IJCRR - 4(4), February, 2012
Pages: 10-18
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
THE EFFECT OF DEEP CRANIO-CERVICAL FLEXOR (DCCF) TRAINING ON SITTING POSTURE IN CHRONIC NECK PAIN
Author: Dharti Hingarajia
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Title: The effect of deep cranio-cervical flexor (DCCF) training on sitting posture in chronic neck pain Objectives : The purpose of this study was to investigate whether a low load DCCF training program is effective in control of sitting posture over conventional Isometric neck Exercise (INE) in subjects with chronic neck pain. Methods: Fifty female students with chronic non-severe neck pain were randomized into experimental or control group: a low load DCCF training plus conventional INE or only conventional INE respectively for 4-week exercise program. The outcome measure was control of sitting posture during 10min computer task and VAS for intensity of neck pain Results: At the end of 4th week follow-up assessment, the experimental group revealed asignificant impr ovement in control of sitting posture. Conclusion: A low load DCCF training is effective in control of sitting posture compared to isometric neck exercise in subjects with chronic non-severe neck pain.
Keywords: DCCF, Isometric Neck Exercises, Sitting Posture, Chronic neck pain
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Neck pain is relatively common complaints, especially with the inherent prolonged sedentary postures at study, work and at home.1 Chronic cervical spine disease is becoming increasingly prevalent in society. Estimations indicate that 67% of individuals will suffer neck pain at some stage of life.2 Neck pain tends to be a persistent and recurrent disorder, and up to 60% of persons can expect some degree of ongoing pain for many years following their first episode of neck pain.3 The overall prevalence of all types of chronic neck pain is higher in females. Almost every other woman, 48% have neck pain.4 Poor neck posture has been suggested to be a most common cause of chronic neck pain in younger age group, as trauma or severe degenerative conditions are found only in a few cases. Neck pain can be because of poor posture at work or study, such as leaning into computer, and during hobbies, such as hunching over workbench.5,6 Evidence is emerging that suggests that people with neck pain drift into more forward head posture (FHP) when distracted, 7 FHP is considered to be inefficient, increasing the antigravity load on the cervical structures instigating abnormal and compensatory activity by them and resulting in pain.8 FHP is a clinical entity that has been identified by multiple authors as a significant factor in a variety of musculoskeletal pain syndromes and also with significant musculoskeletal consequences. 9, 10, 11 The DCCF (longus colli and longus capitis) muscles have a major postural function in supporting and straightening the cervical lordosis and in maintenance of normal RHP 12,13 Recent studies have identified poor endurance and impaired activation of the DCCF muscles in people with neck pain.14,15,16,17 Evidences are available to prove the effect of different exercises and modalities to reduce pain and disability and improve muscle strength. Although static forward head posture is a common cause of chronic neck pain in younger age group at school, college and at work, very few studies carried out to evaluate the effect of exercise on posture maintenance. Among them Falla D et al, 2007 found that following intervention with an exercise program targeted at retraining the DCCF muscles, subjects with chronic neck pain demonstrated improved ability to maintain a neutral cervical posture during prolonged sitting. They compared low load DCCF training with endurance strength training for cervical flexors as a whole for maintenance of sitting posture.18 Isometric neck exercise (INE) is commonly prescribed by physiotherapists for chronic neck pain, the effectiveness of isometric neck exercise on pain and disability has been proved previously, 19 but there is no data available that this training is effective to maintain sitting posture. There is no sufficient data available to check effectiveness of low load DCCF training over INE on sitting posture. So there was need to study whether specific training of the DCCF muscles is required in rehabilitation or a more general NIE was sufficient to improve control of sitting posture in people with chronic neck pain.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This study was an Experimental study, conducted at the College of Physiotherapy, Anand. The experimental procedure was ethically revised and approved by the Research and Ethical committee of College of Physiotherapy, Anand. (Annexure-1).
This study constitutes the double blinded randomized controlled trial devoted to analyze the effectiveness of the low load craniocervical flexor training on sitting posture in people with chronic neck pain. Sample size of the study was 50. 25 subjects being in each group after randomization with age between 15 to 30 years. The study population covers the female students of College of Physiotherapy, Anand and were recruited according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned below.
