IJCRR - 3(8), August, 2011
Pages: 55-64
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY ON THE COLORATION OF CONDUCTIVE TEXTILE SUBSTRATES BY GREENER METHOD
Author: K. Kalapriya, H.Gurumallesh Prabu
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Dyeing on textile substrates such as cotton, silk and polyester was carried out by the conventional
method. Dyeing was carried out in open dye bath. Cotton fabric was dyed with reactive dyes
(Reactive Blue 4, Reactive Orange 4, Reactive Violet 5), direct dyes (Direct Red 7, Direct Black 22,
Direct Blue 1) and vat dyes (Vat Yellow 2, Vat Red 10, Vat Brown 1). Silk fabric was dyed with
acid dyes (Acid Yellow 17, Acid Orange 7, Acid Red 73). Polyester fabric was dyed with disperse
dyes (Disperse Orange 3, Disperse Orange 13, Disperse Red 11). In another method and in order to
produce color on conductive fabric by a greener route (non use of auxiliaries and heat), fresh textile
substrates were subjected to chemical polymerization with pyrrole in the presence of dye at room
temperature. The effects of surfactants (sodium dodecyl sulphate, Cetyl trimethylammonium
bromide) and dopants (n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium
tetrafluoroborate) in the polymerization were studied. The polymerized fabric containing the dye was
then measured using Computer Color Matching (CCM) analysis to assess the dye uptake. Crease
recovery angle of the fabrics was measured. Electrical conductivity of conductive fabrics was
measured by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Surface morphology was tested with
Scanning Electron Microscope.
Keywords: Cotton, Silk, Polyester, Dyeing, conducting polymer, Surfactant.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
In order to obtain textile materials with a desired property, the fibre surface is often modified with polymer, inorganic or hybrid organic/inorganic layers before use.1 The demand for electrically conductive fibres and textiles has increased in recent years because of applications as antistatic materials,2 sensors,3 materials for electromagnetic shielding 4,5 and biomedical use.6 A great deal of work has been carried out on synthetic fibres, especially polyester, 7-9 which takes the leading position in the world fibre production and consumption. As far as natural fibres are concerned, cotton 8,10,11 and wool have attracted a great deal of attention.12-14 Deposition of conducting polymers on a textile surface is relatively simple and there are many publications dealing with this procedure.15–18 Researchers have indicated that modification by conductive polymers seems to be the interesting approach enabling nature fibres, new conductive functionality, 19,20 because of convenient polymerisation and good conductivity. Recent studies have showed that conductive polymers such as polypyrrole (Ppy), polyaniline (PANI) and poly-3,4-ethylene-dioxythiophene (PEDOT) all have good biocompatibility 21-23 and have been proven to be a promising alternative for developing new biodegradable conduits used for restoring the function of injured peripheral nerves or the regeneration of a nerve gap by using electrical stimulation in-situ 24 . Electrically conducting textiles can be prepared by in-situ polymerisation of conducting polymers such as polypyrrole 25 and polyaniline,26 so-called ?intelligent materials?.27 Polypyrrole is comparatively more stable than other conductive polymers. Polypyrrole (PPy) is generally synthesized by chemical or electrochemical means. Chemical synthesis is used when large quantities of material are required and involves mixing a strong oxidizing agent (typically Ferric Chloride) with a monomer solution.28 Polypyrrole coated fabrics have good electrical conductivity, thermal properties 29,30 and flexibility, and they are suitable for numerous applications.31 In addition, the deposition of thin layers of conductive polymers on fabrics or yarns does not noticeably change and sometimes even improves the mechanical properties of the original material.32a,32b,33,34 Polymerisation of pyrrole in the presence of surfactants such as dodecylbenzyl sulphonic acid or sodium dodecyl sulphate, leads to an increase in mass yield due to incorporation of the surfactant into the polymer.35 Cationic surfactants were found to inhibit the polymerization of pyrrole. Doped π- conjugated