IJCRR - 3(5), May, 2011
Pages: 36-47
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PATIENT COUNSELLING: A WAY TO ENHANCE PATIENT COMPLIANCE
Author: Stuti Gupta, Ravindra Pal Singh, Rajendra k. Songara, Sonia Bisla, Heema Naik, Dolly Jain
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Effective patient counseling makes the patient understand his/her illness, necessary lifestyle
modifications and pharmacotherapy in a better way and thus enhance patient compliance. The
pharmacist has immense responsibility in counseling the patients. The counseling pharmacist
should possess adequate knowledge and should be an effective communicator, making use of the
verbal and non-verbal communication skills.
Keywords: patient counseling, pharmacist
Full Text:
1. INTRODUCTION
The availability of and rational use of medicines are critical for a successful therapeutic outcome. Though rapid developments in science and technology have led to easy understanding of etiology and pathophysiological basis of various diseases and development of new molecules, many times clinicians fail to achieve the desired therapeutic goals. One of the major reasons for this can be the patient noncompliance or partial compliance towards the prescribed treatment (World Health Organization, 2003). Patient compliance is defined as the adherence of a patient towards the prescriber‘s instructions. It implies an understanding of how the medicine is to be used, as well as a positive behavior in which the patient is motivated sufficiently to use the prescribed treatment in the manner intended because of a perceived self-benefit and a positive outcome (e.g. enhanced quality of life and well being). Non- compliance can lead to various consequences including underuse, overuse, misuse, abuse etc (Hussar DA, 2000). The most common factors associated with noncompliance are the nature of the disease, multiple drug therapy, frequency of drug administration, duration of drug therapy, adverse events, cost of medications, administration technique, taste of medication etc (Ramesh, 1999). In the present days, the term ?concordance? is used more often in place of ?compliance?.
2. PATIENT COUNSELING [17] Patient counseling may be defined as providing medication information orally or in written form to the patients or their representative or providing proper directions PATIENT COUNSELLING: A WAY TO ENHANCE PATIENT COMPLIANCE Stuti Gupta1 , Ravindra Pal Singh2 , Rajendra k. Songara1 , Sonia Bisla1 , Heema Naik1 , Dolly Jain1 1 School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Jaipur National University, Jaipur, rajasthan 2Gyan Vihar School of Pharmacy, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur E-mail of corresponding author: stutipharmabird@gmail.com 37 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 of use, advice on side effects, storage, diet and life style modifications. It involves a one-to-one interaction between a pharmacist and a patient and/or a care giver. It is interactive in nature. The effective counseling should encompass all the parameters to make the patient/party understand his/her disease, medications and life style modification required (Beardsley , 1997); ASHP, 1997). In general, patient counseling has 3 main objectives: [18] (1) Assessing the patient‘s understanding of the therapy including proper use and adverse effects of the medication. (2) Improving patient adherence. (3) Motivating the patient to take an active role in health management. [19] Studies have shown that patient counseling can improve patient care in various ways [19]:
Reducing medication errors.
• Increasing patients understanding and management of their medical condition.
• Minimizing incidence of adverse drug reactions and drug-drug interactions.
• Improving patient outcomes and satisfaction with care. Although every pharmacist implements individualized techniques to counsel patients, various skills are vital to successful pharmacist-patient interaction during patient counseling sessions.
2.1 FEATURES OF EFFECTIVE PATIENT COUNSELING: [18] (1.) Establish Trust- Pharmacists are among the most accessible and trusted health care professionals. When initiating a patient counseling session, pharmacists should introduce themselves with a brief, friendly greeting to make patients feel comfortable enough to ask questions about their medication therapies and health conditions. Pharmacists who demonstrate a genuine interest in patient care are more likely to encourage dialogue. [20]
(2.) Communicate verbally- Pharmacists can encourage dialogue by asking questions. They should assess what the patient already knows about his or her chosen therapy and tailor the counseling to meet the needs of each individual patient. Ask patients what their physician has told them about the selected therapy and the condition for which they are being treated.
(3.)Communicate Nonverbally- In addition to verbal communication, it is essential for pharmacists to be aware of nonverbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact with the patient, to demonstrate interest in the information the patient is relaying. [21]Pharmacists also should be cognizant of other nonverbal clues, such as facial expressions and tone of voice, when interacting with patients.
