IJCRR - 4(8), April, 2012
Pages: 43-48
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
IS SKELETAL MUSCLE \"A TARGET ORGA\" IN LONG TERM UNCONTROLLED DIABETES MELLITUS? A
COMPARATIVE AND CORRELATIVE STUDY OF TYPE I AND TYPE II DIABETES
Author: Prathamesh Haridas Kamble, Sunil Bhamre
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and Objective: Diabetes Mellitus is the most common endocrinal disorder worldwide. Long term uncontrolled diabetes is associated with complications of eyes, kidney, heart, blood vessels and nerves. Studies have been carried out to see the effect of diabetes on skeletal muscle strength but the results are conflicting; while very few studies have considered the muscle endurance. Moreover, the correlation of glycosylated haemoglobin levels (HbA1c) with handgrip strength (HGS) and hand grip endurance (HGE) has not been studied. So the present study was carried out in 100 type I diabetics and 164 type II diabetics to compare the HGS and HGE with 100 and 160 normal healthy non diabeticsubjects respectively. Also the objective of this study was to determine the relation of HbA1c with HGS and HGE. Research Methodology: HGS and HGE were measured using Handgrip dynamometer. HbA1c was assessed by cation - exchange resin method using Monozyme's Glycohemin kit on Transasia's semiautoanalyzer. Outcome of Study: Results of the study showed that type I & II diabetics had significantly lower HGS than non diabetics. HGE was lower in type II diabetics while it was significantly higher in type I diabetics as compared to controls. This study also indicated that HGS and HGE had no significant correlation with HbA1c. Thus present study reveals that uncontrolled diabetics are at a risk of decreased muscle strength and endurance and the magnitude of affection is highly individual specific. Thus there is a need for development of strategies in the form of strict glucose control and resistant training exercise program to slow or prevent rapid decline in muscle function in diabetics.
Keywords: Handgrip strength, Handgrip endurance, glycosylated haemoglobin, diabetes.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is the most common endocrine disorder. It is a syndrome of impaired carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism which is characterized by hyperglycemia caused by either reduced insulin secretion or decreased sensitivity of tissues to insulin. The worldwide prevalence rate of Diabetes Mellitus (DM) for all ages was about 2.8 % in 2000 and projected to be 4.4 % in 2030 [1]. The chronic hyperglycemia and its associated metabolic deregulation, is associated with potential long term complications that can affect various tissues like kidney, eye, heart, blood vessel and nerve. [2] There is a new concept to explain these long term complications of DM called as ?hyperglycemic memory‘ which proposes that if a cell remains in hyperglycemic environment for certain duration, then it adapts to work in the hyperglycemic state. [3] Meticulous control of blood glucose can decrease the symptoms and improve the diseased condition. Even after the return of plasma glucose to normal or near normal level, the progression of long term diabetic complications still continues. [4] Thus, measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), which provides the information about the average blood glucose concentration over preceding 6-8 weeks, is a good indicator of long term complications of diabetes mellitus. The possibility that the skeletal muscle is also a target organ for diabetic complication was suggested by Sayer A A et al who found reduced muscle strength and impaired physical function in Type 2 diabetes. [5] There have been many studies of handgrip strength in diabetic patients with conflicting results. Many reports have suggested possible patho-physiological mechanism also. Reduction in handgrip strength is generally found in diabetics. [6, 7, 8] It seems that reduction in handgrip strength has a linear relationship with severity of diabetes which in turn is in linear relationship with functional ability of daily living activities. However, at the present time there are no reports of functional limitations in daily activities ascribable to diabetes. The present study attempts to compare handgrip strength and handgrip endurance in type I, type II diabetics and normal subjects (controls), to evaluate whether there is any correlation between glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and magnitude of reduction in hand grip strength and endurance in type I and type II diabetic patients.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The present study was carried out in the diabetic clinic in Indira Gandhi Government Medical College and Mayo hospital, Nagpur. The Institutional Ethics Committee approved the study. The study was divided into two groups: A) Group I, B) Group II.
A) Group I: Based on detailed history and physical examination, subjects were further divided into two sub-groups: (i) Type I diabetic group: Comprised of 100 male subjects in the age group of 31-45 years, having duration of diabetes between 5-10 years, regularly visiting the diabetic clinic and taking regular insulin therapy, were selected. (ii) Control I group: For comparison, a separate group of 100 healthy subjects, with no history of diabetes or disorder of defective sugar metabolism, was selected. They belonged to the same age group and nearly had the same height, built, socioeconomic status and ethnic group, as that of type I diabetic group subjects.
