IJCRR - 3(5), May, 2011
Pages: 23-30
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EVALUATION OF EFFECT OF PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE ON THE BIOAVAILABILITY OF MARKETED FORMULATION OF DICLOFENAC
Author: Mayee R, Rawat S
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:This study involves research to assess the pharmacokinetics of Diclofenac Sodium Marketed formulations
as well as the effect of pressure and temperature on its bioavailability by DermatoPharmacoKinetics
method. This drug is used for the treatment of Local pain. This was a single-dose-one arm, open label
pharmacokinetic study of marketed formulations of Diclofenac Sodium using 12 healthy Indian male
subjects. A marketed Diclofenac Sodium topical formulation was applied on the pre-marked forearms of
the subjects as per the dosing schedule. Subjects received treatment on one arm and same treatment on
another with the application of sufficient pressure in the first period and sufficient heat in the second period
of the study. The study was conducted following open label three way parallel design. A washout period
of two days was kept between the two periods of the study.
Skin Stratum Corneum samples were collected in sterile glass test tubes during each period. The samples
were collected pre-dose and at 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 6.0 hours post-dose application. The Stratum
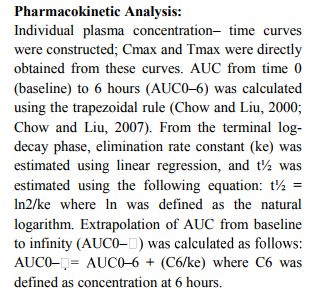
Corneum samples were analysed for Diclofenac Sodium concentrations only. Pharmacokinetic parameters
of Diclofenac sodium were calculated as Cmax, tmax , AUC (0-t) and AUC (0-?) Diclofenac Sodium was
estimated in Stratum Corneum using a validated Spectroscopic method.
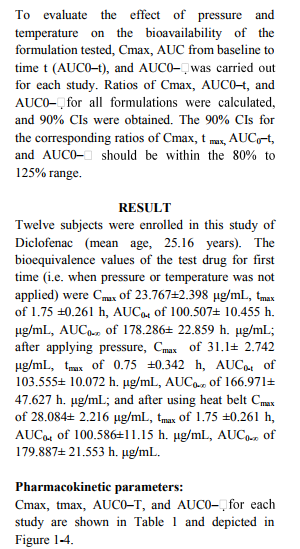
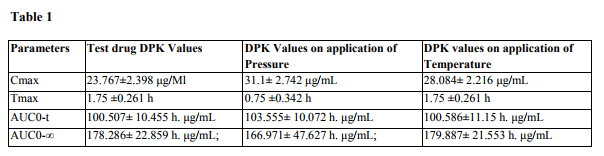
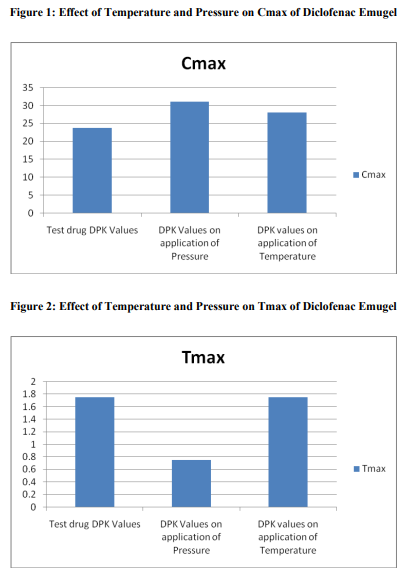
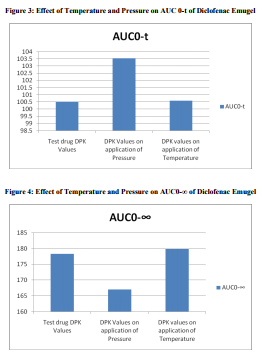
A total number of 12 subjects were enrolled in this study. The bioequivalence values of the test drug A
were Cmax of 23.767\?2.398 \?g/mL, tmax of 1.75 \?0.261 h, AUC0-t of 100.507\? 10.455 h. \?g/mL, AUC0-?
of 178.286\? 22.859 h. \?g/mL; after applying pressure, Cmax of 31.1\? 2.742 \?g/mL, tmax of 0.75 \?0.342 h,
AUC0-t of 103.555\? 10.072 h. \?g/mL, AUC0-? of 166.971\? 47.627 h. \?g/mL; and after using heat belt
Cmax of 28.084\? 2.216 \?g/mL, tmax of 1.75 \?0.261 h,
AUC0-t of 100.586\?11.15 h. \?g/mL, AUC0-? of 179.887\? 21.553 h. \?g/mL. This study demonstrated that
the bioavailability of the topical formulations increased with the help of pressure and temperature.