(4.) Listen- When counseling patients about medication therapy, listening to the concerns, questions, and needs of the patient is essential. Listening skills can be categorized into 4 classes: passive listening, acknowledgment responses, encouragement, and active listening. [22] Passive listening occurs when the pharmacist enables the patient to communicate without interruption. An acknowledgment response such as nodding occurs during passive listening and alerts the patient that the pharmacist is indeed listening. Pharmacists also can use encouragement strategies through the use of words such as "yes" or "go on." Active listening involves 2- way interactions between the patient and the pharmacist and always should be implemented after passive listening. [22]
(5.) Ask Questions- When posing questions to the patient, pharmacists also should state the reason for asking certain questions, so as not to offend the patient. [23,24]Asking open-ended questions enables pharmacists to gather more information that may lead to other questions and/or provide valuable information to the pharmacist to further assess the patient.
(6.) Remain Clinically Objective- It is important for pharmacists not to allow personal belief‘s either ethical or religious‘ to affect their ability to counsel a patient effectively. Pharmacists should make every possible effort to be nonjudgmental and impartial, to focus on patient care, and to maintain a professional demeanor.
(7.) Show Empathy and EncouragementWhen a pharmacist displays empathy and encouragement, a patient may feel more comfortable discussing his or her medical condition and medication use, thus enabling the pharmacist to obtain pertinent information on the patient‘s needs and concerns. Emphasizing to patients the importance of adherence to medication regimens can promote positive therapeutic outcomes and motivate patients to take an active role in the management of their health. During counseling, pharmacists also should remind patients to call the pharmacy or their physician with any concerns about their medications.
(8.) Provide Privacy and ConfidentialityEnsuring complete privacy and confidentiality helps enable patients to feel comfortable discussing personal medical issues. Today many pharmacies are equipped with special counseling areas to address privacy issues. When counseling, pharmacists can reassure patients of privacy by monitoring voice levels and counseling patients away from the dispensing area when possible.
(9.) Tailor Counseling to Meet Patient Needs- The ability to tailor patient counseling to meet individual needs is critical. Pharmacists should be aware of patients with disabilities and be prepared to treat them with respect and understanding. Techniques should be tailored to accommodate the needs of each patient via verbal counseling or the use of visual aids and demonstrations when warranted. When the medication therapy involves certain administration techniques, such as the use of an inhaler, an injection, or a monitoring device, pharmacists should demonstrate the proper technique to ensure that patients are adequately trained.
(10.) Motivate Patients- Effective counseling not only provides patients with the pertinent information they need to use their medication correctly, it also motivates them to adhere to their medication regimens. Pharmacists can motivate patients by discussing the benefits of medication adherence, offering support, and explaining the pros and cons of treatment. For example, when counseling a patient with diabetes, in addition to teaching the patient about medications, the pharmacist can stress the importance of maintaining tight glycemic control to decrease or prevent the complications associated with diabetes. Pharmacists also can make suggestions, such as the use of medication reminder containers, to facilitate patient adherence. Information always should be relayed positively, and pharmacists should look continually for ways to inspire patients to learn more about their treatment plan.
2.2 WHY PHARMACISTS SHOULD COUNSEL PATIENTS? [25] Communicating with patients about their medications provides significant benefits to both the patient and the pharmacist. The 39 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 patient will have a better understanding of the purpose for the prescribed therapy and the appropriate use of the medication. This leads to several potential benefits:
- Improved therapeutic outcomes and decreased adverse effects
• Improved patient adherence to the treatment plan
• Decreased medication errors and misuse
• Enhanced patient self-management by involving the patient in designing the therapeutic plan.
• Potential for decreased health care costs due to appropriate use of medications and prevention of adverse events.
2.3 NECESSITY OF PATIENT COUNSELING [26] Mock asserts that "the concept of effective clinician-patient communication is a necessity, not an option. Because commu¬nication is both a science and an art that can be learned and mastered, there are many resulting benefits for those who work diligently to improve their technique, not the least of which is increased clinician satisfaction." A recent incident was reported in New Brunswick where an incorrect medication was dispensed on transfer. The patient was not counseled and the error was identified by the caregiver when the patient was taking the medication later that night. Had the patient been shown the medication in the counseling process, the incident could have been immediately corrected. Much less harm is done by identifying medications errors before they leave the pharmacy. Therefore, health care profes¬sions education, and specifically pharmacy education, should include specific training in patient communication skills and an understanding of the psychological reactions to illness and treatment.
