IJCRR - 4(11), June, 2012
Pages: 90-96
Date of Publication: 18-Jun-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYLTRANSFERASE (GGT) IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS AND ITS RISK FACTORS
Author: Shrawan Kumar Meena, Alka Meena, Jitendra Ahuja, Vishnu Dutt Bohra
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective \- To study the Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), other liver derived enzymes and
lipid profile in patients of type 2 Diabetes mellitus (DM) and find out the any correlation of liver derived
enzymes with diabetic related risk factor and association between enzyme level and blood sugar level in
diabetic and non diabetic subjects. Research Design and Methods\- This is a cross-sectional
prospective study in 60 cases of type 2 DM randomly selected from medical wards of a tertiary care
hospital and 30 age, sex matched controls. Blood sugar, Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), otherliver enzymes like SGOT, SGPT, ALP, Lipid profile, BMI, waist circumference and prevalence of
obesity and hypertension were assessed. To define the type 2 Diabetes mellitus (DM) we used revised
criteria of ADA, 1997. Results\- GGT, Fasting Blood glucose and BMI increased statistically significant
(p< 0.00l) in type 2 DM subjects when compared with the control subjects. Statistically significant difference (p< 0.05) in SGPT was found in subjects of type 2 DM. Comparison of other parameters like
BP, alkaline phosphates, PL, TG and VLDL were also found Statistically significant difference (p< 0.01).
Conclusions\- serum GGT level within its normal range predicted type 2 diabetes mellitus and may alter
the association between body mass index, lipid profile and type 2 DM.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is located on the external surface of most cells and mediates the uptake of glutathione. It has been found as a useful indicator of an early liver cell damage or Cholestatic disease, due to alcohol consumption. (1) In addition to its diagnostic uses serum gammaglutamyltransferase (GGT) has substantial epidemiological significance(2).Prospective studies have shown a significant relationship between serum GGT and the development of specific conditions including coronary heart disease(CHD) and stroke(3,4). In addition to alcohol, obesity has been found (5) to have a major effect on serum GGT and there is increasing evidence (5-8) that linking raised serum GGT levels with other metabolic disturbance such as glycemic disorders, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL cholesterol.Non alcoholic fatty liver disease obesity, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia (9) are also closely associate with elevated serum GGT. These interrelations between Serum GGT with obesity and other metabolic disturbance raise the possibility – which elevated Serum GGT levels can help in predicting the development of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore serum GGT showed a strong and graded relation with diabetes which suggested a role of GGT in the pathogenesis of diseases (2,9,11).Now ,it is clear from several studies conducted in past decades the raised Serum GGT serves has an independent predictor for type 2 diabetes mellitus.(2,6,8,10,11). Keeping this in mind the present study was planned to evaluate the role of GGT in Diabetes. In Indian population such study was not conducted so far. Indians has specific diabetic phenotype which predisposes them to diabetes even earlier than other populations.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
This study were carried out on randomly selected 60 type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects in age from 35 to 65 years visiting out patients department of endocrinology and general medicine of a tertiary level hospital. A comparison was done with 30 age, sex; socioeconomic status matched healthy subjects serving as control. The questionnaire included age, gender, family history of DM, hypertension and stroke, food habit and physical, activity, social status, history of medication and history of alcohol intake. Anthropometric measurements like BMI, waist circumference were recorded as they are two important predisposing factors for development of insulin resistance.
Sample collection:
Blood sample drawn from anticubital vein in plan via from all subjects after overnight fast of 12-14 hours.Sample was analyzed for sugar, bilirubin, enzymes and lipids.
1. Subject (Case) selection:-
(a) Inclusion criteria: Subjects having fasting blood sugar level >126 mg/dl or subjects on medication for DM. (b) Exclusion criteria: alcohol abuse, obstructive liver disease, hepatitis and presence of any malignancy.
2. Control selection:-
(a) Inclusion criteria: (a) Subjects having fasting blood sugar level 0.05 was taken as insignificant < 0.05 as significant and <0.001 as highly significant. Coefficient of correlation ?r? was determined between two comparable groups with help of SPSS package.
RESULTS
The present study was carried out in department of biochemistry at SMS hospital on randomly selected 60 previously diagnosed patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus and 30 age and sex matched healthy volunteers served as control and assessed correlation of GGT and other risk factors.

