IJCRR - 3(11), November, 2011
Pages: 106-115
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF HOME-BASED AEROBIC AND COMBINED AEROBIC-RESISTED EXERCISE PROGRAM ON
GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN TYPE-2 DIABETES: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL
Author: ShabariV Prem, Gopala Krishna Alaparthi, Vaishali, Vishak acharya
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background & objectives: Diabetes is a strong risk factor for premature coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease mortality. Potential maintenance strategy could be homebased
resistance training, which may foster long-term adherence through greater convenience
and flexibility. Methods: A total of 37 subjects with type 2 diabetes were recruited, 19 in experimental group (Home-based combined aerobic-resisted exercise) and 18 in control group
(aerobic exercise) by block randomization. The experimental group subjects were given brisk
walking gradually progressed to 150min/week at a moderate RPE of 12\?14 for three months
where as in control group, 3 days/week brisk walking (for 30 minutes/day) and resisted exercise
with elastic bands (30min/day) for 2 days/week for 3 months. Glycosylated haemoglobin
(HbA1c) and Diabetes Quality of Life Brief Clinical Inventory questionnaire was assessed
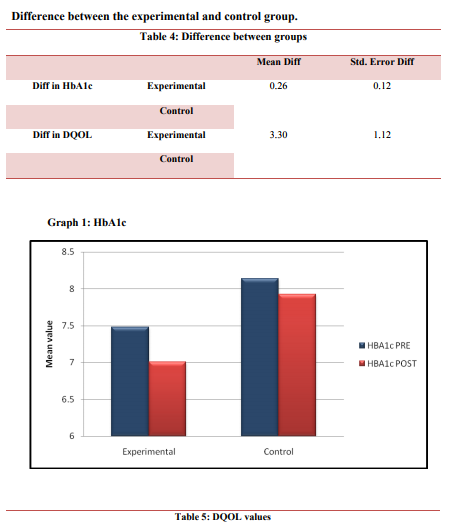
before training (i.e. 0 wk) and after 3months of training. Results: Glycosylated haemoglobin levels decreased significantly (P< 0.05) both in experimental group and control group. There
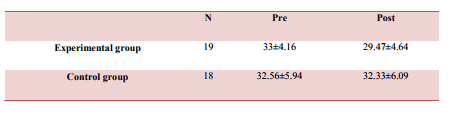
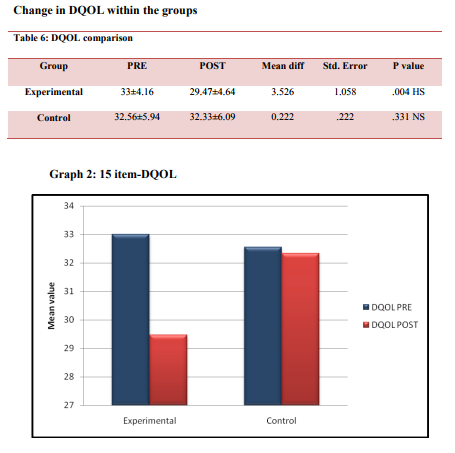
was also an improvement in quality of life on the 15-item DQOL Brief Clinical Inventory.
Conclusions: Home-based combined aerobic-resisted exercise program leads to significant
improvement in values of HbA1C and had effects that were greater than aerobic alone. There
was also an improvement in quality of life in combined group compared to aerobic training
group alone.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defective insulin secretion, insulin action or both.1 It is an epidemic, projected to affect 5.4% of world‘s adult population by 2025. 2 In India 19.4 million population is affected by diabetes and is likely to go up to 57.2million by 2025.3 This increase is alarming because diabetes is a strong risk factor for premature coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease mortality.4 Hyperglycemia causes complications such as peripheral vascular disease, neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy.5 Usually glycemic control can be assessed with fasting plasma glucose, pre-meal glucose concentration, as well as by HbA1c.6 Hemoglobin A1c value reflects overall glycemic control.4 It is a good estimate of how well the diabetes is being managed over 2 to 3 months.7 The measurement of HbA1c is the most accepted indicator of glycemic control.6 Exercise has been found to significantly decrease HbA1c levels and hence improve glycemic control to a clinically significant degree.8 Types of exercise program used in diabetes include aerobic exercise, resisted exercise, and combined aerobic-resisted exercise. 1, 4, 7, 9-14 Most trials have used supervised exercise sessions in laboratories or exercise facilities to assess the effectiveness of training programs. Because maintenance of good glycemic control is a long-term consideration,strategies to facilitate regular long-term participation in training are needed One potential maintenance strategy could be home-based resistance training, because this may foster long-term adherence through greater convenience and flexibility.15 Limited literature is available for evaluating effect of home based exercise programs on glycemic control in type-2 diabetes in India. The aim of the study was to evaluate effect of home-based aerobic and combined aerobic-resisted exercise program in improving glycemic control in type-2 diabetes.