2.4 TECHNIQUES OF COUNSELING [17] Several techniques can be adopted for effective counseling. Some of them include providing written information to the patient and the use of audiovisual materials. The use of various compliance aids include labeling, medication calendars, drug reminder chart and providing special medication containers and caps can also be adopted. The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) medication counseling behavior guidelines divide medication counseling into the following four stages (USP, 1997).
Stage I: Medication information transfer, during which there is a monologue by the pharmacist providing basic, brief information about the safe and proper use of medicine. Stage
Stage II: information exchange, during which the pharmacist answers questions and provides detailed information adapted to the patients‘ situation. Stage
Stage III: education, during which the pharmacist provides comprehensive information regarding the proper use of medicines in a collaborative, interactive learning experience. Stage
Stage IV:counseling, during which the pharmacist and patient have a detailed discussion intending to give the patient guidance that enhances problemsolving skills and assists with proper management
3. COUNSELING OF PATIENT AFTER FILLING PRESCRIPTION [28] After filling the prescription give some advice to the patient about how to use drugs. Some common advices are -
(i) Removing of Drug from the PackageTo the unaware patient, the pharmacist must demonstrate how the drug is to be removed from the package. This seemingly simple task may be quite confusing to some patients. Handling of Dropainer eye preparations, removal of dust cap from suppositories, opening of safety containers are some of the difficulties faced by the untrained patient.
(ii) Administering the Drug- The pharmacist should clearly mention to the patient, how and by which route the medicine has to be administered. The importance of this lies in the fact that inadequate information may lead to faulty administration and consequently to diminution or exaggeration of the desired effect. Consider the example of a tablet. There are at least 9 different ways a tablet can be administered depending upon the type of tablet and the drug it contains. These are (a) place on tongue and swallow with water, (b) chew and swallow (c) not to be chewed (d) let it dissolve in mouth and suck (e) sublingual, do not swallow (f) buccal, let it dissolve (g) dissolve in water and swallow (h) dissolve in water and use extremely (i) moisten with water and insert vaginally or rectally. Inadequate instructions in such cases will lead to wrong administration.
(iii) Ophthalmic preparations- For instillation of an eye drop, the pa¬tient is advised to tilt the head backward or if possible lie down looking up at the ceiling. He should hold the dropper above affected eye and allow a drop of the medicine to fall in the space between the eyeball and the inside the lower eye lid while looking up. The patient should be warned not to touch the tip of the dropper to any surface or the eye lid. The lower lid is released and the eye kept open without blinking for at least 30 sec. Thereafter, the patient is advised to apply gentle pressure with his fingers at the bridge of the nose for about I min to prevent drainage of solution from the eye. Eye preparations should be discarded after 1 month from the date of opening of the container. Eye ointments are administered in a similar manner; about l/4 to l/2 inch of the ointment from a squeezable tube is placed inside the lower eyelid.
(iv) Inhalations- The pharmacist must demonstrate the use of inhalers particularly to the new users, children and elderly. The inhaler requires shaking before use. It should be held between the index finger and the thumb so that the container is upside down. The patient is advised to hold the breath for as long as possible to derive the maximum benefit. The inhaler is removed from the mouth and exhalation is done slowly through pressed lips. Likewise, relevant instructions about the use of other dosage forms like suppositories, creams, lotions solutions etc. should be given to the patient.
(v) Timing of the dose- The pharmacist must use his knowledge of drugs when interpreting the directions of the physician and give in¬structions to the patient to ensure that the drug is maximally effective. If the drug has the propensity to cause GI upset, it is best taken with food or milk. If its bioavailability is affected by the presence of food, the drug should be taken 1 hr before or 2 hr after meals. If steady state blood levels are essential for the desired effect, the dosing schedule can be appropriately adjusted.
(vi) Duration of use- The duration of use of medication is dependent on the nature of the illness and the drug used. For chronic ailments, the length of drug intake is more. The greater the duration of drug intake, the greater is the problem of compliance. The patient is advised to take the medication regularly and visit the physician frequently to get the effectiveness of the therapeutic regimen assessed.
(vii) Storage- Proper storage conditions are necessary for safety and maintenance of the efficacy of drugs. All medication should be kept in a cabinet away from the reach of children. External and internal use preparation should be kept segregated. Exposure• of drug to extremes of temperature and humidity should be avoided. The medication should not be used after its date of expiration.