Abbreviations :BMI –body mass index, SBP-Systolic blood pressure, DBP-Diastolic blood pressure, SGOT-Serum glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase, SGOT-Serum Glutamate Pyruvate Ttransaminase, ALP-Alkaline phosphatase, PL-phospholipids, TG-triglycerides, HDL-high density lipoprotein, Low density Lipoprotein, VLDL-very low density lipoprotein, GGT- Gamma-glutamyltransferase. Table no. 1 shows that a high value of serum GGT in type 2 DM subjects statistically highly significant (p < 0.001) when compare with the control group. Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) in BMI was found in subjects of DM 2 when compared with normal subjects. BP was also found statistically significant (p< 0.01) in diabetic patient on comparison with controls. Fasting blood glucose was come across statistically significantly different (p < 0.001) between case and control. SGPT is another liver marker which was statistically significantly different (0.05) between case and control groups. Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) in alkaline phosphatase, PL, TG and VLDL were obtained in subjects of type 2 DM when compared with normal subjects.
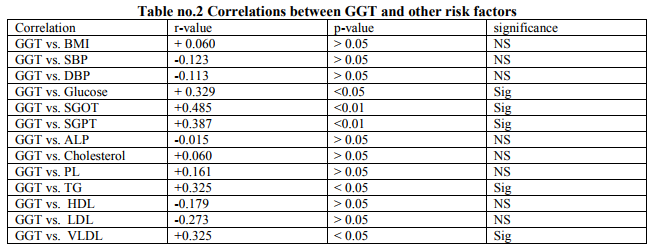
It was observed that there was a positive correlation between GGT and BMI, GGT and Glucose, GGT and SGOT, GGT and SGPT, GGT and cholesterol, GGT and PL, GGT and TG, GGT and VLDL. The correlation between GGT vs. SGOT, SGPT, Glucose, TG and VLDL was established to be good correlation. It was also observed that there was a negative correlation between GGT vs. BP, ALK, HDL, and LDL.
DISCUSSION
DM is a very common clinical condition over 50 year of age in developed countries but the prevalence of diabetes in India is 13-15 % and expected to rise further .India has already become the diabetic capital of world. Various studies have been conducted and are in progress all over the world for early detection and prevention of DM. The object of our study is weighing the relationship of risk factor of DM 2 like HT, age, BP, BMI, dyslipidemia and liver derived enzymes.GGT is liver derived enzyme and our aim to identify the role of GGT in DM2. This study was conducted on randomly selected 60 type 2 DM patients and 30 age and sex matched controls. In all subjects who were selected for this study a through history taking and physical examination was performed. Cases and controls were investigated and all the observations were analyzed. This present study showed that the mean BMI of the type 2 DM group was 27.51 ± 4.34 while that of control group was 24.5 0±2.94, statistically significant difference (p0.05 in study group). 20 out of 60 (33.3%) in type 2 DM group and in control group only 2/30 (3.3%) were hypertensive. The mean SBP ± SD and DBP ±SD in case and control groups were 127.50±8.32 / 122.70±6.80 and 83.73±6.80 / 80.00±4.47respectively which is statistically significant different (p126 mg% out of which 12 had abnormal GGT and 22 had normal GGT. 26 out of 60 subjects were 70-126 mg% FBS in which 20 had normal GGT and rest 6 had abnormal GGT. The mean FBS ± SD of all subjects of DM2 and control were 173.41±57.31 and 81.30±8.40 respectively. Which was statistically significant difference (p=0.01).Correlation between GGT and BMI (r=+0.329, p<0.05) were significant in study groups. Hepatic dysfunction resulting from the insulin resistance syndrome may contribute to the development type 2 diabetes (14) Alanine arninotransferase (ALT) is the most specific marker of this hepatic pathology. Gammaglutamyltransferase (GGT) is considered to be sensitive indicator of liver damage but if not specific (15). Obesity also affects that GGT. A number of Prospective studies (6,8,9,11,16,17) have shown that S. GGT or ALT help predict the development of type 2 diabetes independent of obesity and alcohol intake. These are an independent risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes and It is hypothesized that S.GGT might be a marker for visceral and hepatic fat deposition and, by inference, marker of hepatic insulin resistance (4). A number of cross-sectional studies (7) have since shown relationships between GGT/ALT and the metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance, suggesting that GGT/ALT may serve as a marker for insulin resistance. (18) Several possible mechanisms, how serum GGT increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Elevation of serum GGT could he the expression of an excess