Inclusion criteria:
1. Subjects with a history of chronic (between 3 months to 5 years), non severe (≤7cm on VAS) neck pain.
2. Only female students of college of physiotherapy, Anand.
3. The subjects who scored ≤15 (out of possible 50) on Neck Disability Index (NDI).
Exclusion criteria:
1. Subjects having significant history related to cervical spine i.e. trauma, surgery, any congenital deformity or neurological signs.
2. Subjects who participated in a neck exercise program in the past 12 months.
After meeting suitable criteria, the written informed consent (Annexure-2) was obtained from each subject after explaining the details of various non-invasive tests and training to be conducted and baseline measures had been measured before allocating them into two groups.
Outcome measures:
1. Sitting posture analysis:
Subjects were positioned in front of the computer in sitting with their knees in 90 degrees of flexion and their feet flat on the ground. A plumb line was positioned in the background. The starting position was standardized by placing the subject in an upright posture, which was defined as a vertical pelvic position (no anterior or no posterior tilt) with the assumption of a lumbar lordosis and thoracic kyphosis. (Figure-1A) Subjects were asked to maintain the position while they were distracted by playing the game of solitaire on the computer for 10minutes. Subjects used the mouse with their right hand and the left hand rested motionless on the desk in front of them.

Cervical and thoracic posture was measured at the beginning and at the end of the 10 minute computer task from a lateral photograph taken with a digital camera (Canon Digital IXUS 1600×1200 pixels) positioned on a tripod at a distance of 0.8 m. the axis of the lens of the camera was placed orthogonal to the sagittal plane of the patient at a height that corresponded with the seventh cervical vertebra. Markers were positioned on the tragus of the ear and spinous processes of the seventh cervical and seventh thoracic vertebrae. (Figure-1B). The digital technique used to quantify angular displacement in this study has been previously described. The technique has been shown to produce reliable angular measurements (intra class correlation coefficient [ICC] (2, 2) > .93) and the criterion validity of the technique has been established when compared to the universal goniometer by no significant mean absolute difference between the 2 measurement techniques. The angle of forward head posture was measured from a line drawn from the tragus of the ear to the seventh cervical vertebra subtended to the horizontal. The software produced a horizontal line perpendicular to the vertical plumb line captured in the background of the image. Thoracic posture was calculated as the angle between the horizontal line and a line drawn between the seventh cervical spinous process and the seventh thoracic spinous process.(figure-1C) Changes in angles from an erect starting posture (time 0) to the angles measured after 10-minute task were calculated and expressed relative to the angle at time0.
2. Pain Intesity was measured by using Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and subjects were asked to tick their perceived pain intensity at that moment.
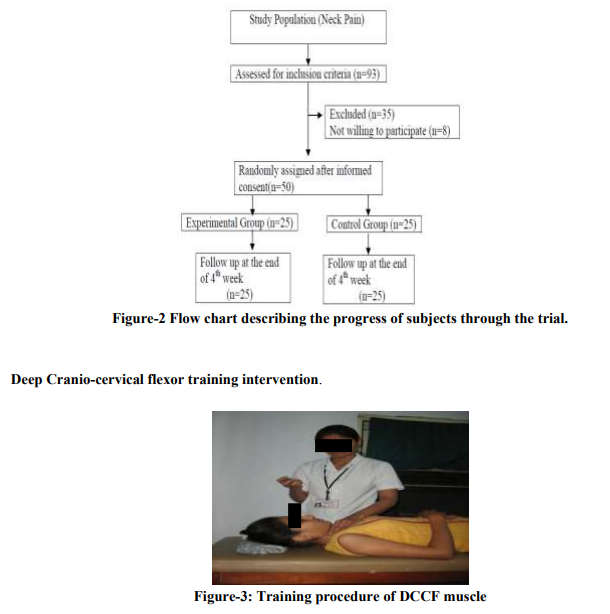
Following baseline measurements, the subjects with chronic neck pain were randomized into experimental and control groups: a training regimen of the deep craniocervical flexor muscle training plus neck isometric exercise regimen and only neck isometric exercise regimen respectively. The allocation sequence was generated by using 2×2 random table; the progression of subjects through the exercise trial is illustrated below. (Figure-2)
Exercise Regimens: The exercise regimen was conducted over a 4- week period and subjects in each group received personal instruction and supervision by an experienced physical therapist twice per week for the duration of the trial. None of the exercise sessions were longer than 30 minutes. Subjects were asked not to receive any other specific intervention for their neck pain. All subjects were requested to practice their respective regimen twice per day for the duration of the task. The exercises were performed without any provocation of neck pain.
