IJCRR - 9(14), July, 2017
Pages: 14-18
Date of Publication: 28-Jul-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence and Gender Differentials of Metabolic Syndrome Among College Students of Kolkata, West Bengal, India
Author: Tanima Paul Das Minati Sen, Indranil Saha, Debnath Chaudhuri
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The study aims to determine the prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MS) and assess gender differences among college students of Kolkata, West Bengal, India using International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria.
Materials and Methods: Design: A cross sectional study was conducted among 397 college going students comprising of 235 females and 162 males aged 18 to 24 yrs from August 2011 to December, 2013. Measurements: Anthropometric measurements were performed by standardized techniques, blood pressure (BP) by sphygmomanometer. Serum glucose, HDL-C and TG were measured in fasting blood. Diagnostic criteria used: MS was identified using IDF criteria.
Results: Prevalence of MS among total population was 4.5%. Significant differences exist between genders with respect to age, BP and HDL-C (p ? 0.05). 9.1% had only central obesity while 12.1% students had any one of the metabolic syndrome components in addition to central obesity.
Conclusion: Many of the college students of Kolkata were having MS or its predisposition. Early identification can be beneficial for planning intervention strategies in college and university settings.
Keywords: Metabolic Syndrome, College students, Kolkata, India
DOI: 10.7324/IJCRR.2017.9144
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Metabolic Syndrome (MS) has been defined as clustering of cardiovascular disease risk factors, including hyperinsulinemia / insulin resistance, hypertension, atherogenic dyslipidemia, obesity and glucose intolerance (1-3).The definitions with distinct differences which helps in the interpretation of metabolic syndrome are given by World Health Organization (WHO, 1998); European Group of Insulin Resistance (EGIR); Adult Treatment Panel III (ATPIII, 2001); American Association for Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE,2003), International Diabetes Federation (IDF, 2005) with ethnic specific cut-offs and modified NCEP-ATP III criteria (2). According to the IDF definition, for a person to be defined as having the metabolic syndrome must have central obesity (defined as waist circumference with ethnicity specific values) plus any two of the other four risk factors of MS (4). In adults, MS has been reported to predispose to an increased risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) (2), particularly in Asian Indians (5). Prevalence of obesity and MS is rapidly increasing in India and other South Asian countries, leading to increased mortality and morbidity due to CVD and T2DM.About one third of urban South Asians have evidence of MS (6-8).
College students are an understudied population in respect to prevalence of MS. Experts emphasize that MS is becoming increasingly prevalent and parallels the emergent pandemic of overweight and obesity (9) even in young adults (10). Studies document that college students experience weight gain faster than average adults (11-12). Huang et. al. (13) concluded that overweight students are more predisposed to the components of MS. It was also reported that college students make unhealthy food choices and do less physical activities (14).
Therefore, objectives of this study were to find out the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and to assess its pre-disposition among college students of Kolkata, West Bengal, India.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study participants
Three hundred ninety seven (397) college students comprising of 235 females and 162 males aged 18 to 24 yrs living in Kolkata were randomly selected from ten colleges for this study. Purpose of the study was explained to them and written consent was obtained. Participation in the study was voluntary and non-remunerative.
Exclusion criteria
Students who were suffering from metabolic abnormalities e.g. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) or with a medical history of previous cardiovascular events with prescribed usage of antihypertensive drugs or on hormone therapy (e.g. insulin), pregnant and lactating women, athletes or unwilling participants were excluded from the study.
Ethical considerations
The study protocol has been approved by the Bioethics Committee for Animal and Human Research Studies, University of Calcutta (Ref no. BEHR/1098/2304 dated 22/06/11).
Study Design
Cross sectional study was conducted from August 2011 to December 2013. Participants were recruited via classroom announcements, flyers and word-of-mouth. Survey along with blood sample collection was done randomly in respective institutions.
Anthropometric estimations
Participants were requested to wear light clothes and not to wear shoes/socks for the measurements. Height (nearest 0.5cm), weight (nearest0.1kg), waist (nearest0.2 cm) and hip circumference (nearest 0.2 cm) were obtained using standardized techniques (15). Blood pressure was measured on the right arm of the participants in a relaxed, sitting position with the arm supported at heart level, using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer. All measurements were done in duplicate and the average was recorded (16).