Keywords: DermatoPharmacoKinetics, Stratum Corneum, Diclofenac, Skin stripping.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Bioavailability is typically defined as the rate and extent at which a drug reaches the general circulation from an administered dosage form. In case of topical formulations, the drug has to penetrate through the layers of skin to reach the local site of action which is a complex process only due to the rate limiting barrier of the Stratum Corneum[1] . The penetration of a drug through the skin is a complex process typically rate-limited by the stratum corneum (SC). This external layer of the skin is composed of terminally differentiated corneocytes embedded in a complex lipid matrix comprising primarily of ceramides, cholesterol, and free fatty acids. Delivery of drug by passive diffusion and the pharmacological effect elicited are dose-related: the better the drug permeates the skin, the greater the therapeutic effect. It follows, therefore, that formulation plays an important role in topical drug delivery as the composition of the vehicle will influence the partitioning and/or the diffusivity of the drug and hence the absolute amount delivered. The determination of the Bioequivalence of topical products involves the DermatoPharmacoKinetic (DPK) approach. The DPK approach includes measure of drug concentration in the skin, whether directly or indirectly related to the drug‘s therapeutic action, which can be determined continuously or intermittently for a period of time. This may include the measurement of either drug concentration in Stratum Corneum over time and/or drug concentration in serial biopsy samples. The measurement of the change in the Stratum Corneum drug concentration as a function of time is the objective of DPK approach and thus is a valid means of comparing a generic and innovator product for their ability to deliver drug to the deeper layers of the skin. DPK studies offer certain advantages such as: it is painless, the active drug substances (moieties) are protected from gastric enzymes, it avoids first pass effect, and it is simple to terminate if any adverse or undesired effect is observed. [2-4]
Various Techniques and Methods Practiced in DermatoPharmacoKinetics: - There are many in vitro and in vivo methods for pharmacokinetic assessment of the dermal products, of which the most important and easiest method is the in vivo tape stripping technique. Some of the other techniques are as mentioned below: Tape Stripping Technique:
- Microdialysis[2,4]:
- In Vitro Permeation Assessment[4,6];
- Confocal Laser Scanning[4]:
- Cadaver Skin Permeation[5]:
- Vasoconstrictor Assay[5]:
Tape Stripping Technique: - The method consists of the standardized protocol of repeated applications and removal of adhesive tape on the skin surface, whereby consecutive layers of Stratum Corneum cells are sampled. Tape stripping is a standard measuring method for the investigation of the DermatoPharmacoKinetics of topically applied substances using adhesive films. These tape strips are successively applied and removed from the skin after application and penetration of topically applied substances; thus, the layers of the corneocytes and certain amount of topically applied substances are removed. The amount of the substances and the amount of Stratum Corneum removed with the single tape strip is determined for calculation of the penetration profile. The topically applied substances removed from the skin can be thus determined by various analytical methods like HPLC, Mass Spectroscopy and other spectroscopic measurements. [4,5] Diclofenac is an acetic acid non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Diclofenac is used to treat pain, dysmenorrhea, ocular inflammation, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and actinic keratosis. Diclofenac has pharmacologic action similar to those of other prototypical NSAIDs. The exact mechanisms have not been clearly established, but many of the actions appear to be associated principally with the inhibition of prostaglandins synthesis. Diclofenac inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins in body tissues by inhibiting cyclooxgenase; at least 2 isoenzymes, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-1) and -2 (COX-2) (also referred to as prostaglandin G/H synthase- 1[PGHS-1] and [PGHS-2], respectively), which have been identified to catalyze the formation of prostaglandins in the arachidonic acid pathway. The pharmacodynamic effect is thought to reduce prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthesis.