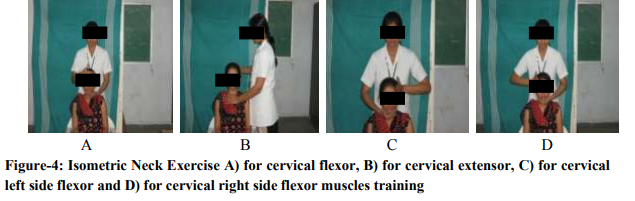
Training of the deep craniocervical flexor muscles followed the protocol described, by Jull et al. The exercise targets the deep flexor muscles of the upper cervical region, the longus capitis and longus colli muscles, rather than the superficial flexor muscles, the sternocleidomastoid and anterior scalene, which flex the neck but not the head. In addition, the exercise is a low-load exercise in nature to more specifically train the deep cervical flexors, rather than the neck flexors as a whole, which occurs in a head lift exercise. The exercise used a roll of towel which was placed suboccipitally to monitor the subtle flattening of the cervical lordosis that occurs with the contraction of the longus colli muscle. Subjects were instructed to "gently nod their head as though they were saying 'yes'." The physical therapist identified the target level that the subject could hold steadily for 10 seconds without resorting to retraction, without dominant use of the superficial neck flexor muscles, and without a quick, jerky craniocervical flexion movement. Contribution from the superficial muscles was monitored by the physical therapist in all stages of the training using palpation (Figure-3) Training was commenced at the level which the subject could achieve with a correct movement of craniocervical flexion and without dominant use or substitution by the superficial muscles (sternocleidomastoid, hyoid, and anterior scalene muscles). The subjects were taught to perform a slow and controlled craniocervical flexion action. They then trained to be able to sustain progressively increasing ranges of craniocervical flexion. At each level patient asked to perform 3 sessions of 10 repitions with 10 seconds hold with the 1min rest between the sessions.
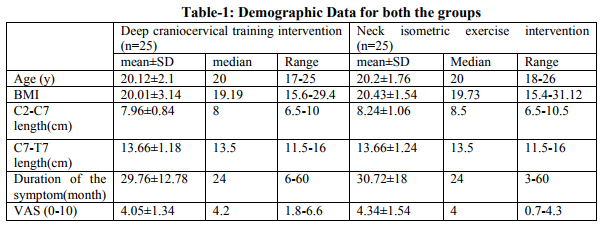
Neck – isometric exercise regimen: In upright sitting position subject was asked to perform a single series of 15 repetitions with 10 seconds hold of isometric exercises for cervical flexors, extensors and left and right side flexors (Figure-4 A,B,C and D). Resistance provided at right angle from the plan of the movement by the therapist‘s one hand placed on forehead for flexion, back of the head for extension and on the sides of the head, just above the ear for side flexions. Patient was asked to place their own hand instead of therapist for home exercise. Resistance applied was judged and progressed every weekly according to patient capacity.
Both the outcome measures were assessed in the week immediately after the 4-week intervention period for both the groups.
STATISTICAL METHODS
Of the 50 participants with neck pain who participated in the study, none were lost to follow up assessment at the end of the study. All participants in the experimental group and control group received the full 8 treatments and performed their respective exercise at home twice daily, measured by home exercise record diary. No patients reported any adverse events. Unpaired t tests were used to find out homogeneity of two groups for all the parameters at baseline and to compare the outcome measurement data between two groups after 4-week intervention. Paired t tests were conducted to determine whether sitting posture (cervical and thoracic angle) and Pain intensity (VAS) were significantly different before and after the intervention. Each calculated t-value is compared with ttable value to test one tailed hypothesis at 0.005 level of significance. Data analysis software SPSS 13.0 version has been used for the data analysis of the present study.
