IJCRR - 3(11), November, 2011
Pages: 138-148
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
COMPARISON OF ACAPELLA AND RC-CORNET FOR AIRWAY CLEARANCE IN BRONCHIECTASIS-A PILOT STUDY
Author: Shabari, V Prem, Gopala Krishna Alaparthi, Vaishali, Vishak acharya
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Rc-cornet is a hand held PEP device used in facilitating airway clearance. Acapella is also a PEP device already known to be effective in airway clearance. Objective: The objective of the study was to compare Acapella and Rc-cornet device as airway clearance
in bronchiectasis subjects and to determine patient preference between the two devices.
Method: Forty patients (20 male and 20female) mean age 52.20 \? 15.66 with history of expectoration of more than 30ml sputum per day were recruited. The sequence of the therapy
was allocated by block randomization. Assessment and familiarization session was performed
on day 1. Treatment employing the Acapella and Rc-cornet were done on days 2 and 3 .
Treatment order and allocation was determined by block randomization. Sputum volume was
measured during and 2hours after the treatment and patient treatment preference was recorded.
Results: A statistically significant difference was found in the sputum volume expectorated with Rc-cornet (36.58 \? 7.21) compared with Acapella (34.63\?9.03). Patients preferred Rccornet
in terms of clearing secretions. Conclusion: The present study proved there was
increased sputum clearance following the use of Rc-cornet when compared to Acapella. In
addition Rc-cornet was preferred by patients who judged that it was more useful in clearing
secretions.
Keywords: chest physiotherapy, sputum volume, oscillation, positive expiratory pressure, Acapella, RC-cornet, secretion clearance, bronchiectasis
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Bronchiectasis is a term used to describe as a permanent and irreversible abnormal dilatation of the bronchi and bronchioles. It is usually acquired but results from underlying genetic or congenital defects of airway clearance 1 . Bronchiectasis in India it is known to be the 3rd commonest non – tubercular respiratory disease in adults 2 . In Bronchiectasis, irreversible dilatation of bronchi occurs and is associated with destruction of muscular and elastic components of the bronchi wall this result in permanent dilatation and inflammation of bronchial wall3 . The distended bronchi have the tendency of retaining secretion; these secretions become infected triggering an ongoing and persistent host inflammatory response leading to loss of respiratory cilia and progressive airway obstruction as a result of oedema and excessive mucus 4 .
Bronchiectasis most frequently involves both the lower lobes, when the involvement is unilateral it affects the terminal bronchi and bronchioles and is more frequently seen on the left lingula and right middle lobe. Clinical manifestation includes productive cough, fever, shortness of breath, purulent voluminous expectoration with a fetid odour and occasional hemoptysis 5 . Bronchiectasis is treated with medicines, hydrations, and chest physical therapy. Medicines include bronchodilators, corticosteroids and antibiotics. Physiotherapy is regarded as standard treatment when dealing with Bronchiectasis. This include traditional methods like chest physiotherapy which includes breathing techniques, manual percussion and vibration, postural drainage, forced expirations and coughing and mechanical devices includes high frequency chest wall oscillation, high frequency oral oscillation, oscillatory positive expiratory pressure devices like flutter, Acapella, RC- Cornet and PEP mask 6 .
RC-Cornet is a modern physiotherapeutic device for patients with bronchiectasis and disorders of lungs accompanied by sputum production. RC cornet is a hand held device with curved plastic tube containing a flexible latex-free valve-hose. During expiration through the Cornet, a positive expiratory pressure and oscillatory vibration of the air within the airways are generated. It can be used in any position as it is gravity independent 7 . A recent study comparing RC-Cornet at settings 3-4 i.e. at maximum pressure variation, compared with flutter on bronchiectasis sputum cohesiveness based on the same throughput rate in the two devices, the study concluded that RCCornet reduces cohesiveness more than flutter does 7.
Another study comparing RC-Cornet with and without physiotherapy concluded RCCornet is comfortable, effective small accepted tool and also had positive effects on pulmonary functions and treatment 8 . Acapella is a hand held device, incorporates two therapies, positive expiratory pressure and vibration, it enabling patients to clear their congested lung and airways. Acapella was widely used as it is easier to use and take less than half the time of conventional sessions and facilitates airway opening 9 A RCT done on comparing Acapella versus active cycle of breathing technique in bronchiectasis subjects concluded that Acapella is as effective as Active cycle of breathing technique and offers a user friendly alternative to Active cycle of breathing technique for patients and also greater portion of patients preferred Acapella 10 .