polymers produced by oxidative polymerisation, contain positive charges on the backbone chain. It is supposed that the charged species are polarons and bipolarons, which are delocalized over portion of several monomer units. The mobility of charged species along the polymer chain is responsible for the electrical conduction. The charges are neutralized through the introduction in the polymer structure of negative charged counter-ions. The counter-ions (also called dopants) play an important role in the synthesis of conducting polymers, because they promote the stability of polarons and bipolarons producing complexes.36,37 Recent research has shown that ionic liquids have the potential to be used in place of water in some textile processes. An alternative to use of water as solvent in the dyeing process of textiles is to use ionic liquids. Because of their unique set of properties not exhibited in any other material, they have gained overwhelming interest in the past decade. The term ?room temperature ionic liquids? has been assigned to organic salts that are liquid at ambient conditions. A truly green ionic liquid would need to be sustainable, easy and clean to prepare, non-toxic and biodegradable.38 The objective of this study is to experiment and discuss the fixation (binding) of dye on cotton, silk and polyester by (i) conventional dyeing method and (ii) chemical polymerisation of pyrrole in the presence of dye method. The second method has been attempted by greener concept with an aim to avoid the use of dye auxiliaries and heat to impart coloration in polymerized (conductive) substrates.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Desized, scoured and bleached cotton fabric, dilute hydrochloric acid treated silk and polyester fabrics were used in this study. All chemicals used were of AR grade from Merck. In the first conventional method, dyeing on textile substrates such as cotton, silk and synthetic polyester was carried. For this, cotton fabric was dyed with Reactive dyes such as Reactive Blue 4 (RB 4), Reactive Orange 4 (RO 4), Reactive Violet 5 (RV 5) and Direct dyes such as Direct Red 7 (DR 7), Direct Black 22 (DB 22), Direct Blue 1 (DB 1) and Vat dyes such as Vat Yellow 2 (VY 2), Vat Red 10 (VR 10), Vat Brown 1 (VB 1). Silk fabric was dyed with Acid dyes such as Acid Yellow 17 (AY 17), Acid Orange 7 (AO 7), Acid Red 73 (AR 73).
Polyester fabric was dyed with Disperse dyes such as Disperse Orange 3 (DIO 3), Disperse Orange 13 (DIO 13) and Disperse Red 11 (DIR 11). The stock solutions of dyes were prepared at 1% concentration. In the second modified method to produce color on conductive fabric by a greener route (non use of auxiliaries and heat), fresh textile substrates were subjected to chemical polymerization with pyrrole in the presence of dye at room temperature. The effects of surfactants (sodium dodecyl sulphate, Cetyl trimethylammonium bromide) and dopants (n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, 1- butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate) in the polymerization were studied. The polymerized fabric containing the dye was then measured using Gretagmacbeth 2180 UV Computer Color Matching instrument to assess the dye uptake. Crease recovery angle of the fabrics was measured. Electrical conductivity of conductive fabrics was measured by using AUTOLAB electrochemical impedance bridge in the frequency range of 50 mHz to 100 KHz at an amplitude of 20 mV, by sandwiching the polymer coated conductive fabric (1 cm dia) between two stainless steel (SS304) electrodes contacts. Surface morphology was tested with Scanning Electron Microscope using Hitachi S3000H instrument. Conventional method of dyeing was carried out in an open dye bath at a material to liquor ratio (MLR) of 1:30. In the dyeing of cotton, the fabric was entered into the dyebath containing sodium hydroxide and hydrose. 2% sodium chloride was added and dyeing was continued for 45 minutes at a temperature of 90 C. Then the dyed fabric was taken out and washed well. In the dyeing of silk, the fabric was entered into the dyebath containing 0.2% acetic acid. After 10 minutes, dye was added. 