shows the upward propagation of 30 min. to 1h and 1-2 h period waves respectively, on 18/19 November 1998. Fig.3(c) shows the mean temperature profile on 18/19 November 1998. Figs.3(d) and 3(e) and 3(f) are same as (a,b,c), but on 11/12 January 1999. Usually, the waves with low periods (or high frequency) can propagate to the mesosphere (above 60 km) and others get filtered as their phase speed match with the background wind speeds. On 11 January 1999 (Lower panel), the 30 min. to 1h and 1-2 h period waves (Figs.3(d) and 3(e)) continuously existed in the mesosphere altitudes without breaking and hence no inversions in resulting mean temperature. In contrast, on 18 November 1998 (Upper panel), 30 min. to 1h and 1-2 h period waves (Figs.3(a) and 3(b)) are continuously observed above 75 km altitude and below that they are not frequent, which tells that the waves are breaking at ~ 75 km throughout the day and hence at 75 km large inversion appeared in the mean temperature (Fig.3(c)). So far it is unresolved that whether due to inversion waves will break or due to the breaking of the waves inversion occurs. Further, to elucidate the GW breaking at mesosphere altitudes, the characteristics of short-period GWs have been estimated and displayed in Figure 4.
Fig.4(a) shows the vertical wavelength of short-period GWs during the observational period, Fig.4(b) depicts the GW amplitude with height, Fig.4(c) presents the momentum flux deposition by short-period GWs, and Fig.4(d) exhibits the variation of Brunt Väisala Frequency (BVF) of short-period GWs. From the figure, it is evident that the significant 10-20 km vertical wavelength GWs exist during the span of observational period, and the amplitude is increasing with height and peak amplitude is reaching ~ 75 km and results in the wave breaking by producing the large zonal momentum flux at 75 km (Fig.4(c)). Sudden variation in BVF can be seen when the wave breaking and depositing large flux into the background. The analysis further supports the vertical propagation of short-period GWs and their breaking at ~ 75 km.
Using the procedure given in section 2, the time variation of zonal and meridional momentum flux of 20 min. to 2 h GWs during the inversion day(18 Nov.1998) are estimated and presented in Figure 5.The fluxes are evaluated using the procedure shown above and averaged over about 15 min. Even though a high degree of temporal variability in zonal momentum fluxes are seen from Figure 5, a significant momentum flux determination can only be obtained by averaging it over reasonably long periods (Kudeki and Franke, 1998). In the mesosphere, at times of (Figure 2) dominant wave presence, sudden enhancement in flux is observed (Figs.5(a) and 5(b)). The zonal flux is quite low after ~ 14:00 h IST (Fig.5(a)) whereas the meridional flux (Fig.(5b)) continues to be strong and fluctuating. As shown in Figure 5 at 70.8 km in the forenoon hours the dominant flux is eastward, and later it is southward. Momentum fluxes are mainly eastward (~7 m2/s2) between 11:30-12:30 h IST and later observed in southward (~ 10 m2/s2) direction between 14:30-15:30 h IST. In the troposphere, no significant changes are noticed in the fluxes which could be attributed to small wave amplitudes due to high density.
Conclusions
By Utilizing the combined observations of MST Radar, and Rayleigh LIDAR, at a tropical station, Gadanki (13.5oN, 79.2oE), India, the existence and propagation of the short-period (~of periods 20 min. to 2 h) gravity waves during the mesospheric temperature inversion (MTI) has presented. Further, the coupling between the Stratosphere and mesosphere has been investigated during MTI through LIDAR temperature measurements and estimating the momentum fluxes in the mesosphere.
The main outcomes or conclusions of the present study are summarized below:
- The relation between MST Radar mesospheric echoes and mesospheric temperature inversion (MTI) obtained with LIDAR daily mean temperatures have been noticed and it is consistent with earlier reports.
- Using LIDAR temperature profiles, the propagation of short-period GWs during the MTI and non-MTI cases and their breaking at 75 km leads to mesospheric turbulence and the formation of MTI has been observed.
- Upward propagation of GWs and their breaking has been tested by studying the characteristics of the short-period GWs using the LIDAR temperature profiles.
- The present case study during MTI showed the rise in momentum fluxes with ~7 m2/s2 in the eastward flux and ~10 m2/s2 in southward flux at mesospheric altitudes with no significant variation in the lower atmosphere. This could be due to large wave breaking at mesosphere altitudes.
The present study suggests that during MTI, the Stratosphere and the mesosphere are coupled through the propagation of short-period GWs, and hence the waves are transporting energy and momentum from lower atmosphere to the mesosphere. The role of GWs in causing the turbulence to form the mesospheric radar echoes is highly substantial.