A recent study done on Acapella versus threshold inspiratory muscle trainer for sputum clearance in bronchiectasis subjects concluded that there was increased sputum clearance following the use of Acapella compared to threshold inspiratory muscle trainer and Acapella was preferred by patients as useful in clearing secretion 11 . We hypothesized that RC-cornet will be more effective than Acapella for airway clearance.
To our knowledge, no studies have been done on Acapella versus RC-Cornet in airway clearance in bronchiectasis subjects. In addition, no studies have compared the airway clearance of RC- cornet to the Acapella in patient with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis .therefore the purpose of the study was to compare the effects of the RCcornet and a Acapella as methods of airway clearance in bronchiectasis and to compare the patient preference between the devices/techniques
MATERIAL AND METHODS
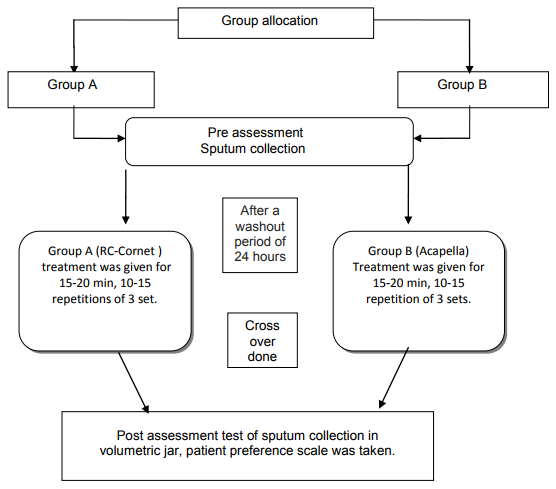
The study was approved by local institutional ethics committee. Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients. Thirty patients with a history of sputum expectoration of more than 30 ml per day, diagnosed to have bronchiectasis, were recruited from hospital setting at kastruba medical college hospitals. Patients with uncontrolled hemoptysis, rib fractures, or history of recent myocardial infraction were excluded from the study
Study design
An approval was obtained from the scientific committee and time the sequence of the therapy (RC-cornet/Acapella) was allocated by block randomization. Patients attended the teaching and treatment sessions for 3 consecutive days. Assessment /familiarization session was done on the first day. Patient had no used either the RC- cornet or Acapella previously. Patients performed treatments using either the RC-cornet or Acapella at the same time over the next 2 consecutive days (days 2 and 3). Patient who performed RC-cornet on day 1 were crossed over to the Acapella on day 2 and vice versa. Patients were instructed to administer medications (bronchodilators, steroids, antibiotics whenever applicable) at least one hour before the treatment and at the same time on both the treatment days. The same physiotherapist administered all the treatment sessions. The volume of sputum expectorated (during treatment and for up to 2 hours after treatment) was measured with a volumetric jar and patient preference scale was taken.
In Group A patients performed RCCornet
It produces a combined PEP when patient blows into it, i.e. it builds up a continuous positive pressure of about 20 cm head of water when blown into with additional pressure oscillations of about 5 cm head of water depending on how strongly the patient blows. The pressure and airflow oscillations generated by expiration through the RC- cornet are imparted to the bronchial tree by way of the mouthpiece, causing calibre fluctuations in the bronchi and thus helping to prevent respiratory tract collapse.
The patients could choose any preferable starting position as this device works independent of gravitational forces. The patient was instructed to tightly enclose lips to the mouthpiece and was advised to take a deep breath in through nose and blow through RC-Cornet. A high pitch harsh sound and vibration was felt in the chest. The patients were instructed to repeat the same 10-15 times which is followed by huff and coughs if needed. The cycle was repeated for 15-20 minutes or 3 sets of 10- 15 repetitions were given. The twisting of mouthpiece produced more positive expiratory pressure and vibration in the airway.
In group B, patients performed Acapella
It consists of counter weighted plug and metal strip attached to a lever, and a magnet. Airflow oscillations are created by the breaking and reforming of a magnetic attraction by the plug as it intermittently occludes air passing through the device during expiration .the device incorporates a frequency/resistance dial that adjusts the proximity of the magnet to the metal strip, thereby regulating expiratory pressure and the amplitude and frequency of oscillations.