Biochemical estimations
Blood sampling of the students were performed by a trained phlebotomist by venipuncture after10 to 12 hr overnight fast. Samples were transported to the laboratory in an ice bucket within 2hrs of collection and serum was separated by centrifugation of whole blood for 20 minutes at 2000rpm. Fasting blood measures included serum glucose by glucose oxidase – peroxidase method(17), serum total cholesterol (TC) by cholesterol oxidase peroxidase-aminoantipyrine method(18) and serum triglycerides (TG) by glycerol oxidase peroxidase amino antipyrine method (19) using assay kits from Span Diagnostics Limited in a semi autoanalyzer. High density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was determined by cholesterol oxidase peroxidase-amino antipyrine method after precipitation of low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and very low density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C). LDL-C and VLDL-C were calculated using Friedwald’s equation: LDL-C = TC – (HDL-C + TG/5); VLDL-C = TG/5 (18).
Definition and diagnostic criteria used
Metabolic syndrome (MS) was defined according to IDF criteria for MS. According to new IDF definition: for a person to be defined as having MS they must have:: Central obesity (defined as waist circumference ≥ 90 cm for males and ≥ 80 cm for females) as for Asians and any two of the following four factors: raised triglycerides (≥ 150 mg/dl), reduced HDL-C(<40mg/dl) in males and (<50mg/dl) in females, raised blood pressure; (Systolic BP ≥ 130 mm Hg or Diastolic BP ≥ 85 mm Hg) and raised fasting plasma glucose ( ≥ 100 mg/dl) (4).
Statistical analysis
Data were entered into Microsoft Excel spreadsheet (Microsoft, Redwoods, WA, USA) and accuracy was checked. Categorical data was expressed in proportions. Continuous data were checked for normality by Kolmogorov Smirnov Test. Significant P value from this test indicated skewed distribution; so continuous data were expressed in median and inter quartile range (IQR). Analyses were performed using Windows based SPSS software, version 19.0 (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Demographics were calculated using median and frequencies. Non Parametric Mann Whitney U test was performed to see the overall distribution of values between two independent groups i.e. males and females regarding all anthropometric, clinical and biochemical parameters. Pearson’s Chi square tests were used to find out if any difference exists between categorical variables i.e. occurrence of MS components and percentage of individual MS components between males and females.p values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Participant information
Participant information on individual MS component along with the differences in the anthropometric, clinical and biochemical parameters between males and females participating in the study are shown in Table 1. Approximately 59% were females (n = 235) and 41% were males (n = 162). Median age of females and males was (20.5 ± 3 yrs) and (20 ± 2 yrs), respectively.
Non parametric Mann Whitney U test between two independent groups revealed significant differences between males and females with respect to age, SBP, DBP and HDL-C ( p < 0.05) [Table 1].

Prevalence of metabolic syndrome
Prevalence of MS among total college students was 4.5% (6% females and 2.5% males). Overall 9.1% students (2.5% males and 13.6% females) had only central obesity while 12.1% of them (3.1% males and 18.3% females) had any one of the components of MS in addition to central obesity as shown in Table 2.
A statistically significant difference between genders with respect to the presence of MS components was revealed by Chi square tests (p ≤ 0.05).
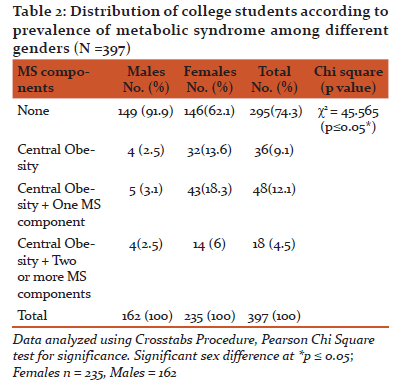
Prevalence of MS of the college students based on individual components
Table 3 shows that a total of 25.7% of the college goers (n = 102) comprising of 89 females and 13 males had the obligatory metabolic component i.e. Central obesity as per IDF criteria for Asians. Of the individual metabolic syndrome components, low HDL had by far the highest prevalence (28.7%).Central obesity had the second highest prevalence (25.7%).14.9% students had hypertriglyceridemia, 13.9% had raised blood pressure and 7.8% had raised fasting blood glucose levels. Hypertriglyceridaemia (p = 0.008) and elevated blood pressure (p = 0.000) were significantly higher in males whereas females had significantly higher prevalence of low HDL (p = 0.000) and central obesity (p = 0.000).