2% sodium chloride was added and dyeing was continued for 45 minutes at 80 C. Then the dyed fabric was taken out and washed well. In the dyeing of polyester, the fabric was entered into the dyebath containing ammonium acetate and acetic acid. Dyeing was continued for 45 minutes at 130 C. Then the dyed fabric was taken out and washed well. In the proposed second method, chemical polymerization of pyrrole (Py) was carried out at room temperature. Pyrrole was dissolved in acetonitrile and suitable dilutions were made. Ferric Chloride was used as an oxidising agent to initiate the polymerization of pyrrole. The surfactants sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) and cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) were used in the study. Dopants such as ntetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate (TBATFB) and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (BMimTFB) were used to study the effectiveness of polymerization. Variables such as dye, dopant and surfactant were varied. A material to liquor ratio of 1:30 was maintained. Required amount of dye was added to produce 0.5% shade. The fabric was subjected to stirring in the bath containing dye, monomer, surfactant and dopant for 1 h and Ferric Chloride was added and the polymerisation was continued for 1 h. Polymerized fabric containing the dye was then taken out, washed with water, dried and subjected to dye uptake and other tests.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
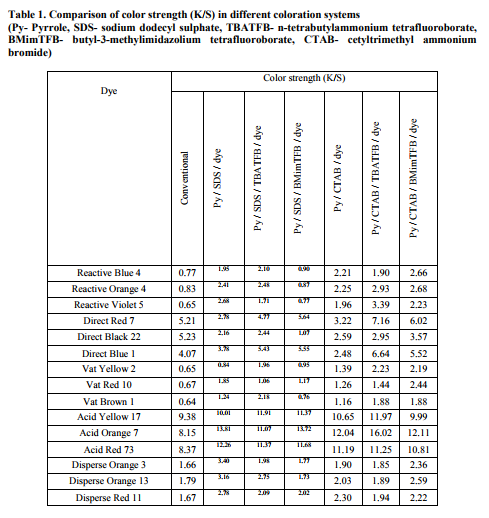
Under the specified conditions employed in the conventional dyeing of cotton, Direct Black 22 has resulted better dyeability with K/S value of 5.23 (Table 1) and its wash fastness tested gave a K/S of 4.50. Thus, the dyeability and dye fixation were good. The minimum K/S value of 0.64 was obtained with Vat Brown 1 dye. In the dyeing of silk, the maximum K/S value of 9.38 was obtained with Acid Yellow 17 dye (figure 1). The wash fastness was also good. In the dyeing of polyester, the dyeability was moderatein the fabric dyed with Disperse Orange 13 and the K/S value of 1.79 was obtained. Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M Pyrrole, 3x10-2 M sodium dodecyl sulphate, 5x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. With cotton, the K/S value showed its maximum at 3.78 with Direct Blue 1 dye and the wash fastness result was acceptable. Direct Blue 1 dye has resulted the highest chroma value of 24.14. With silk, the maximum K/S value of 13.81 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye and the wash fastness was good. A chroma value of 54.89 was obtained with this Acid Orange 7 dye. The wash fastness result was very good. With polyester, the maximum K/S value of 3.40 was obtained with Disperse Orange 3 dye and the wash fastness was good. The highest chroma value of 26.53 was obtained with Disperse Orange 3 dye. Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M pyrrole, 3x10-2 M sodium dodecyl sulphate, 5x10-2 M n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, 2x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. For cotton, the maximum K/S value of 5.43 was obtained with Direct Blue 1 dye. The wash fastness test showed dye fixation. The highest chroma value of 24.62 was obtained with Direct Blue 1 dye. With silk, the maximum K/S value of 11.37 was obtained with Acid Red 73 dye and the wash fastness was noticed as good. The highest chroma value of 56.47 was obtained with Acid Red 73 dye. For polyester, the maximum K/S value of 2.75 was obtained with Disperse Orange 13 dye and the wash fastness was observed as moderate. The highest chroma value of 16.06 was obtained with Disperse Orange 13 dye. Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M pyrrole, 3x10-2 M sodium dodecyl sulphate, 5x10-2 M 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, 2x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. Maximum K/S value of 5.64 was obtained with Direct Red 7 dye and the wash fastness observed as good for cotton. The highest chroma value of 36.75 was also obtained with Direct Red 7 dye. Maximum K/S value of 13.72 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye and the wash fastness was noticed as good for silk. The highest chroma value of 51.02 was obtained with the same Acid Orange 7 dye. With polyester, the maximum K/S value of 2.02 was obtained with Disperse Red 11 dye and the wash fastness tested sample showed moderate results. The highest chroma value of 16.39 was obtained with Disperse Red 11 dye.