During the initial teaching session, the patient was seated in a chair and was taught to exhale through the device for 3 to 4 seconds. If exhalation was too slow or too fast, patients were encouraged to exhale more or less forcefully. The patients was instructed to take a deep breath and hold it for 3-5 seconds and the patients were instructed to place the mouthpiece into mouth and were asked to exhale completely at a slightly faster rate than normal. The same procedure was recommended to be repeated at 10-15 times and the patients were advised to suppress the desire to cough during these cycles. The patient was then advised to remove the Acapella from mouth and exhale forcefully to aid airway clearance. If it does not trigger a productive cough, an attempt to huff/ cough to help force secretion was advised. Immediately after end of treatment session in either group the post assessment test including sputum collection (volumetric jar), was carried out for 2hrs, and then wash out period of 24 hours was taken so as to neutralize the effects of given intervention, then the subjects were crossovered to other group. End of the treatment session were determined when the subjects were treated with maximum of 15-20 min, or when the subjects were no longer expectorating sputum or when subjects fell too tired to continue the treatment
Patient preference scale
The patient preference scale (PPS) has previously been described and used in the assessment of treatment effect in patients with chronic bronchial sepsis. It has four components rated on a 5- point scale. The PPS components include (1) usefulness in clearing secretions ;(2) convenience; (3) comfort; and (4) overall performance. It was scored as much better(+2); better(+1); no difference(0); worse(-1); and much worse (-2)

compared with Acapella with a mean difference of 1.95ml. A recent study comparing Acapella and inspiratory muscle trainer concluded that Acapella usage produced more sputum than inspiratory muscle trainer with a mean difference of 0.70 ml11, another study on airway clearance in bronchiectasis comparing Acapella and ACBT, also proved that Acapella was effective in sputum clearance with mean difference of 4.23 ml. The present study showed that RC-Cornet is useful in clearing secretions. No patients in either group reported any Side effects from either airway clearance treatment. A great proportion of patients preferred RC-Cornet when compared to Acapella in sputum clearance, convenience, comfort and overall performance. Statistically RC-Cornet shows higher significance than Acapella in patient preference.
RC-Cornet is a modern physiotherapy device for patients in airway clearance. RC-Cornet works on the principal that at starting position the valve hose rests in a bent tube. At initial position a continuous positive pressure of about 20 cm head of water is formed. Three pressure oscillation frequencies are superimposed, a low frequency at about 20Hz, a middle frequency at 80Hz and high frequency pressure oscillation of 300Hz. On blowing the valve hose is forced into two compartments with a flexible valve at each compartment end. If on exhalation the critical pressure of the first valve is exceeded the air enters the second compartment which is still closed by its valve. Until the second valve opens, the first valve is shut again. This induces a constant PEP with superimposed pressure fluctuations.
Turning the mouth piece into positions 1-4 diagonally twists the valve hose, this gradually reduces the effectively of second valve, this explains the reduction of the static positive pressure in favour of the amplitude of the pressure oscillation. This valve sequence technology also induces a stop and go of the airflow which supports the removal of bronchial secretions 12-13 . Besides the pressure oscillation, airflow oscillations are also generated by expiration. These pressure and airflow oscillation are imparted to the bronchial tree by way of the mouthpiece, causing calibre fluctuation in bronchi and resulting in increased collateral ventilation, through the canals of Martin and Lambert and pores of Kohn. This renews entry of air into region that are collapsed or filled with bronchial mucus, thus reducing residual volume; it also activates the surfactant with its oscillation resulting in a stabilization of the bronchioalveolar system 8 . Acapella is a mucous clearing device, consisting of counterweighted plug and metal strip attached to a lever, and a magnet. Airflow oscillations are created by the breaking and reforming of a magnetic attraction by the plug as it intermittently occludes air passing through the device during expiration. The device incorporates a frequency/resistance dial that adjusts the proximity of the magnet to the metal strip, thereby regulating expiratory pressure and the amplitude and frequency of oscillations enhance airway clearance thinning of mucus through mechanical oscillation and increased expiratory flow 10 . The Acapella treatment may have assisted secretion clearance by altering rheology of the mucus and increased ciliary beat through stimulation of the ciliated epithelial cells. The oscillation frequency of Acapella (13.5Hz) is close to the cited