DISCUSSION
Rates of overweight and obesity have escalated rapidly among Indian adolescents (20) who typified typical college going students transitioning from adolescence to young adulthood. Indians, as an ethnic group, are particularly at high risk for MS and central obesity, both forerunners of diabetes, CHD and other “life style" disorders (7, 8, 21).Overweight and obesity significantly contribute to the development of MS among college students (13,22,23). Apparently, no study report is available on the prevalence of MS among college students in Kolkata.
As evident from the present study, prevalence of MS as per IDF criteria among the total college students was 4.5%; however 9.1% students had only central obesity while 12.1% students had any one component of MS in addition to central obesity. Overall MS prevalence observed in our study is similar to the MS prevalence (5-7%)reported by Jadhav et. al. (24) possibly due to similar Asian ethnic composition as well as age range but higher than the MS prevalence reported by Huang et. al. (0.6%) (25), Fernandes et. al (3.7%)(26) and Rashidi et. al. (3.2%)(27).
On the other hand, MS prevalence reported by Keown et. al. (10.0%) (28), Cha et. al.(12%)(29), Tope et al.(12%)(23),Morrell et al ( 9.9% men and 3 % women)(22) were higher than the results of the present study which may be due to the fact that most of these studies used NCEP-ATP III criteria for diagnosis of MS in which central obesity is not mandatory component (3).A remarkable observation in this study is the lower percentage (9.1%) of students having only the obligatory component of MS i.e. central obesity in comparison to students having any one of the other components in addition to central obesity (12.1%) which differs from earlier studies (22-30) implicating the increasing trend of other components of MS along with central obesity among the college students of Kolkata. Therefore, it may be stated that the students having high central obesity and/or any other MS components are at risk for the development of MS and subsequently they may become the victim of T2DM or CVD.
Furthermore, the present study indicates that females were having significantly (p < 0.05) lower metabolic profile than males corroborating some of the previous studies (26, 27) but differing from some other studies (22, 23), which may be due to the difference in the origin of study population.
Looking at specific components of MS, this study elicited the most prevalent component amongst the female students was central obesity (37.9%) which differs from most of the earlier studies (22-30) whereas, low HDL observed to be the second most predominant MS component (37.4%) amongst them. This finding differs from most of the earlier studies (22-30) which reported low HDL as the most prevalent MS component among female students. High incidence of central obesity among female students have made them at risk of developing metabolic syndrome which may be due to ethnicity or poor awareness or faulty lifestyle or more than any of these factors.
In contrast to females, present study revealed raised BP as the most predominant component of MS in male students (24.7%) which is similar to some earlier studies(22,23,27,28) but differs from the report of Fernandes et.al. (26). Raised TG (20.4%)was the second most prevalent risk factor of MS amongst them, which is similar to report by Rashidi et. al.(27) but differs from most of the earlier studies(22,23,26,27,28).Poor metabolic profile of male students as revealed from our study indicates they can naturally progress to early onset of CVD if not addressed in time.
CONCLUSION
So, it can be concluded that considerably high prevalence of MS or its risk exists among both male and female college students aged 18 to 24 yrs in Kolkata, India. Effective additional screening needs to be implemented to target interventions focusing on risk reduction of MS among this cross-section of the population.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Authors also acknowledge student participants who voluntarily agreed to participate in this study as also supportive staffs, professional phlebotomist and laboratory technicians of All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Kolkata for their technical support.
SOURCE OF FUNDING
UGC ERO Minor Research Project Grant Reference No. PSW-112/12-13(ERO) dtd. 05-Feb-13.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None
References:
- Reaven GM. Banting Lecture. Role of insulin resistance in human disease .Diabetes. 1988; 37:1595-607.
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, Donato KA, Eckel RH, Franklin BA, Gordon DJ, Krauss RM, Savage PJ, Smith SC, Spertus JA, Costa F. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement [published corrections appear in Circulation 2005;112:e297 and 2005;112:e298]. Circulation. 2005; 112:2735–2752.
- Expert Panel on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults. Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert panel on detection, evaluation and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001; 285: 2486-97.
- IDF (2006).The IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome. http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/IDF_Metasyndrome_definition.pdf (Last accessed on 23.03.16.
- Misra A, Misra R. Asian Indians and insulin resistance syndrome: Global perspective. Met Syndr Relat Disord. 2003; 1:277-85.
- Mohan V, Rao GHR. Type 2 Diabetes in South Asians. 1st ed. New Delhi: South Asian Society on Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis; 2007.