B) Group II: Similarly, on the basis of detailed history and physical examination, subjects were further divided into two sub-groups (i) Type II diabetics group: 164 males, belonging to age group of 41-55 years, having duration of diabetes between 5-10 years, regularly visiting the diabetic clinic and taking only oral anti diabetic drugs regularly, were included. (ii) Control II group: A group of 160 healthy non diabetic male subjects in the age group of 41-55 years and having nearly the same height, weight, built, ethnicity and socioeconomic status were selected. Subjects, who were left handed, involved in regular handgrip exercise or constant method of working with handgrip or suffering from asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, congestive cardiac failure, Myasthenia gravis and hypothyroidism, were excluded from the study. Also factors that interfere with HbA1c test results like diagnosed cases of hyperbilirubinemia and chronic alcoholism were excluded from the study. After selection, written informed consent was obtained from all the participants. Then anthropometric measurements like standing height and weight were taken. Early morning 5 cc fasting blood sample was obtained under all aseptic precautions. Serum was separated and fasting blood sugar and glycosylated haemoglobin levels (HbA1c %) were estimated. Blood sugar levels were assessed by glucose oxidase biosensor method using glucometer and glycosylated haemoglobin levels (HbA1c %) were assessed by cation - exchange resin method using Monozyme‘s Glycohemin kit on Transasia‘s semiautoanalyzer. Handgrip strength was determined by using handgrip dynamometer. The use of this instrument was illustrated to participants prior to testing. Handgrip dynamometer was given in the right hand of subjects in standing position and arm by their side, not touching the body and were asked to squeeze the dynamometer with as much force as possible, taking care to squeeze only once for each measurement. 3 trials were performed with a pause of about 10- 20 seconds between each trial to avoid the effect of fatigue. Best amongst the 3 measurements was noted. The handgrip endurance was also measured. The subjects were asked to maintain 80% of their handgrip strength for as long as they could and time in seconds was recorded using a stop watch.
STATISTICAL METHODS
The statistical analysis of observations was carried out. Mean and standard deviation were calculated and significance of difference was tested statistically by the unpaired student‘s ?t test? at P ≤ 0.05. Correlation coefficient (r) was calculated and tested for statistical significance.
RESULTS
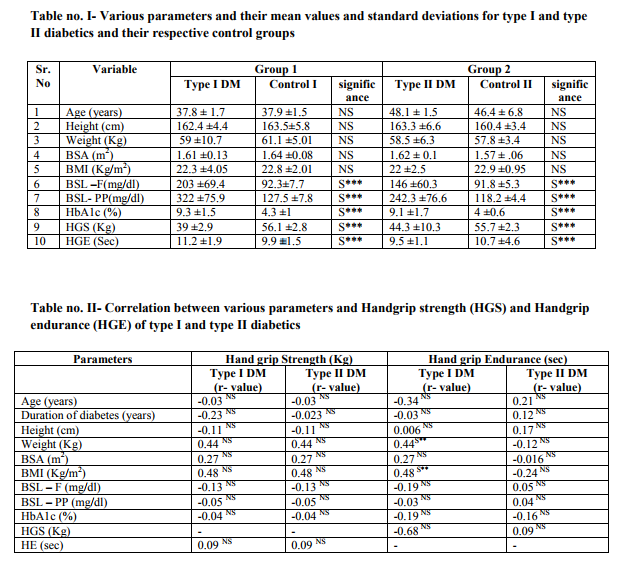
Table no. 1 shows the various parameters and their mean values and standard deviations for both type I diabetics and type II diabetics and their respective control groups. The mean age of Group 1 (type I DM and control I) was 37.8 years and 37.9 years, while for Group 2 (type II DM and control II) it was 48.1 and 46.4. There was no significant difference in the age of Group 1 and Group 2. Thus both the groups were age matched. There was no significant difference in height, weight, BSA and BMI; indicating that the groups were homogenous in this respect. Fasting and post meal blood sugar levels were higher in type I and type II diabetics than respective controls. For HbA1c the normal reference value is < 6 %. [4] It was observed that for both type I and type II diabetics, HbA1c was on a statistically higher side than controls indicating poor control of long term blood sugar levels. The handgrip strength (HGS) was significantly lower in type I and type II diabetics as compared to controls. Handgrip endurance (HGE) was significantly higher in type I diabetic subjects as compared to controls, while for type II diabetics, HGE was lower than the controls. Table II depicts the correlation of Handgrip strength and Handgrip endurance with various parameters. It indicated that there was no statistically significant correlation existing between HGS and HGE with any of the parameters of present study for both Group I and Group II diabetics. This shows that the magnitude of skeletal muscle strength and endurance changes produced due to uncontrolled diabetes were based upon individual susceptibility of subjects.