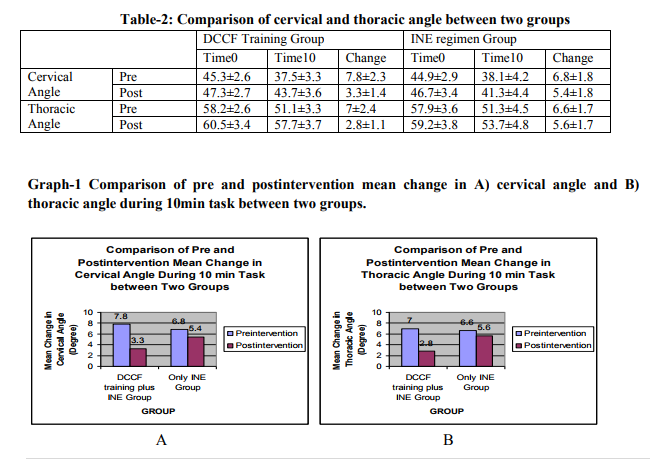
Subject‘s descriptive data is presented in table- 1. All the descriptive data for both the experimental and control groups were homogenous for all possible confounding factors at baseline. There were no co-relation found between these parameters and cervical and thoracic angle at baseline and at the end of the study. After 4-week intervention program both the groups showed significant reduction in change of cervical and thoracic angle during 10min computer task compared with pre-intervention measurement. However after intervention the experimental group showed significantly higher reduction in change of cervical and thoracic angle during 10min computer task compared with the control group. (Table-2)
After 4-week intervention program both the groups showed statistical significant reduction in pain intensity. Mean± S.D of intensity of pain (VAS) preintervention for experimental group was 4.05±1.3 and for Control group was 4.3±1.5.
DISCUSSION
Following a 4-week intervention with either DCCF training plus INE or only INE, the participants with neck pain improved their ability to maintain an upright posture of the cervical and thoracic spine however; the group who received additional specific training targeting DCCF muscle has significantly more improvement than that of the only INE group subjects. DCCF training involves performing and holding inner range positions of craniocervical flexion, the anatomical action of the deep cervical flexor muscles. This training has been shown to increase the activation of these muscles.20 The improved ability to maintain an upright position of the cervical and thoracic spine, which was observed for the experimental group, is a direct reflection of an improved endurance of the DCCF muscles, which was also increased in this group. This improvement occurred even though there was no exercise instruction on postural correction in sitting. This finding supports that inadequate control of the head in prolonged sitting may be a functional correlate of deep cervical muscle impairment. Moreover, craniocervical flexion directly activates the deep cervical flexor musculature, 21,22 which have a relatively high density of muscle spindles.18 Improved cervical kinesthetic sense following craniocervical flexor training23 also may explain the improved ability to maintain an upright position of the cervical spine. It is notable that the only INE regimen did not influence postural parameters of the cervical and thoracic spine. Although there is some evidence to suggest that an strength regimen for the neck flexor muscles reduces neck pain,18,40,41 improves strength, 18,41 and reduces fatigue of the sternocleidomastoid and anterior scalene muscles,18 it does not appear to improve the ability to maintain an upright posture of the cervical and thoracic spine in a sitting task. Sitting posture and DCCF endurance is directly related but no relationship was found between sitting posture and strength of DCCF. Only INE improved the strength of the cervical muscles while DCCF training improved the endurance of DCCF muscles and hence the sitting posture as the DCCF have a predominantly stabilizing role providing a holding mechanism to maintain balance and stability for the head. The maintenance of cervical and thoracic postural angle with the craniocervical flexor training during the 10-minute distraction task reached statistical significance when compared with the only INE regimen. The magnitude of change in cervical and thoracic posture during 10min computer task following craniocervical flexion training is similar to the magnitude of difference observed in the asymptomatic subjects in previous study.44, 64 .
CONCLUSION
This study concluded that following intervention with an exercise program targeted at retraining the deep craniocervical flexor muscles and isometric neck exercise, subjects with chronic neck pain demonstrated improved ability to maintain a neutral cervical and thoracic posture during sitting compared with only isometric neck exercise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
There are no words to gratitude sufficient enough to thank my honorable guide Prof. C.G. Padole, Principal, College of physiotherapy, Anand, who inspired me to undertake study related to postural problem in chronic neck pain and helped me choose such a valuable topic for my dissertation. He was always willing to answer all my questions through out my study, without his direction, support and encouragement this work would not have been possible. I am thankful to ?Research Ethical Committee? of College of physiotherapy, Anand, for granting me permission to commence on the thesis. I am also thankful to my institute to providing me an opportunity to carry out research on the students who suffer from chronic neck pain and providing internet excess. I am greatly thankful to all the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. I am also grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. My heartfelt thanks are due to my parents for supporting and encouraging me to pursue this work, their encouragement and love supported me throughout the study. Last but not the least I am thankful to all my subjects who participated with full cooperation and showed voluntary interest, without them this study would not have been possible. Finally I am thankful to all those who directly or indirectly contributed to this study.