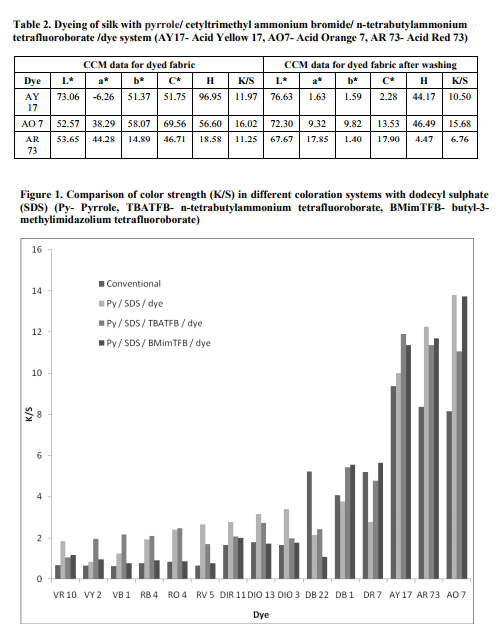
Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M pyrrole, 3x10-2 M cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide, 5x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. With cotton, the maximum K/S value of 3.22 (figure 2) was obtained with Direct Red 7 dye and the wash fastness was good. The highest chroma value of 23.61 was obtained with the same Direct Red 7 dye. With silk, the maximum K/S value of 12.04 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye and the wash fastness was very good. The highest chroma value of 37.65 was obtained with Acid Orange 7. With polyester, the maximum K/S value of 2.30 was obtained with Disperse Red 11 dye and the wash fastness was moderate. The highest chroma value of 17.21 was obtained with Disperse Red 11 dye. Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M pyrrole, 3x10-2 M cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide, 5x10-2 M n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, 2x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. With cotton, the maximum K/S value of 7.16 was obtained with Direct Red 7 dye and the wash fastness was good. The highest chroma value of 37.52 was obtained with Direct Red 7 dye. With silk, the K/S value obtained its maximum at 16.02 with Acid Orange 7 dye and the wash fastness was very good. The highest chroma value of 69.56 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye. With polyester, the maximum K/S value of 1.94 was obtained with Disperse Red 11 dye and the wash fastness was moderate. The highest chroma value of 14.53 was obtained in Disperse Red 11 dye. Polymerization of textile substrates with reactants in the bath containing 5x10-2 M pyrrole, 3x10-2 M cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide, 5x10-2 M 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, 2x10-2 M Ferric Chloride with dye was employed. With cotton, the maximum K/S value of 6.02 was obtained with Direct Red 7 dye and the wash fastness was good. The highest chroma value of 34.46 was obtained with Direct Red 7. With silk, the maximum K/S value of 12.11 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye and the wash fastness was very good. The highest chroma value of 59.09 was obtained with Acid Orange 7 dye. With polyester, the maximum K/S value of 2.59 was obtained with Disperse Orange 13 dye and the wash fastness was good. The highest chroma value of 19.36 was obtained with Disperse Orange 13 dye. ?L?, ?a? and ?b? data represent the lightness or darkness, redness or greenness and yellowness or blueness respectively. It is inferred that higher the L value, lower the dyeability and lower the L value, higher the dyeability. ?H? is a measure of hue and is represented as an angle ranging from 0 to 360 . LabCH results were obtained for the samples. If ?a? and ?b? are both positive, then the hue angle should be between 0° and 90º. In our results, both a and b were positive for Acid Red 73 dye and Acid Orange 7 dye. In all these dyed samples, the hue angle falls between 18.58 and 56.60 for dyed fabric. If ?a? is negative and ?b? is positive, then the hue angle should be between 90° and 180º. It is found that with Acid Yellow 17, a is negative and b is positive and the hue angle was 96.95 for dyed fabric (Table 2). Effect of sodium dodecyl sulphate surfactant: Fabrics subjected to chemical method of polymerisation in the presence of dye have produced improved dyeability in majority of the systems studied than the unpolymerized fabrics dyed in the conventional dyeing method. In the chemical polymerization, the improved K/S values were noted when pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate /1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate /dye system was used with acid and direct dyes. In the case of reactive and vat dyes, pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate / ntetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate /dye system showed increased K/S values. The improved K/S values was noted when pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate /dye was used for disperse dyes. Among the two dopants studied, dyeing in pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate /1- butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate /dye system was more effective in the dyeability than pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate / ntetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate /dye system. Considering the dye uptake and washing fastness, acid dyes produced better dyeability when compared to other dyes studied. Among the acid dyes, Acid Orange 7 has resulted better dyeability than other two. Effect of Cetyl trimethylammonium bromide surfactant: In the chemical polymerization in the presence of dye, improved K/S values were noted when pyrrole / cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide / n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate /dye system was used for all classes of dyes studied except with disperse dyes. In the case of disperse dyes, pyrrole / cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide /1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate /dye system has showed improvement in the K/S values. Considering the dye uptake and washing fastness, acid dyes produced better dyeability when compared to other dyes studied. Among the acid dyes, Acid Orange 7 has resulted improved dyeability. The dyeability of cotton and silk fabrics was higher when dopant was used. This could be due to the improved bond formation between dopant and free hydroxyl groups in cotton and -NH2 group in silk, thus fixing the dyes in the fabrics accordingly. The conductivity results were obtained for cotton, silk and polyester fabrics. Significant conductivity was observed for cotton only; better conductivity of 1.72 x 10-6 S/cm was obtained with Direct Blue 1 dye in pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate /1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate /dye system.