DISCUSSION
The present study has demonstrated that both type I and type II diabetic subjects had lesser muscle strength than non diabetics. This finding is consistent with the findings of Park SW [6], Savas S [7] and Lord SR [8].The probable explanations for this finding are: (1) diabetes is associated with increased systemic inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-6. These cytokines have a detrimental effect on muscle function. [9,10, 11] (2) Uncontrolled diabetics are associated with glycation of skeletal muscle proteins such as actin and myosin leading to a significant reduction in vitro speed of actin and myosin filament. [12] (3) Cotter M 1989 [13], Klueber KM 1989 [14] and Medina -Sanchez M 1991 [15] demonstrated a significant and selective atrophy of type II b fibers in diabetic rats although this mechanism remains unclear in human (4) As suggested by Anderson H 1996 [16] motor neuronal neuropathic processes give rise to peripheral neuropathy which might be associated with decreased muscle strength in type I and type II diabetic subjects, and (5) long term uncontrolled diabetes leads to metabolic consequences like muscle protein catabolism and inadequate energy use, which results in potential reduction in muscle strength. Handgrip endurance in the present study was significantly longer in type I diabetics than non diabetics, while for type II diabetics it was significantly shorter than the controls. Though the mechanism of this finding is unclear in humans, in experimental diabetic rats it has been demonstrated that prolonged increased or decreased blood insulin levels lead to a change in the composition of muscle fiber type. Hypoinsulinemia shifts the muscle fiber composition towards red muscle fiber also known as fatigue resistant fibers [10, 11] and hyperinsulinemia induces an increase in the number of white muscle fibers which are least fatigue resistant. Thus due to hypoinsulinemia seen in type I diabetics, there is an increased proportion of fatigue resistant red muscle fibers which might be responsible for increased handgrip endurance in them. While type II diabetes is a condition characterized by insulin resistance and high blood insulin levels. So this prolonged hyperinsulinemia induced-easy fatigable white muscle fiber composition of in case of type II diabetics, might be the reason for their lower endurance as compared to non diabetics. In the present study, there was no linear correlation of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c %) with handgrip strength and handgrip endurance for both type I and type II diabetics. These findings suggest that in uncontrolled diabetics skeletal muscle weakness is produced but the magnitude of affection depends upon individual subject's susceptibility to the glycemic changes as well as the irregularities in the treatment compliance of each subject. Thus considering these two factors the linear correlation might not have been observed.
CONCLUSION
From the present study it is clear that if the blood sugar level in diabetics remains uncontrolled then they are at risk of decreased skeletal muscle strength and its magnitude of affection is highly individual specific. It is important because the accelerated loss of muscle strength may lead to functional limitation and physical disability and morbidity. We need to develop strategies to slow or prevent rapid declines in muscle function in high risk population of adults with diabetes to decrease morbidity. Every potential way such as strict glucose control and resistive training exercise programs should be introduced.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Rathmann W, Giani G. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27(10):2568-9.
2. Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998; 15(7):539- 53.
3. Wright A. Metabolic memory in type 1 diabetes. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 1998; 9:254-257.
4. Foster DW. Diabetes Mellitus. In: Fauci AS, Martin JB, Kasper DL, Hauser S. (eds), Harrison‘s Principles of Internal Medicine. 2011. Volume 2, (pp.2078-2080.) New York; McGraw Hill.
5. Sayer AA, Dennison EM, Syddall HE, Gilbody HJ, Phillips DIW, Cooper C. Type II Diabetes, muscle strength and impaired physical function. Diabetic Care. 2005; 28 (10): 2541-2542.
6. Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Strotmeyer ES, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Schwartz AV, et al. Decreased muscle strength and quality in older adults with type 2 diabetes: the health, aging, and body composition study. Diabetes. 2006; 55(6):1813-8.
7. Savas S, Koroglu BK, Koyuncuoglu HR, Uzar E, Celik H, Tamer NM. The effects of the diabetes related soft tissue hand lesions and the reduced hand strength on functional disability of hand in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007; 77(1):77-83.
8. Lord SR, Caplan GA, Colagiuri R, Colagiuri S, Ward JA. Sensori-motor function in older persons with diabetes. Diabet Med. 1993; 10(7):614-8.
9. Temelkova-Kurktschiev T, Henkel E, Koehler C, Karrei K, Hanefeld M. Subclinical inflammation in newly detected Type II diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia. 2002; 45(1):151.
10. Visser M, Pahor M, Taaffe DR, Goodpaster BH, Simonsick EM, Newman AB, et al. Relationship of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha with muscle mass and muscle strength in elderly men and women: the Health ABC Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2002; 57(5):M326-32.
11. Helmersson J, Vessby B, Larsson A, Basu S. Association of type 2 diabetes with cyclooxygenase-mediated inflammation and oxidative stress in an elderly population. Circulation. 2004; 109(14):1729-34.
12. Ramamurthy B, Hook P, Jones AD, Larsson L. Changes in myosin structure and function in response to glycation. FASEB J. 2001; 15(13):2415-22.
13. Cotter M, Cameron NE, Lean DR, Robertson S. Effects of long-term streptozotocin diabetes on the contractile and histochemical properties of rat muscles. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989; 74(1):65-74.
14. Klueber KM, Feczko JD, Schmidt G, Watkins JB 3rd. Skeletal muscle in the diabetic mouse: histochemical and morphometric analysis. Anat Rec. 1998; 225(1):41-5.
15. Medina-Sanchez M, Rodriguez-Sanchez C, Vega-Alvarez JA, Menedez-Pelaez A, Perez-Casas A. Proximal skeletal muscle alterations in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: a histochemical and morphometric analysis. Am J Anat. 1991; 191(1):48-56.
16. Andersen H, Poulsen PL, Mogensen CE, Jakobsen J. Isokinetic muscle strength in long-term IDDM patients in relation to diabetic complications. Diabetes.1996; 45(4):440-5.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License