(viii) Side Effects- No drug is without side effects and it is necessary that the pharma¬cist makes some of the commonly occurring side effects known to the patient. However, the manner in which the pharmacist tells this to the patient is important. The pharmacist should not drive away the patient from using the medication or create a scare in him; rather the informa¬tion should be presented in a manner so as to encourage compliance. The pharmacist must also mention how to cope with these side effects if it is possible, e.g. headache with the use of metronidazole may be relieved by taking aspirin or paracetamol. For drugs which cause drowsiness, the patient should be advised against driving during the period of drug intake. With some drugs like metronidazole, the use of alcohol has to be avoided. The patient should be specifically cautioned against it. With some drugs the incidence of side effects decrease on continued use.
(ix) Drug Interaction- The patient should be clearly mentioned of the possible interaction of his prescribed drug with factors like food, tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption, and with other. Nonprescription drugs, that he may be taking. Unfortunately, there is a common notion, that all OTC drugs are safe. The pharmacist should dispel this notion and advise the patient accordingly
(x) Allergies- Careful documentation of the past medication history and ascer¬taining any known allergy to any drug will undoubtedly• reduce the incidence of druginduced allergies. However, since many drugs are foreign to the body, they do have the capability to cause allergy. This fact should be carefully detailed to the patient. The patient should be advised that if he experiences rashes, itching or burning of skin, he should discontinue the drug and consult the physician.
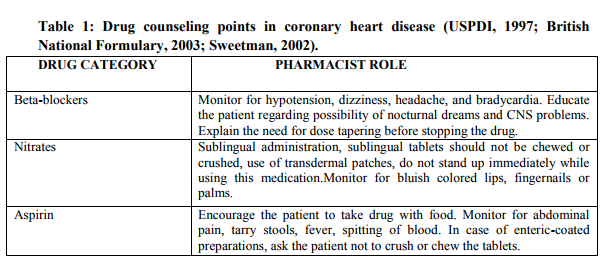
4. COUNSELING OF SOME COMMON DISEASE [29] (i) CORONARY HEART DISEASE [30] As with other chronic diseases, the aim of treatment is to reduce the mortality, morbidity and associated impairment in the quality of life. A pharmacist can play an active role in the management of this chronic illness in several ways.
Non-pharmacological measures: It includes education regarding diet, smoking, and exercise and encouraging the patients to maintain a diary on anginal attacks, pain symptoms etc.
Pharmacological measures: Educating the patients on the use of nitrates in case of an acute anginal attack is one of the important roles of pharmacists. Some of the important pharmacological measures are listed in (Table 1).
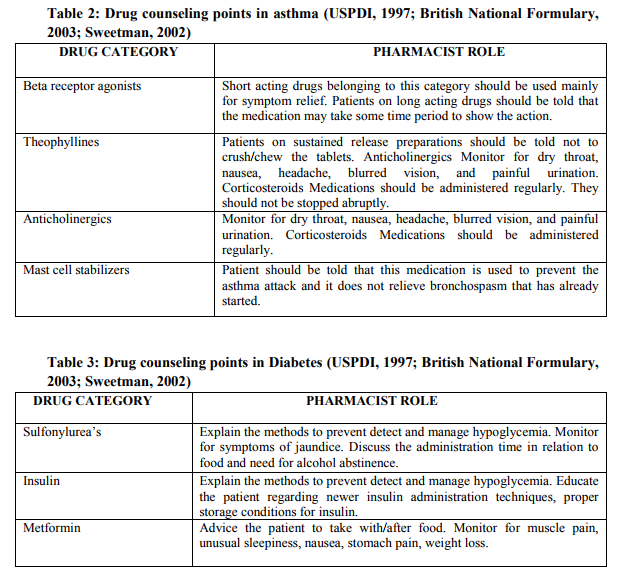
(ii) ASTHMA [31] Asthma is a chronic condition requiring lifelong drug therapy. Pharmacist can play an active role in counseling the patient regarding self monitoring of drug therapy, other life style modifications and usage of specialized dosage forms such as metered dose inhalers, dry powder inhalers, spacers etc.
Non-pharmacological measures: Safety measures while traveling, prophylactic use of drugs before exercise, avoidance of allergens, stopping cigarette smoking etc.
Pharmacological measures: Patient involvement in management of asthma is very important. Specific counseling on drug therapy should concentrate on three areas; drugs to relieve symptoms, drugs used to prevent asthma attack and those drugs which are given only as reserve treatment for severe attacks (Gibbs and Small, 2003). Training regarding use of the metered dose inhaler is one of the important roles of the counseling pharmacist. Some of the pharmacological measures to be included while counseling these patients are summarized in (Table 2).