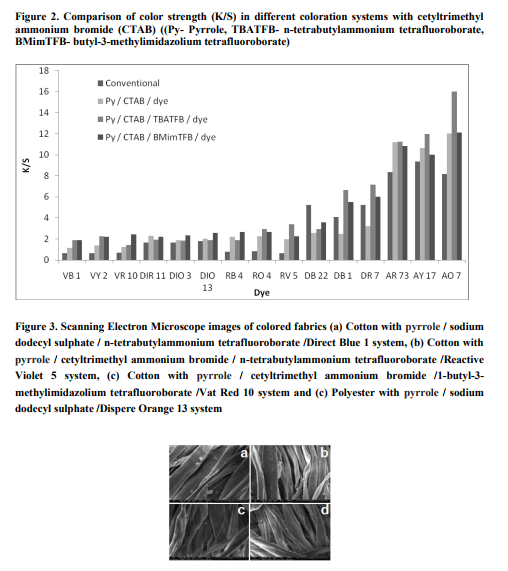
It is assumed that the pyrrole radical cations generated during the polymerisation reaction by the addition of Ferric Chloride are having a preferential affinity for the cotton fibres. Silk and polyester fabrics have shown poor conductivities, which could be due to poor doping during polymerization. Among the surfactants studied, Cetyl trimethylammonium bromide has resulted better dyeability than sodium dodecyl sulphate. Among the dopants studied, n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate has shown better dyeability than 1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, which is supported by the increase in crease recovery angle values. Scanning Electron Microscope images showed the nature of coating on the fabric, which reveal the deposition of polypyrrole on to the fibres. The surface morphology of the fabrics obtained by Scanning Electron Microscope analysis was found to be better with (i) pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate / n-tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate /Direct Blue 1 system (ii) pyrrole / cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide / ntetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate /Reactive Violet 5 system (iii) pyrrole / cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide /1-butyl-3- methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate /Vat Red 10 system and (iv) pyrrole / sodium dodecyl sulphate /Dispere Orange 13 system (Figure 3).
CONCLUSION
Colored conductive fabrics were prepared by incorporating polypyrrole. These polymerized fabrics showed better dye fixation than conventional dye fixation. The advantage in the proposed method is that conductive fabrics could be colored effectively without the use of dyeing auxiliaries and heating. Acid dyes produced better dye fixation when compared with other dyes studied. This approach is a novel and greener way of effective coloration on conductive textile substrates, which could be useful in the field of technical textiles.
References:
1. B. Mahltig, D. Knittel, E. Schollmeyer, H. Bottcher, J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol., 2004, 31, 293.
2. T. Derrick, P. Kathirgamanathan, M. J. Toohey, J. N. Chubb, Electrostat.1999 Inst. Phys. Conf. Ser., 1999, 163, 313.
3. Z. Li, G. Luo, F. Wei, Y. Huang, Comp. Sci. Technol., 2006, 66, 1022.
4. H. H. Kuhn, A. D. Child, W.C. Kimberly, Synth. Met., 1995, 71, 2139.
5. H. K. Kim, M. S. Kim, K. Song,Y. H. Park, S. H. Kim, J. Joo, J.Y. Lee, Synth.Met., 2003, 135, 105.
6. D. Tessier, L. H. Dao, Z. Zhang, M.W. King, R. Guidoin, J. Biomater. Sci.Polym. Edn., 2000,11, 87.
7. A. Harlin, P. Nousiainen, A. Puolakka, J. Pelto, and J.Sarlin, J. Mater. Sci., 2005, 40, 5365.
8. P. Lekpittaya, N. Yanumet, B. P. Grady, and E. A. ORear, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2004, 92, 2629.