METHODOLOGY
The study was approved by the time bound ethical committee of Kasturba Medical College under Manipal University, Mangalore, Karnataka. Subjects were recruited from the patients diagnosed with diabetes type 2 and referred for physiotherapy during August and February 2010. The purpose of the study was explained to the volunteered and interested participants and an informed consent form was obtained. Subjects were screened for inclusion with full and pain-free active range of motion of upper extremity and lower extremity, subjects who were able to walk self-paced at least for 15 minutes without any symptoms and excluded if presence of cardiac or respiratory disease, severe musculoskeletal impairment,
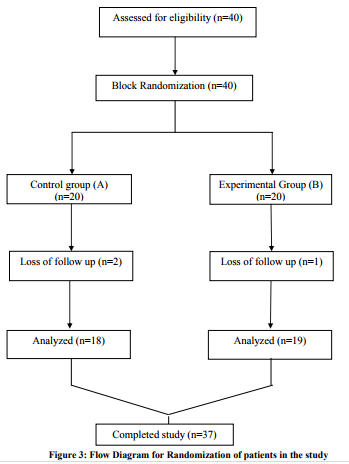
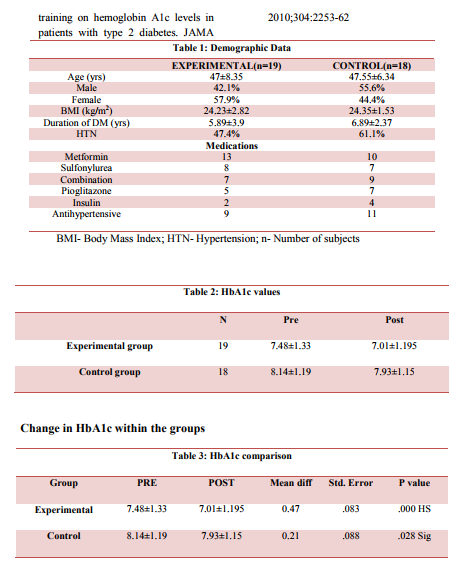
uncontrolled HTN ( baseline BP > 165/95) and vascular diseases of lower extremities. A total of forty subjects with type 2 diabetes fulfilled the inclusion criteria, out of which 37 subjects were recruited for this study, there was 1 drop out in experimental group as patient withdrew from the study and 2 subjects were excluded out of the study in control group due to lack of follow up. Consequently 19 participants in experimental group and 18 participants in control group were included. For both the groups: at the beginning of each exercise session five minutes warm up (free movements of all joints) and at the end of each session five minutes cool down was given (stretching and slow walking). Subjects in both the groups were instructed to keep a daily record of the time and date of exercise in the diary.