(iii) DIABETES [32] Diabetes is a chronic disease with altered carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism (Kapur et al., 1998). The chronic complications of diabetes are known to affect the quality of life of diabetic patients. Various factors like understanding of the patients about their disease, dietary regulation, self-monitoring of blood glucose are known to play a vital role in diabetes management. Patient counseling and education are known to improve the quality of life of these patients (Rasheed et al., 2002). Some of the non-pharmacological and pharmacological measures are listed below.
Non-pharmacological approaches: The pharmacist can give an overview of diabetes, stress and psycho-social adjustment, family involvement and social support, nutrition, exercise and activity, monitoring and use of results, relationship between nutrition, exercise, medication, and blood glucose level.
Pharmacological measures: Studies suggest that the complications of diabetes can be reduced by tight glycemic control (The diabetes control and complications trial research group, 1993; UKPDS Group, 1998.The drugs used in diabetes are also known to possess certain peculiar features such as ?Taken half an hour before food? in case of Sulfonylureas; ?awareness of hypoglycemia? during insulin therapy etc. (Table 3) lists some of the important pharmacological measures a pharmacist should stress while counseling diabetic patients.
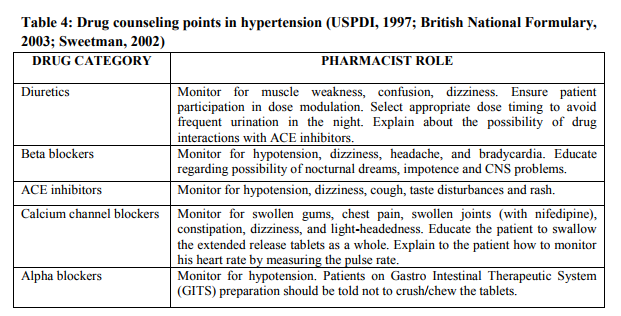
(iv) HYPERTENSION [32] Though hypertension is not a disease, it is known to be an important risk factor for several complications resulting in end organ damage (Thomas, 2003). If uncontrolled it can lead to a huge adverse impact on quality of life. The management of hypertension requires non-pharmacological as well as pharmacological methods (Chobanian et al., 2003).
Non-pharmacological measures: In many occasions nonpharmacological treatment alone may suffice in the management of hypertension. A pharmacist can counsel the patients regarding weight loss and regular exercise, sodium and calorie restriction, restriction of saturated fats and increased intake of dietary fibers, restriction of alcohol intake, smoking cessation, caution while using cold remedies containing sympathomimetics, self-monitoring of blood pressure etc.
Pharmacological measures: In a majority of patients, drug therapy is required. The patients often underestimate hypertension as by itself it usually does not exhibit any major symptoms. Thus non-compliance becomes very common. Added to this is the fact that many of the antihypertensive drugs causes side effects that are very serious such as Angiotension Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors induced cough, beta blockers induced bradycardia etc. In some cases the dose modulation of the drugs is also very essential. Some of the pharmacological measures that can be taken by the pharmacist during counseling are listed in (Table 4).
5. STATUS OF PATIENT COUNSELING IN INDIA [32] Basic act of patient counseling will take miles ahead of the present pharmacy professional situation in India. Patient counseling in USA is very well comparing to India. USP medication counseling guidelines suggests four stages in counseling such as counseling introduction, content, process and counseling conclusion.USP has listed about 175 various counseling items that can be used during counseling. But in India condition to begin with, about 15 items may be sufficient. As per the need and time, few or all these items can be used. Following are the counseling items which are distributed into four stages such as counseling introduction, counseling content, counseling process, and counseling conclusion.
References:
1. Roter DL, Hall JA, Merisca R, et al. Effectiveness of interventions to improve patient compliance: a meta-analysis. Med Care. 1998; 36:1138-61.
2. National Association of Boards of Pharmacy. 1999-2000 Survey of Pharmacy Law. Park Ridge, Ill.; 1999.
3. (3.)Svarstad BL. Development of behavioral science curricula and faculty in pharmacy: some issues requiring attention. American J Pharm Educ. 1994; 58:177-83
. 4. Beardsley RS. Communication skills development in colleges of pharmacy. American J Pharm Educ. 2001; 65:307- 14.