deposition of fat in the liver, termed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Fatty liver is though to cause hepatic insulin resistance and to contribute to the development of systemic insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia. GGT could serve as a marker of the insulin resistance syndrome in the pathogenesis of diabetes. Another possible mechanism is that GGT plays an important role in antioxidant systems. Experimental studies have reported that GGT has a central role in the maintenance of intracellular antioxidant defenses transport into most types of cells. Hence, raised GGT concentrations could be a marker of oxidative stress, which might also pay a role in the cause and development of diabetes. Other studies suggested that elevated serum GGT could be the expression of subclinical inflammation which also contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes. (19) Nakanishi et al (2003) said that the risk for development of IFG or type 2 diabetes increased in a dose-dependent manner as serum GGT increased in middle-aged Japanese men. The increased relative risk for IFG or more pronounced in obese men. (8) Noriyuki et al (2004) revealed with adjustment for age, family history of diabetes. BMI alcohol intake, cigarette smoking, regular physical activity (fasting plasma glucose the risk for type 2) and white blood cell (WBC) count, the risk of metabolic syndrome an type 2 diabetes increased in correlation with the levels of serum GGT, ALT aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase.These concluded serum GGT may be an important predictor for developing metabolic syndrome and type-2 diabetes in middle aged Japanese men. (10) A.O. Rantala et al (2000) revealed that significant association between GGT and the components of the metabolic syndrome. Elevated levels of GGT may not always indicate increased alcohol consumption, but may also suggest the existence of the metabolic syndrome with its subsequent deleterious consequences. (7) Lee DH, et al (2005): GGT within the physiologic range predicted microalbuminuria among patients with hypertension or diabetes and may act as a predictor of microvascular and / or renal complications in these vulnerable groups. (20). Up to 57% diabetics, especially those with vascular Complications have raised Gamma - glutamyltransferase activities. Such rises occur in the absence of liver disease, and the possibility of enzyme induction was put forward after a study of a group of serum enzyme values, such as alkaline phosphatase and glucose 6- phosphatase with increased activity in some diabetic patients. (15) Serum GGT showed a strong and graded relation with DM (Messinger et al 2005). (19)Association between serum GGT and risk for diabetes Perry et. al. has recently demonstrated that a raised serum GGT is an independent risk factor for the development of type 2 DM.(6) Out of 60 subjects in DM2 group 1 had abnormal SGOT and GGT and rest 59 had normal SGOT.All controls had normal GGT and SGOT.The mean SGOT ± SD of all subjects of DM2 and controls were 28.07±8.79 and 24.80±6.97 respectively. Taken together, statistically insignificant difference (p>0.05) was noted when comparison were made between type 2 DM and control. Correlation between GGT and SGOT were significant (r=+0.485, p=<0.Ol).
Association between other liver enzyme SGOT, SGPT and ALP and development of IFG or type 2 DM have also been observed by Perry et al 1998 and Nakanishi et al 2003 (6,8). The mean SGPT±SD of all subjects of DM2 and controls were 32.96±14.66 and 26.80±10.80 respectively. Comparison were made between diabetes mellitus type 2 and control groups, statistically significant difference (p0.05) in our study group. The mean PL ± SD subjects of DM2 and control were 2 10.97±38.87 and 188.40±34.85 respectively. Which was statistically significant difference (p<0.01). The mean TG ± SD subjects of DM2 and control were 198.33±157.56 and 131.10±68.13 respectively. The mean TG ± SD were also showed statistically significant difference (p<0.001). Lee et al (2003), observed association between serum GGT and high fasting TG, high blood cholesterol and low blood HDL (11). But in our study observed that the correlations were normal between serum GGT v/s TG and serum GGT v/s VLDL. In conclusion, above study recommend that serum GGT is a superior predictor of type 2 diabetes, irrespective of alcohol consumption. We hypothesize that it might be had some role in the pathogenesis in diabetes. The first explanation it might be related with oxidative stress and secondly associations of obesity (BMI) with diabetes may be modified by serum GGT level. For the prophecy of type 2 diabetes in obese subjects, it may be helpful to establish serum GGT because it is simple, easy and economical to measure and modifies the obesity related type 2 diabetes risk.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Lee — DHO, Ho Mir, Kim JH Christiana DC, Jacob DR Jr. — Gamma- GT and diabetes — A 4 year follow — up study. Dialectologies 2003 March 46 (3): 359 — 64