Group A: Subjects in this group, brisk walking gradually was progressed to 150min/week for duration of three months. Subjects were encouraged to work up to a slight sweat and a faster respiratory rate, thus working at a moderate RPE of 12–14, or ?somewhat hard‘ according to the Borg scale of perceived exertion. Group B: Subjects in this group were given 3 days/week brisk walking (for 30 minutes/day) and resisted exercise with elastic bands (30min/day) for 2 days/week at least one day gap in between was been given for 3 months. Resisted exercise program: larger muscle groups-Shoulder-abductors, shoulderflexors and extensors, elbow flexors, knee extensors, hip abductors adductors-flexorsextensors, and pectorals. Proper instructions and technique for the exercise were taught to the subjects. Each exerciser started with the lightest band and changed bands when no longer felt difficult by the end of the exercise. To aid participants with their subjective




an up regulation of mitochondrial proteins involved in respiration (citrate synthase), increased glycogen synthase activity, and increase in GLUT4 protein content. Structural adaptations from resistance training include increase in contractile protein content (hypertrophy), resulting in a higher basal metabolic rate and, therefore, potentially greater absolute glucose uptake. Aerobic exercise results in increased mitochondrial proteins and improvements in the capillary to muscle fiber ratio, thereby increasing the distribution of substrates. Finally, regional adiposity, specifically visceral and intramuscular fat stores, is directly related to insulin insensitivity via fat-specific cytokine mediated pathways, as well as a direct influence of intramyocellular fat storage on insulin receptor function within muscle tissue. Therefore, reduction in fat mass via exercise reduces the adverse influence of these factors.21 This reduction in HbA1c may be due to the increase in muscle mass that may result from resistance training could contribute to blood glucose uptake without altering the muscle‘s intrinsic capacity to respond to insulin, whereas aerobic exercise enhances its uptake via a greater insulin action, independent of changes in muscle mass or aerobic capacity. It is likely that, due to different mechanisms of action, the addition of resistance exercise to aerobic training can help achieve the targets in shorter time than achievable by isolated aerobic exercise alone.16 In a Cochrane review by Thomas DE et al ascertained that the exercise intervention significantly improved glycemic control as indicated by a decrease in glycated haemoglobin levels of 0.6%. This result was both clinically and statistically significant.8
One of the possible reasons that our results were not clinically significant (0.6%) as compared to Cochrane review could be due to the use of elastic bands for resistance training wherein the progression of resistance was difficult and also the aerobic exercise session consisted of walking. In most of the studies the modes exercise compared to our study was different, in aerobic exercise program the usual mode of exercise used were treadmill, stationary bicycles, recumbent steppers, elliptical trainers, rowing machines, whereas for resistance exercise program the modes used were dumbbells, barbells, leg press, leg curls, hip extension, chest press, latissimus pull down using weight machines. Another major limitation was that the program was a home based and not a supervised training program which could lead to reduction in adherence to exercise training volume and intensity which seem to impede the effectiveness of home-based training on glycemic control. A study by Dunstan DW et al showed that the improvement in glycemic control associated with supervised resistance training was not maintained during the home-based training.10 Our study has also showed amendment in quality of life on the 15-item DQOL Brief Clinical Inventory, the quality of life was better in the combined training group compared to the aerobic only training group. Likewise ACSM and the ADA: joint position statement also stated improvements in health-related (SF-36 physical component scores) quality of life.16 Potential mechanisms of exercise include psychological factors, such as increased self-efficacy, a sense of mastery, distraction, and changes in self-concept, as well as physiological factors such as increased central norepinephrine transmission, changes in the hypothalamic adrenocortical system, serotonin synthesis and metabolism, and endorphins. Thus regular physical activity may improve psychological well-being, health-related QOL.16 The rationale behind better improvement in QOL in combined training group compare to aerobic only training group could be because of the satisfaction with diabetes control and the amount exercise done.
LIMITATIONS One of the predicaments that were encountered in the present study was the durability of the bands, the bands tore and did not last for long and had to be change regularly, the possible reason could be the bands might have been over stretched by the subject during the exercises leading to its damage. Adherence to the prescribed intensity and volume of exercise could not be evaluated.
FURTHER RESEARCH Studies with longer duration of six to twelve months follow up with home based exercise program should be done. Comparison of elastic band exercise program with other modes like free weights, or weight machines in diabetic population can be studied. Incorporate measures to evaluate adherence to the prescribed intensity and volume of exercise at home based training to be studied.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE Adding on resistance exercise over the regular aerobic exercise leads to considerable improvement blood glucose control. An integrated exercise program with 3 days/week of brisk walking (for 30 minutes/day) and resistance exercise with elastic bands (30min/day) for 2 days/week, at least one day gap in between can be performed. Based on the results found in our study, home-based combined aerobic-resisted exercise program leads to significant improvement in values of HbA1C and had effects that were greater than aerobic alone. There was also an improvement in quality of life in combined group compared to aerobic training group alone.