Acknowledgements: We deeply appreciate the National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL) for providing the data used in the present study. SE acknowledges for financial support by the Korea Polar Research Institute (PE17020), Korea and Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. We alsoacknowledge the technical staff who helped to retrieve the data from the MST radar and Rayleigh Lidar.
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
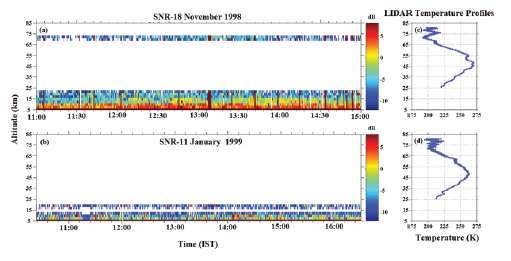
Figure 1. Time-Altitude plot of signal to noise ratio (SNR) observed on (a) 18 November 1998 and (b) 11 January 1999. (c) and (d) are nightly mean temperature profile observed on respective nights along with standard deviation.

Figure 2.Wavelet analysis applied to the radial velocities obtained using MST radar on 18 November 1998 at 70.8 km and 18 km (a,b,e,f) and for Lidar temperature at 45.1 km and 77.2 km (c,d). The black line represents the cone of influence.
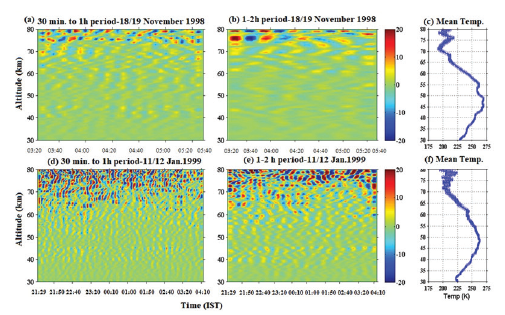
Figure 3. (a) and (b) show 30 min. to 1 h and 1 to 2 h period oscillations along with mean temperature (c) on the Inversion day (18 November 1998) (top panel). (d), (e) and (f) are same as Figs.3(a), (b) and (c) but during Non-Inversion day (11 January 1999) (bottom panel).
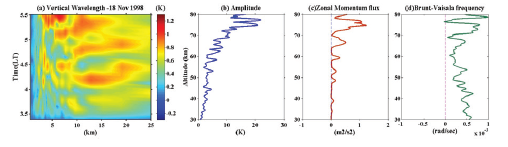
Figure 4. (a)Vertical wavelength of 20 min.-2 h GWs and vertical profiles of (b) Amplitude, (c) Zonal momentum, and (d) Brunt-Vaisala frequency on Inversion day (18 November 1998).
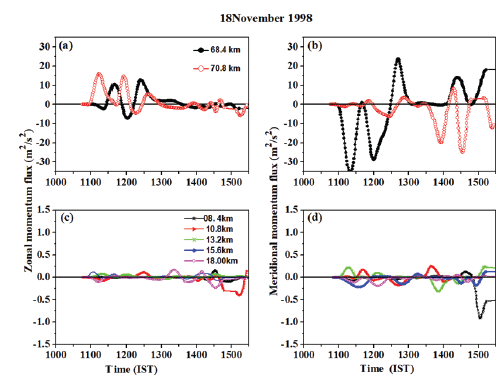
Figure 5. Zonal (left panels) and meridional (right panels) momentum fluxes at different altitudes observed on 18 November 1998 in the troposphere (bottom panels) and mesosphere (top panels).
References:
- Bhavani Kumar, Y., Siva Kumar, V.S., Jain, A.R., Rao, P.B.MST radar and polarization lidar observations of tropical cirrus. Ann Geophys 2001;19: 873–882.