References:
1. Jull G: Diagnosis of cervical disorders: exploring a mechanistic approach: Hong Kong. Phys. J. 2004; 22:2-6.
2. Côté P, Cassidy J D, Caroll L, Kristman V. The annual incidence and course of neck pain in the general population: a population-based cohort study. Pain 2004; 112: 267-273
3. Gore D, Sepic S, Gardner G, et al. Neck pain: a long-term follow-up of 205 patients. Spine 1987;12:1–5.
4. Michel G., Christer H. et al; ?The prevalence of neck pain-A populationbased study; Acta Orthop Scand 2002; 73 (4): 455–459
5. Fichground JS. Neck Pain. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Monograph Series 27. 2004.
6. Greigel Morris P, Larson K, Mueller Klaus K et al. Incidence of common postural abnormalities with pain in two age groups of healthy subjects. Phys Ther, 1992:72, 6:425-431
7. Szeto GP, Straker LM, O'Sullivan PB. A comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic office workers performing monotonous keyboard work, 2: neck and shoulder kinematics. Man Ther. 2005;10: 281-291
8. Janda V. Muscle and cervicogenic pain syndromes. In:Grant R.Physical therapy for cervical and thoracic spine.2ed.clinics in Physical Therapy. Vol.17,1988. Churchill Livingstone Inc. p195-216
9. Braun BL. Postural differences between asymptomatic men and women and craniofacial patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabill,1991: 72:653-6
10. Hertling D, Kessler RM. Management of common musculoskeletal disorders, Physical Therapy Principles and Methods. 3ed, 1996. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins
11. Hanten WP, Olsen SL, Russell JL et al. Total head Excursion and Resting Head Posture – normal and patient comparisons. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2000:62-6
12. Mayoux-Benhamou MA, Revel M, Vallee C, et al. Longus colli has a postural function on cervical curvature. Surg Radiol Anat. 1994;16:367-371.
13. Vasavada AN, Li S, Delp SL. Influence of muscle morphometry and moment arms on the moment-generating capacity of human neck muscles. Spine. 1998;23: 412-422.
14. Falla DL, Jull GA, Hodges PW. Patients with neck pain demonstrate reduced electromyographic activity of the deep cervical flexor muscles during performance of the craniocervical flexion test. Spine. 2004;29:2108-2114.
15. Falla D, Jull G, Hodges PW. Feed-forward activity of the cervical flexor muscles during voluntary arm movements is delayed in chronic neck pain. Exp Brain Res. 2004; 157:43-48.
16. Darnell MW. A proposed chronology of events for forward head posture. J craniomandibular Pract, 1983: 1: 50-4.
17. Gelb H. new concept in craniomandibular and chronic pain management. 1ed, 1994. Times mirror international Publishers Ltd, Mosby – Wolfe
18. Falla D, full G, Russell T, et al. Effect of neck exercise on sitting posture in patients with chronic neck pain. Phys Ther. 2007;87: 408-417
19. Jari Ylinen, Esa-Pekka Takala, Matti Nykänen, et al; Active Neck Muscle Training in the Treatment of Chronic Neck Pain in Women JAMA. 2003;289:2509-2516
20. Jull G, Falla D, Hodges P, et al. Cervical flexor muscle retraining: physiological mechanisms of efficacy. Paper presented at: 2nd International Conference on Movement Dysfunction; September 23-25, 2005; Edinburgh, Scotland.
21. Falla D, Bilenkij G, Jull G. Patients with chronic neck pain demonstrate altered patterns of muscle activation during performance of a functional upper limb task. Spine. 2004;29:1436-1440.
22. Falla D, Jull G, Dall' Alba P, et al. An electromyographic analysis of the deep cervical flexor muscles during craniocervical flexion. Phys Ther. 2003;83:899-906.
23. Jull G, Falla D, Treleaven J, et al. Retraining cervical joint position sense: The effect of two exercise regimes. J Orthop Res. 2006 Dec1
24. Grimmer K. The relationship between cervical resting posture and neck pain. Physiotherapy. 1996;82:45-51.
25. Jull G, Barrett C, Magee R, Ho P. Further clinical clarification of the muscle dysfunction in cervical headache. Cephalalgia 1999;19(3):179–85.
26. Szeto GP, Straker L, Raine S. A field comparison of neck and shoulder postures in symptomatic and asymptomatic office workers. Appl Ergon. 2002;33:75-84.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License