5. Morris LA, Tabak ER, Gondek K. Counseling patients about prescribed medication: 12-year trends. Med Care. 1997; 35:996-1007.
6. Perri M, Kotzan J, Pritchard L, et al. OBRA '90: the impact on pharmacists and patients. Am Pharm. 1995; NS35:24- 28, 65. 46 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011
7. Erickson SR, Kirking DM, Sandusky M. Michigan medicaid recipients' perceptions of medication counseling as required by OBRA '90. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1998; 38:333-8.
8. Schommer JC, Wiederholt JB. A field investigation of participant and environmental effects on pharmacistpatient communication in community pharmacies. Med Care. 1995; 35:567- 84.
9. Sleath B. Pharmacist-patient relationships: authoritarian, participatory, or default? Patient Educ Couns. 1996; 28:253-63.
10. Scott DM, Wessels MJ. Impact of OBRA '90 on pharmacists' patient counseling practices. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1997; 37:401-6.
11. Cook K, Shortell SM, Conrad DA, et al. A theory of organizational response to regulation: the case of hospitals. Acad Manage Rev. 1983; 8:193-205.
12. Nichol MB, Michael LW. Critical analysis of the content and enforcement of mandatory consultation and patient profile laws. Ann Pharmacother. 1992; 26:1149-55.
13. Kirking D. Evaluation of an explanatory model of pharmacists' patient counseling activities. J Soc Admin Pharm. 1984; 2:50-6.
14. Mason HL, Svarstad BL. Medication counseling behaviors and attitudes of rural community pharmacists. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1984; 18:409-14.
15. Svarstad BL, Mason H, Schuna A. Factor‘s affecting pharmacists' communication behavior: an observational study. Paper presented at: Annual Meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy; July 1979; Denver, Col.
16. Svarstad BL, Bultman DC, Mount JK. Evaluation of written prescription information provided in community pharmacies: a study in 8 states. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2003; 43:383-93.
17. Palaian S, Prabhu M and Shankar PR ,A Review on Patient counseling by pharmacist -a focus on chronic illness. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci., 2006, Vol.19 (1), 62-65.
18. Terrie YC, Review on 10 Behaviors of Effective Counselors Published Online: May 1, (EDT).
19. Rantucci, M. Pharmacists Talking With Their Patients: A Guide to Patient Counseling. 2nd Edition. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006:3-4.
20. Rantucci, M. Pharmacists Talking With Their Patients: A Guide to Patient Counseling. 2nd Edition. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006:158-159.
21. Rantucci, M. Pharmacists Talking With Their Patients: A Guide to Patient Counseling. 2nd Edition. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006:167-168.
22. Rantucci, M. Pharmacists Talking With Their Patients: A Guide to Patient Counseling. 2nd Edition. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006:170
. 23. Isetts, B, Brown, L. Patient Assessment and Consultation. In: Berardi R, Kroon L, Newton G, et al, eds. Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs. 15th Edition. Washington, DC: American Pharmacists Association; 2006:15-34.
24. Rantucci, M. Pharmacists Talking With Their Patients: A Guide to Patient Counseling. 2nd Edition. Baltimore, 47 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2006:70.
25. Herfindal T. Eric, Gourley R. Dick; ?Text book of therapeutics: Drug and disease management?, 6th Edition, Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins 1996.
26. Roger walker, Clive Edwards; ?Clinical pharmacy and therapeutics?, 3rd Edition, Churchill Livingstone Publisher, 2003.
27. The Pharmacist-Patient Consultation Program PPCP-Unit 2, How to Counsel Patients in Challenging Situations: New York: Pfizer, 1993.
28. Antucci MJ. Pharmacists Talking with Patients: ?A Guide to Patient Counseling. Philadelphia? Williams and Wilkins, 1997.
29. Beardsley RS (1997). Review of literature: oral patient counseling by pharmacists. Proceedings of the national symposium on oral counseling by pharmacists about prescription medicines. September 19-21; Lansdowne, Virginia.
30. Lewis RK, Lasack NL, Lambert BL and Connor SE (1997). Patient counseling – a focus on maintenance therapy. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm., 54(18): 2084-2098.
31. Gibbs KP and Small M Asthma (2003). In: Walker R, Edwards C. Clinical pharmacy and therapeutics. Churchill Livingstone publishers, Philadelphia, 3 rd Ed.., pp.375-395.
32. Diabetes Control and complications trial research group (1993). The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med., 329: 977-986.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License