optimal frequency for secretion clearance (13Hz). The natural frequency of the ciliary beat is 11 to 15Hz, and if airflow oscillates at a similar frequency, this resonance may increase the amplitude of the cephaladciliary beat, which could in turn increase mucus transport. The Acapella might have increased mucus transport due to the application of resonance mechanism 6, 11 . Other mechanism is that airflow oscillation might have caused unfolding of the physical entanglements between the primary network of mucous glycoprotein and other structural macromolecules, the rupture of cross-linking bonds such as disulfide bridges, or perhaps the fragmentation of larger molecules such as DNA or F-actin, leading to decreased viscoelasticity and thereby further enhancing the mucus transport 11 . Another possible mechanism may be the variable positive expiratory pressure during Acapella treatment within the airways during expiration. This increased pressure is proposed to stabilize collapsible airways, thus increasing expiratory flow in the airways, and to recruit the collateral ventilation, allowing gas behind the secretions, thus aiding the movement of these secretions towards the oropharynx 6 . In comparison to Acapella, RC-Cornet uses the entire expired air volume to produce pressure and fluctuation vibrations. The success of the therapy depends on these vibrations, especially for patients with a low expiratory volume (FEV1). RC-Cornet when compared to Acapella has ability to oscillate even at low flow at about 2 cm of H2O were as Acapella oscillation starts at 5cm of H2O. With the RC-Cornet the patient can determine the optimal personal pressure and flow characteristics by turning the mouthpiece. Positions 1 and 2 create PEP with added pressure oscillations successfully. Positions 3 and 4 create a slowly rising pressure with a sudden pressure drop. This pressure drop is useful in shedding mucous from bronchial walls. Acapella shows no such mechanism of pressure drop, which is present in RC-Cornet. In comparison with Acapella, RC-Cornet has performed better because of slow rising of pressure followed by sudden pressure drop. Sputum volume was recorded as the primary outcome measure rather than sputum weight, as the volume provides information that establishes a short-term clinical efficacy10.The present study showed that RC-Cornet helps in clearing secretions when compared to Acapella. Previous studies have suggested that sputum volume and weight are comparable and that each gram of sputum is considered to have a volume equivalent to 1ml 10, 16 . The patient preference scale (PPS) has previously been described and used in the assessment of treatment effect in patients with bronchiectasis. It has four components rated on a 5 point scale. The PPS components include (1) usefulness in clearing secretions; (2) convenience; (3) comfort; and (4) overall performance. It was scored as much better (+2); better (+1); no difference (0); worse (-1); and much worse (-2). A recent study done on Acapella and inspiratory muscle trainer also used patient preference scale which suggested that patients preferred Acapella, in clearing secretion, convenience, comfort and overall performance11,16 . Present study showed a great proportion of patients preferred RC-Cornet when compared to Acapella in sputum clearance, convenience, comfort and overall performance. RC-Cornet produces oscillations at low flow which helps in clearing secretions. Sound produced during oscillations may be one of the reasons as it provides a feedback to the subjects. It gives the subjects an idea 145 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 about the presence of secretions there by making the subjects involved in the decision making and better convenience, comfort and overall performance. RCCornet can be used by any age subjects. The present study showed that a great proportion of subjects preferred RC-Cornet when compared to Acapella in sputum clearance, convenience, comfort and overall performance.
Study limitations The limitation of the study is the possibility of bias, as the same physiotherapist delivered both interventions and collected sputum volumes, and the single treatment design, which may not truly reflect clinical practice where treatments are incorporated over a long period of time. The study was a short term study.
Future research
- In the present study, our goal was to investigate the short term effect of RCCornet and Acapella treatment in airway clearance.
- Further studies should address the effect of long term outcome, such as frequency of hospitalization and quality of life.
- Further studies required to investigate the mechanism of mucous transport through radioactive aerosol tracer technique.
Clinical implication
Compared with other physiotherapy PEP devices used for the airway clearance, RCCornet is the most effective and comfortable device which can be used easily in the clinical setting for the patients with bronchiectasis.
CONCLUSION
this short-term study demonstrated increased sputum clearance following the use of the RC-cornet when compared to the Acapella.in addition, the RC-cornet was preferred by patients who judged that it was more useful in clearing secretions.


References:
1. Haslett C, Chilvers, Corris PA. Davidson?s principles and practices of medicine. 19th ed. Churchill Livingstone; 2002. p. 521.
2. Khanna KK, Sivakami M, Puri RK. Bronchiectasis in childhood. Indian J Pediatr 1976;43:306-12.
3. Emmons EE. Bronchiectasis. [Online]. 2011 [cited 2011 mar 9];[9 screens]. Available from: URL:http://emedicine.medscape.com/ article/296961-overview
4. Farley AH, Hendry C, Johnstone CC, Fernandes T. Bronchiectasis pathophysiology, presentation and management. Nurs Stand 2008;23:50- 6.
5. Lamari NM, Martins AL, Oliveira JV, Marino LC, Valerio N. Bronchiectasis and clearance physiotherapy: emphasis in postural drainage and percussion. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc 2006;21:206-10.