9. E. Hakansson, A. Amiet, and A. Kaynak, Synth. Met., 2006, 156, 917.
10. S. N. Bhadani, M. Kumari, S. K. Sen Gupta, and G. C.Sahu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1997, 64, 1073.
11. S. Subianto, G. D. Will, and S. Kokot, Int. J. Polym.Mater., 2005, 54, 141.
12. A. Varesano, L. DallAcqua, and C. Tonin, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2005, 89, 125.
13. A. Varesano, A. Aluigi, C. Tonin, and F. Ferrero, Fiber.Polym., 2006, 7, 105.
14. S. S. Najar, A. Kainak, and R. C. Foitzik, Synth. Met., 2007, 157,1
15. C. Tonin, R. Peila, F. Ferrero, M. Lavelli, Tech. Text., 2002, 8, 120.
16. L. DallAcqua, C. Tonin, R. Peila, F. Ferrero, M. Catellani, Synth. Met., 2004, 146, 213.
17. E. Hakansson, A. Kaynak, T. Lin, S. Nahavandi, T. Jones, E. Hu, Synth.Met., 2004, 144, 21.
18. A. D. Child, H. H. Kuhn, Synth. Met., 1997, 84, 141.
19. M. Micus?k, M. Omastova, J. Prokes, I. Krupa, J Appl Polym Sci., 2006, 101,133.
20. S. H. Hosseini, A. Pairovi, Iran Polym J., 2005, 149, 34.
21. H. G. Xue, Z. Q. Shen, Talanta., 2002, 57, 289.
22. J. W. Lee, F. Serna, J. Nickels, C. E. Schmidt, Biomacromolecules., 2006, 7,1692. 22. F. O. Toribio, T. C. Maria. Adv Mater., 2003, 15, 279.
23. A. Kotwal, C. E. Schmidt, Biomaterials., 2001, 22, 1055.
24. R.V. Gregory, W. C. Kimbrell, H. H. Kuhn, Synth. Met., 1989, 28, 823.
25. K.W. Oh, K.H. Hong, S.H. Kim, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 74 (1999) 2094.
26. G. G.Wallace, G. M. Spinks, L. A. P. KaneMaguire, P. R. Teasdale, Conductive Electroactive Polymers—Intelligent Materials Systems, CRC Press, 2003.
27. J. Duchet, R. Legras and S. D. Champagne, Synth. Met., 1998, 98, 113.
28. H. H. Kuhn, A. D. Child, W.C. Kimberly, Synth. Met., 1995, 71, 2139.
29. L. DallAcqua, C. Tonin, R. Peila, F. Ferrero, M. Catellani, Synth. Met., 2004, 146, 213.
30. E. Hakansson, A. Amiet, A. Kaynak, Synth. Met., 2006, 156, 917.
31. (a) S.E. Artemenko, L.P. Nikulina, T.P. Ustinova, D.N. Akbarov, E.P.Krainov, V.I. Dubkova, Fibre Chem., 1993, 24, 300.
32. (b) I. Novak, I. Krupa, I. Chodak, Synth. Met., 2004, 144, 139.
33. X. H. Yin, K. Kobayashi, K. Yoshino, H. Yamamoto, T. Watanuki, I. Isa, Synth. Met., 2005, 69, 367.
. 34. A. Kaynak, L. Wang, C. Hurren, X. Wang, Fibre Polym. 2002, 3, 24.
35. J. Stejskal, M. Omastova, S. Fedorova, J. Prokes, M. Trchova, Polymer., 2003, 44, 1353.
36. N. Kirova and S. Brazovskii, Synthetic Metals, 1996, 76, 229.
37. G. Paasch, Solid State Ionics, 2004, 169, 87.
38. K.Anderson, August 2008, Ionic liquids: An Environmentally Friendly Alternative, http://www.techexchange.com/thelibrary/ion ic.html. Accessed December 2010.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License