SUBJECT AND METHOD
Study Subjects: Sufficient numbers of healthy Indian male human subjects was screened, out of those 09 male subjects were enrolled in the study and 03 male subjects were taken as standby. A total of 12 male subjects were applied with the study medication in the beginning of the study. The screening consent and study consent was taken respectively before drug application. Thereafter, subject‘s medical records were documented and physical examination was conducted. Inclusionexclusion criteria was also based on successful completion of a clinical health evaluation, which consisted of a personal interview; a complete physical examination (BP, pulse, weight, temperature, and respiratory rate); diagnostic testing that included a 12-lead electrocardiogram and chest radiograph; a laboratory testing that included a complete blood cell count, metabolic and hepatic tests (alanine amino transferase [reference range, 5-55 U/L], aspartate amino transferase [5-34 U/L]), urine analysis, blood chemistry for glucose (70-109 mg/dL), blood urea nitrogen (7-23 mg/dL), and creatinine (0.- 1.3 mg/dL), as well as serology tests for hepatitis (B and C), and HIV antibodies. Testing was performed by Central Pathology Laboratory, Shree Pathology Lab CIDCO, Aurangabad (MS). Subjects were excluded if laboratory values were significantly above or below the reference range and/or if all tests had not been performed. In addition, the laboratory data were reviewed by the investigators of the clinical unit prior to the enrollment of the subjects. Subjects were compensated for participation.
Study Design: This study was carried out as per the ICH (Step 5), ?Guidance for Good Clinical Practices (GCP)‘ and the principles of Declaration of Helsinki (Scotland, October 2000).The Independent Ethics Committee reviewed the protocol and the informed consent form for this study. A single-dose-one arm, open label, threeway parallel design was used. Subjects were admitted and housed in the clinical facility at least 2 hour before the application of the dose during each period of the study. Informed consent for the dosing / sampling procedure was obtained from each subject on admission to the clinical facility for the first study period. The marketed formulation of Diclofenac Sodium [Voveran Emulgel, Lic. No.: KTK/25/460/2001, Batch No.: 8Z099T, Mfg. Date: 12/2008 Exp. Date: 11/2011, Mfg. By: Novartis India Ltd., Bangalore] was applied on the forearm of the study subjects as per the dosing schedule. The dosing procedure was as mentioned below:
- Both the forearms were washed with mild soap and copious amount of water and dried in air.
- Both the forearms were marked for total of 08 application sites of 1 sq.cm area each.
- 5 mm length product was applied on all the sites so that the product completely and smoothly covers the site area.
- The stratum corneum samples were collected from the sites on the desired pre decided time. The stratum corneum samples were collected for the first time as mentioned in the above procedure. After the pre decided time period the same procedure was repeated, but with simultaneous application of sufficient amount of pressure using pressure belt on all the sites. Then, the stratum corneum samples were collected from the sites after a desired pre decided time. Next, the above procedure was repeated with simultaneous application of a heat belt for a sufficient time period on all the sites where the study product was applied.
Stratum Corneum Sampling: Skin Stratum Corneum samples were collected in sterile glass test tubes during each period. The samples were collected pre-dose and at 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and 6.0 hours post-dose application. The stratum corneum samples were analysed for Diclofenac Sodium concentrations only. For each subject the total number of blood draws were 02 (01 for screening and another during post study assessment); the total volume of blood withdrawn (10 ml for the pre-study evaluation and 10 ml for the post study) through the vein puncture did not exceed 20 ml.
Procedure Study samples were collected as follows. The pre-dose samples were collected within one hour prior to drug application. The post-dose samples were collected within 2 minutes of the scheduled time where the end time of collection to the nearest minute was recorded.
- Before sampling, the drug remaining on the site was removed by mild force using three cotton swabs to ensure the complete removal of residual drug from the site.
- The pre cut (1 sq. cm) adhesion tape was applied on the site and the mild force was applied to ensure the proper adhesion of the tape on the site area. The tape was removed and discarded.
- Eight adhesion tape pieces were applied on the site area in the same manner and each tape was removed from the site before the next one was applied. The removal was done using the forceps and was done in one stroke to ensure the complete removal of stratum corneum.