- Dhaka, S.K., Choudhary, R.K., Malik, S., Shibagaki, Y., Yamanaka, M.D., Fukao, S. Observable signatures of a convectively generated wave field over the tropics using Indian MST radar at Gadanki (13.5°N, 79.2°E). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002,29:1872. doi:10.1029/2002GL014745
- Eswaraiah, S., Ratnam, M.V., Murthy, B.V.K., Guharay, A., Rao, S.V.B.Short period gravity wave momentum fluxes observed in the tropical troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere. J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys.2013, 105:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2013.07.001
- Eswaraiah, S., Venkat Ratnam, M., Krishna Murthy, B.V., Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S. Low-latitude mesospheric vertical winds observed using VHF radar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2011, 116: D22117. doi:10.1029/2011JD016385
- Fritts, D.C., Alexander, M.J.Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41:1003. doi:10.1029/2001RG000106
- Fritts, D.C., Nastrom, G.D.Sources of Mesoscale Variability of Gravity Waves. Part II: Frontal, Convective, and Jet Stream Excitation. J. Atmospheric Sci. 1992,49:111–127. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1992)049<0111: SOMVOG>2.0.CO;2
- Garcia, R.R., Solomon, S. The effect of breaking gravity waves on the dynamics and chemical composition of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 1985,90:3850–3868. doi:10.1029/JD090iD02p03850
- Gardner, C.S., Yang, W. Measurements of the dynamical cooling rate associated with the vertical transport of heat by dissipating gravity waves in the mesopause region at the Starfire Optical Range, New Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 1998,103: 16909–16926. doi:10.1029/98JD00683
- Hauchecorne, A., Chanin, M.-L.Density and temperature profiles obtained by lidar between 35 and 70 km. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1980,7:565–568. doi:10.1029/GL007i008p00565
- Hauchecorne, A., Chanin, M.L., Wilson, R.Mesospheric temperature inversion and gravity wave breaking. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1987,14: 933–936. doi:10.1029/GL014i009p00933
- Kishore Kumar, G., Venkat Ratnam, M., Patra, A.K., Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S., Russell, J.Mean thermal structure of the low-latitude middle atmosphere studied using Gadanki Rayleigh lidar, Rocket, and SABER/TIMED observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2008,113: D23106. doi:10.1029/2008JD010511
- Kudeki, E., Franke, S.J.Statistics of momentum flux estimation. J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1998,60:1549–1553. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(98)00104-7
- Kumar, G.K., Ratnam, M.V., Patra, A.K., Rao, V.V.M.J., Rao, S.V.B., Rao, D.N. Climatology of low-latitude mesospheric echo characteristics observed by Indian mesosphere, stratosphere, and troposphere radar. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2007,112: D06109. doi:10.1029/2006JD007609
- Meriwether, J.W., Gerrard, A.J. Mesosphere inversion layers and stratosphere temperature enhancements. Rev. Geophys. 2004,42: RG3003. doi:10.1029/2003RG000133
- Nath, D., Venkat Ratnam, M., Jagannadha Rao, V.V.M., Krishna Murthy, B.V., Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S. Gravity wave characteristics observed over a tropical station using high-resolution GPS radiosonde soundings. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2009, 114: D06117. doi:10.1029/2008JD011056
- Parameswaran, K., Sasi, M.N., Ramkumar, G., Nair, P.R., Deepa, V., Murthy, B.V.K., Nayar, S.R.P., Revathy, K., Mrudula, G., Satheesan, K., Bhavanikumar, Y., Sivakumar, V., Raghunath, K., Rajendraprasad, T., Krishnaiah, M. Altitude profiles of temperature from 4 to 80 km over the tropics from MST radar and lidar. J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2000, 62:1327–1337. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(00)00124-3
- Ramesh, K., and Sridharan, S. Large mesospheric inversion layer due to breaking of small-scale gravity waves: Evidence from Rayleigh lidar observations over Gadanki (13.5°N, 79.2°E). J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2012, 89: 90–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jastp.2012.08.011
- Ramesh, K., Sridharan, S., Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S. Causative mechanisms for the occurrence of a triple layered mesospheric inversion event over low latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys.2014, 119: 2013JA019750. doi:10.1002/2013JA019750
- Rao, P.B., Jain, A.R., Kishore, P., Balamuralidhar, P., Damle, S.H., Viswanathan, G. Indian MST radar 1. System description and sample vector wind measurements in ST mode. Radio Sci. 1995, 30: 1125–1138. doi:10.1029/95RS00787
- Sato, K. Small-Scale Wind Disturbances Observed by the MU Radar during the Passage of Typhoon Kelly. J. Atmospheric Sci. 1993, 50: 518–537. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1993)050<0518: SSWDOB>2.0.CO;2
- Siva Kumar, V., Bhavani Kumar, Y., Raghunath, K., Rao, P.B., Krishnaiah, M., Mizutani, K., Aoki, T., Yasui, M., Itabe, T. Lidar measurements of mesospheric temperature inversion at a low latitude. Ann Geophys 2001, 19:1039–1044. doi:10.5194/angeo-19-1039-2001
- Venkat Ratnam, M., Nee, J.B., Chen, W.N., Siva Kumar, V., Rao, P.B. Recent observations of mesospheric temperature inversions over a tropical station (13.5°N,79.2°E). J. Atmospheric Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2003, 65:323–334.
- Vincent, R.A., Reid, I.M. HF Doppler Measurements of Mesospheric Gravity Wave Momentum Fluxes. J. Atmospheric Sci. 1983, 40: 1321–1333
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License