References:
1. Snowling NJ, Hopkins WG. Effects of different modes of exercise training on glucose control and risk factors for complications in type-2 Diabetic patients: A Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2518-27.
2. Smith TC, Wingard DL, Smith B, Silverstein KD, Connor BE. Walking provides strong protection from cardiovascular disease mortality in older adults with Diabetes. J Clin Epidemiol 2007;60:309-17.
3. Pradeepa R, Deepa R, Mohan V. Epidemiology of diabetes in India-- current perspective and future projections. J Indian Med Assoc 2002;100:144-8.
4. Marcus RL, Smith S, Morrell G, Addison O, Dibble LE, Wahoff SD et al. Comparison of combined aerobic and high force- eccentric resistance exercise with aerobic exercise only for people with type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Phys Ther 2008;88:1345-54.
5. Amos AF, McCarty DJ, Zimmet P. The rising global burden of diabetes and its complications: estimates and projections to the year 2010. Diabet Med 1997;14:1-85.
6. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Edward SH, Lebovitz H, Reaven G, Rizza RA et al. How to diagnose diabetes and measure blood glucose control? view 2: 112 International Journal of Current Research and Review www.ijcrr.com Vol. 03 issue 11 November 2011 consensus statement: post prandial glucose. Diabetes spectrum 2001;14:71-4
7. Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Boule NG, Wells GA, Prud‘homme D, Fortier M et al. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type-2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007;147:357-69.
8. Thomas DE, Elliott EJ, Naughton GA. Exercise for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006;3:1-16
9. Misra A, Alappan NK, Vikram NK, Goel K, Gupta N, Mittal K et al. Effect of supervised progressive resistance exercise training protocol on insulin sensitivity, glycemia, lipids and body composition in Asian Indians with type-2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1282-7.
10. Dunstan W, Courten M, Shaw J, Zimmet P. High- intensity resistance training improves glycemic control in older patients with type-2 Diabetes. Diabetes care 2002;25:1729-36.
11. Ibanez J, Izquierdo M, Arguelles I, Forga L, Larrion JL, Garcia UM et al. Twice-weekly progressive resistance training decreases abdominal fat and improves insulin sensitivity in older men with type-2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28:662-7.
12. Lambers S, Laethem CV, Acker KV, Calders P. Influence of combined exercise training on indices of obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular risk in type-2 diabetes patients. Clin Rehabil 2008;22:483-92.
13. Cuff DJ, Ignaszewski A, Meneilly GS, Tildesley HD, Martin A, Frohlich JJ. Effective exercise modality to reduce insulin resistance in women with type- 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2003; 26:2977-82.
14. Maiorana A, O‘Driscoll G, Goodman C, Taylor R, Green D. Combined aerobic and resistance exercise improves glycemic control and fitness in type-2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2002;56:115-23.
15. Dunstan DW, Daly RM, Owen N, Jolley D, Vulikh E, Shaw J, Zimmet P. Home-based resistance training is not sufficient to maintain improved glycemic control following supervised training in older individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28:3-9.
16. Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Fernhall B, Regensteiner JG, Blissmer BJ, Rubin RR et al. American college of sports medicine; american diabetes association. Diabetes Care 2010;33:147-67.
17. Praet FE, van Rooij EJ, Wijtvliet A, Boonman LM, Enneking T, Kuipers H et al. Brisk walking compared with an individualized medical fitness programme for patients with type-2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Dibetologia 2008;51:736-46.
18. Rooijen AJ, Rheeder P, Eales CJ, Becker PJ. Effect of exercise versus relaxation on haemoglobin A1c in Black females with type 2 diabetes mellitus. QJM 2004;97:343-51.
19. Damush TM, Damush JG. The effects of strength training on strength and health –related quality of life in older adult women. Gerontologist 1999;39:705-10.
20. Sigal RJ, Kenny GP, Boule NG. Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2007;147:357–69.
21. Church TS, Blair SN, Cocreham S, Johannsen N, Johnson W, Kramer K et al. effects of aerobic and resistan
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License