- All 8 samples tapes were collected in a single test tube which were then sealed and stored in the refrigerator at -200 c till analysed.
Analytical Method: A validated UV spectroscopic method was employed by using Chemito-Spectroscan UV 2600, Double Beam UV-Visible Spectrophotometer for the estimation of Diclofenac Sodium in human stratum corneum. This method involved the extraction of the Diclofenac Sodium form sample by using methanol and measuring the absorbance at 285nm. The concentration of Diclofenac Sodium in sample was determined from calibration curve. The standard stock solution of Diclofenac sodium was prepared by weighing 50mg of Diclofenac Sodium powder and shaking it with 60 ml of methanol in a 200-ml volumetric flask, which was then diluted with methanol. From the Diclofenac sodium stock solution 4ml was taken and diluted up to 100ml with methanol, to get the solution of 10µg/ml concentration. The test solution was prepared by taking 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ml from the standard stock solution in six different, labelled (1µg/ml, 2µg/ml, 4µg/ml, 6 µg/ml, 8 µg/ml) test tubes and making volume 27 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 05 May 2011 up to 10ml by adding methanol. (Note: no need to add methanol in last µg/ml sample). Methanol was used as blank solution. Calibration Curve was prepared by using various dilutions (1 µg/ml -10µg/ml) as transferring required quantity of blank solution in to the cuvette and recording the absorbance, then taking the first test tube (1µg/ml), the required quantity of the test solution was transferred into the cuvette and the absorbance was measured recorded at 285 nm. The step 2 and 3 was repeated for remaining dilutions. Finally the graph of concentration versus absorbance Optical Density (OD) was
DISCUSSION
The results of our study showed that when we apply pressure on all the sites of drug application, the time required to achieve the Cmax gets reduced; also Cmax achieved was greater. On the other hand, when we use heat belt the Cmax was increased but the time required for this remained constant. No moderate or serious Adverse Events (AEs) were reported by the investigators. Potential recall bias of AEs in this study was not likely because only one dose of each formulation was administered during each treatment period, subjects were under medical surveillance in the clinical unit, and the duration of the washout period was only 2 days.
CONCLUSION
This study has demonstrated that for the topical formulations, the physical parameters like pressure or temperature acts as an aid not only to achieve higher tissue concentration but also to give the rapid onset of action.

DISCUSSION
The results of our study showed that when we apply pressure on all the sites of drug application, the time required to achieve the Cmax gets reduced; also Cmax achieved was greater. On the other hand, when we use heat belt the Cmax was increased but the time required for this remained constant. No moderate or serious Adverse Events (AEs) were reported by the investigators. Potential recall bias of AEs in this study was not likely because only one dose of each formulation was administered during each treatment period, subjects were under medical surveillance in the clinical unit, and the duration of the washout period was only 2 days
. CONCLUSION
This study has demonstrated that for the topical formulations, the physical parameters like pressure or temperature acts as an aid not only to achieve higher tissue concentration but also to give the rapid onset of action.
References:
1. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Guidance for Industry: Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Orally Administered Drug Products — General Considerations. US FDA. 2003.
2. Benfeld E, Steen H, Aage V., Torkil M and Shah VP. Bioequivalence of Topical Formulations In Humans: Evaluation By Dermal Microdialysis Sampling And The Dermatopharmacokinetic Method. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2007; 127:170- 178.
3. Shah VP, Glynn GL, Yacobi A. Bioequivalence of Topical Dermatological Dosage Forms –Method of Evaluation of Bioequivalence. Pharma. Research. 1998; 15(2):167-171.
4. Shah VP. Progress in Methodologies for Evaluating Bioequivalence Of Topical Formulations. Am. J. of Cl. Dermatology. 2001; 2(5):280.
5. Franz TJ, MD. Assessing The Validity Of Stratum Corneum Tape Stripping To Determine The Bioavailability / Bioequivalence Of Topical Drug Products. A letter to Roger Williams, FDA-CDER. 1999.
6. Herkenne C, Naik A, Kalia YN, Hadgraft J, Guy RH. Ibuprofen Transport into and through skin from topical formulations: In vitro-In vivo Comparison. The society of investigative dermatology. 2006.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License