6. McCool FD, Rosen MJ. Non pharmacologic airway clearance therapies: ACCP Evidence –based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2006;129:250-9.
7. Cegla UH. Physiotherapy with oscillating PEP systems (RC-Cornet, VRP1 in COPD). Pneumologie 2000;54:440-6.
8. Celga UH, Jost HJ, Harten A, Weber T, Wissmann S. Course of severe COPD with and without 146 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 physiotherapy with the RC-Cornet. Pnumologie 2002;56:418-24.
9. Patterson JE, Bradley JM, Hewitt O, Bradbury I, Elborn JS. Airway clearance in bronchiectasis: A randomized crossover trial of Active cycle of breathing technique versus Acapella. Respiration 2005;72:239- 42.
10. Patterson JE, Hewitt O, Kent L, Bradbury I, Elborn JS, Bradley JM. Acapella versus usual airway clearance during acute exacerbation in bronchiectasis: A randomized crossover trial. Chron Respir Dis 2007;4:67-74.
11. Naraparaju S, Vaishali K, Venkatesan P, Acharya V. A comparison of the Acapella and threshold inspiratory muscle trainer for sputum clearance in bronchiectasis – A pilot study. Physiother Theory Pract 2010;26:353- 7
12. Cegla HU, Beauty M, Frode G, Werner T. Physical therapy in patients with COPD and tracheobronchial instability-comparison of 2 oscillating PEP systems(RC Cornet versus VRP1 Destin). Pneumologie 2002;56:498- 502.
13. Cegla UH, Jost HJ, Harten A, Weber T. Rc- cornet improves the efficacy of inhalation therapy with ipratropiumbromide in COPDpatients. Pneumologie 2001;55:465-9.
14. Faarc VR, Difiore JD, Chatburn RL. Performance comparison of two oscillating positive expiratory pressure device: Acapella versus flutter. Respir Care 2003;48:124-30.
15. Rayan AHA, Afifi MKM, Othman HAH, Ganady A, Mikhael BN. Evaluation of the single and combined roles of oscillating positive expiratory pressure device and conventional multimodality chest physiotherapy in mechanically ventilated COPD patients. Bull Alex Fac Med 2009;45:355-64.
16. Kaminska TM, Pearson SB. A comparison of postural drainage and positive expiratory pressure in the domiciliary management of patients with chronic bronchial sepsis. Physiotherapy 1988;74:251-4.
17. Van der schans CP, Postma DS, Koeter GH, Rubin BK. Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport. Eur respire J 1999;13:1477-86.
18. Kasper DL, Fauci AS, Longo DL, Braunwald E, Hauser SL, Jameson JL. Harrison‘s principles of internal medicine. 16th ed. New York: Mc graw-hill; 2005. p. 1541-43.
19. Frownfelter D, Dean E. Cardiovascular and pulmonary physical therapy evidence and practice. 4th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2006. p. 325.
20. Anne E, Donnell O. Bronchiectasis. Chest 2008;134:815-23
21. Prayor JA. Physiotherapy for airway clearance in adults. Eur Respir J 1999;14:1418-20
22. Morrison L, Agnew J. Oscillating devices for airway clearance in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009;1:1-30
23. Hristara A, Tsanakas J, Diomou G, Papadopoulou O. Current devices of respiratory physiotherapy. Hippokratia 2008;4:211-220
24. Douglass H, Kendall BJ. In the world of airway clearance. 2006;3:162-7
25. Tsang KW, Bilton D. Clinical challenges in managing bronchiectasis. Respirology 2009;14:637-50. 147 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011
26. Ling Su C, Ling Chiang L, Yi Chiang T, Teng Yu C, Pin Kuo H, Chyuan Lin H. Domiciliary positive expiratory pressure improves pulmonary function and exercise capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Formos Med Assoc 2007;106:204-11.
27. Lavery K, O‘Neill B, Elborn JS, Reilly J, Bradley JM. Self management in bronchiectasis: the patients perspective. Eur Respir J 2007;29:541-7.
28. Alan F, Barker AF. Bronchiectasis. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1383-93.
29. Murray MP, Turnbull K, Mac quarrie S, Hill AT. Assessing response to treatment of excerbration of bronchiectasis in adults. Eur Respir J 2008;60:239-43.
30. Prasad SA, Tannenbaum EL, Mikelsons C. Physiotherapy in cystic fibrosis. J R Soc Med 2000;93:27-36.
31. Ahmad HY, Hegele RG. COPD. Chest 1998;114:318-22
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License