- Misra A, Khurana L. The metabolic syndrome in South Asians: Epidemiology, clinical correlates and possible solutions. International Diabetes Monitor 2009;21:92-101.
- Misra A, Misra R, Wijesuriya M, Banerjee D. The metabolic syndrome in South Asians: continuing escalation and possible solutions. Indian J Med Res. 2007; 125(3):345–354.
- Eckel R.H, Grundy S.M, Zimmet P.Z, The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005; 365:1415-28. http://www.thelancet.com(last accessed on 23/03/16).
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Liu K, Colangelo LA, et al. Consistently stable or decreased body mass index in young adulthood and longitudinal changes in metabolic syndrome components: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults study. Circulation. 2006; 115:1004–1011.
- Holm-Denoma JM, Joiner TE, Vohs KD, Hearthertob TF: The freshman fifteen (the freshman five actually): predictors and possible explanations. Health Psychol. 2008; 27:S3-S9.
- Levitsky DA, Halbmaier CA, Mrdjenovic G: The freshman weight gain: a model for the study of the epidemic of obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metabol Disord.2004; 28:1435-1442.
- Huang, TT, Kempf, AM, Strother, ML, et al. Overweight and components of the metabolic syndrome in college students. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27(12):3000-3001.
- Huang, TT, Harris, KJ, Lee, RE, et al. Assessing overweight, obesity, diet, and physical activity in college students. J Am Coll Health. 2003; 52(2):83-86.
- Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 1988.
- Motamed, N, Perumal, D, Zamani, F, Ashrafi, H, Haghjoo, M, Saeedian, FS, Maadi, M, Akhavan-Niaki, H, Rabiee, B and Asouri, M. Conicity Index and Waist-to-Hip Ratio Are Superior Obesity Indices in Predicting 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk Among Men and Women. Clin Cardiol.2015; 38: 527–534.
- Trinder P. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with on alternative oxygen receptor. Ann Clin. Biochem.1969; 6: 24-27.
- Herbert K. Lipids, In Clinical Chemistry; Theory, Analysis and Co-relation, Kaplan L.A and A.J Eds. C. V. Mosby, Toronto.1984; 1182-1230.
- McGowan MW, Artiss JD, Strandbergh DR, Zak B. Clin. Chem. 1983; 29 (3):538-42.
- Rohilla R, Rajput M, Rohilla J, Malik M, Garg D, Verma M. Prevalence and Correlates of Overweight/Obesity Among Adolescents in an Urban City of North India. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 2014;3(4):404-408. doi:10.4103/2249-4863.148127.
- Misra A, Vikram NK. Insulin resistance syndrome (metabolic syndrome) and obesity in Asian Indians: evidence and implications. Nutrition.2004; 20:482–91.
- Morrell JS, Lofgren IE, Burke JD, Reilly RA. Metabolic syndrome, obesity, and related risk factors among college men and women. J Am Coll Health. 2012; 60(1):82–9.
- Topè AM, Rogers PF. Metabolic syndrome among students attending a historically black college: prevalence and gender differences. Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome. 2013;5:2. doi:10.1186/1758-5996-5-2.
- Jadhav K, John R, Agrawal V. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in College Students in Navi Mumbai. International Journal of Medicine and Allied Health Sciences. 2014; 1(2):76-84.
- Huang TT, Shimel A, Lee RE, Delancey W, Strother ML. Metabolic risks among college students: prevalence and gender differences. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2007; 5(4):365–371
- Fernandes J, Lofgren IE. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and individual criteria in college students. J Am Coll Healt. 2011 Jan; 59(4): 313-21
- Rashidi AA, Parastouei K and Shahaboddin ME. Metabolic syndrome among medical university students in Kashan, Iran. Scientific Research and Essays 2012; 7(41): 549-553.
- Keown, Terri L.Metabolic Syndrome Among College Students. The Journal for Nurse Practitioners.2009;5(10): 754 –759.
- Cha E, Burke LE, Kim KH, Shin YA, Kim HY. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among overweight and obese college students in Korea. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2010; 25(1):61-8.
- Al Dhaheri AS, Mohamad MN, Jarrar AH, Ohuma EO, Ismail LC, Al Meqbaali FT, et al. (2016) A Cross-Sectional Study of the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome among Young Female Emirati Adults. PLoS ONE 11(7): e0159378. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159378
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License