2. Whitfield JB: Gamma — glutarnyl transferase. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 38 : 263 — 355. 2001 [Medline]
3. Wannamethee G. Ebrahirn S. Shaper AG: Gamma — glutamyltransferase : determinants and association with mortality from ischemic heart disease and all causes. Am J Epidemiol 142: 699—708. 1995
4. Bots ML. Salonen JT. Elwood PC. Nikitin Y. Freire de Concalves A. Inzitari D. Sivenius J. Trichopoulou A. Tuomilehto J. Koudstall PJ. Grobbee DE: Gamma — glutamyltransferase and risk of stroke:the EUROSTROKE project. J Epidemiol Community Health 56 (Suppl. 1): 125— 129. 2002
5. Nilssen 0. Forde OH. Brenn. T: The Tromso Study : distributin and population determinants of gamma — GT. Am J Epidemiol 132: 18—326.1990
6. Perry IJ. Wannarnethee SG. Shaper. AG: Prospective study of serum GT and risk of NIDDM. Diabetes Care 21: 737. 1998
7. Rantala AO. Lilja M. Kauma H. Savolainen MJ. Reunanen A.Kesaniemi YA: Gamma — GT and the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med248:230—238.2000
8. Nakanjshj N. Nishina K. Li W. Sato M. Suzuki K. Tatara K Serum gamma — GT and development of impaired fasting glucose or type 2 diabetes in middle — aged Japanese men . J Intern Med 254:287— 295.2003
9. Lee DH. Jacobs DR Jr. Gross M. Kiefe CI. Roseman J. Lewis CE. Steffes M : Gamma — GT is a predictor of incident diabetes and hypertension : the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Clin Chem 49: 1358 — 1366. 2003.
10. Nakanishi N, Suzuki K. Tatara K. Serum Gamma- GT and risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in middle —aged Japanese men. Diabetes Care 2004 : 27: 1427-32
11. Lee DH. Ha MH. Kim JH et al. Gamma-GT and diabetes — a 4 year follow —up study. Diabetologia 2001 46: 3 59-64.
12. Bombelli M, Facchetti R, Seqa R,Caruqo S,Fodri D,Brambilla G,Giannattasio,Grassi G,Manicia G, Impact of body mass index and waist circumference on the long-term risk of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and cardiac organ damage. Hypertension. 2011 Dec;58(6):1029-35. Epub 2011 Oct 24.
13. Duk-Hee Lee et al. GGT is a predictor of incidence diabetes and hypertension : The coronary artery risk development in young adults (cardia) study. Clinical Chemistry 49 : 8: 1358-1366 : 2003.
14. Marhesini G, Brizi M, Bianchi G, Tomassetti S Bugianesi E,Lenzi M, McCullough Aj Natatle S, Forlani G, Meichionda N:Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease : a feature of the metabolic syndrome, Diabetes 50: 1844— 1850, 2001
5. Penn R, Worthington DJ. Is serum GammaGT a misleading test? (Review) .BMJ 286: 531 — 535, 1983
16. Sattar N, Scherbakova 0, Ford 1,0‘ Reilly DS, Stanley A, Forrest E, Macfarlane PW, Packard CJ, Cobbe SM, Shepherd J, the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study, Elevated alanine saminotranslerase predics new-onset type 2 diabetes independently of classical risk factors, metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 53:2855- 2860, 2004.
17. Lee Dli, Silventoinen K, Jacobs DR. Jousilathi P. Tuomleto J. Garrnma glutamyltransferase, obesity, and the risk of type 2 diabetes observational cohort study among 20, 1 58 middle-aged men and women. J. Clin Endocrinol Metab 89.5410- 54 14, 2004.
18. Wannamethee Lucy Lennon et a!. Hepatic enzymes, the metabolic syndrome and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetic Care Vol. 28, 12 : 2005.
19. Meisinger H. Lowe!, et al. Serum GOT and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in-men and women from the general population. J. of Internal Med. 2005 ; 258 ; 527-53 5.
20. Lee DH, Jacobs DR. Serum gammaglutamyltransferase was differently associated with micriabuminuria by status of hypertension or diabetes : the coronary artery risk development in young adults (Cardia) study. Clin Chem. 2005 July 51(7): 1185-91.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License