IJCRR - 4(12), June, 2012
Pages: 41-47
Date of Publication: 22-Jun-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DESIGN ISSUES OF EMBEDDED SYSTEM USING REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEM IN LINUX ENVIRONMENT
Author: Anant Mittal, Sunil Kr. Singh
Category: Technology
Abstract:The world of embedded system faces many challenges. Due to availability of several sections of modern
applications in the present era of technology, today's demand is very high performance from systems but
with minimum resources. Embedded systems are also known as real time systems since they respond to
an input or event and produce the result within a guaranteed time period. Usage of RTOS will enable us to break the complex system into simpler tasks without disturbing the inter task timing problems. Embedded systems require only the basic functionalities of an operating system in real-time environment- a scaled down version of an RTOS. It demands reliability and the ability to customize the OS to match an application's unique requirements. But, due to the advancements in technology, we need an open source environment i.e. Linux which has the capability to provide reliable and flexible configuration to any embedded application in the next generation of embedded system design. Linux offers powerful and refined system management facilities, it is a rich tool of device support, an excellent status for reliability, robustness and broad documentation. In this paper, we try to summarize some current trends in embedded systems design and point out some of their environment characteristics, such as RTOS and Linux platform which can provide a flexible and efficient ground for satisfying the area, performance, cost, and power requirements of many embedded systems.
Keywords: RTOS, Embedded Linux, Embedded processor, ASIC.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The embedded system is a combination of computer hardware, software and, perhaps, additional mechanical parts, designed to perform a specific function. An embedded computing system uses microprocessors to implement parts of functionality of non-general-purpose computers. Early microprocessor based design emphasized on input and output. Modern high performance embedded processors are capable of providing a great deal of computation in addition to I/O task. An embedded system is not a new and exotic topic confined to research. There are many live examples of embedded systems around us. MP3 players (computing capability built into a music system), PDAs (computing in what essentially is an organizer), car-control systems, and intelligent toys are a few examples of such systems already in place. Linux was developed specifically as an operating system for the desktop/server environment. More recently, there has been a growing interest in tailoring Linux to a very different hardware and software needs of the embedded applications environment.
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS VERSUS GENERAL PURPOSE SYSTEMS:
An embedded system is usually classified as a system that has a set of predefined specific functions that are to be performed and in which the resources are constrained. Each embedded design satisfies its own set of functions and constraints. This is different from general purpose systems, such as the computer that sits on a desk in an office, the processor running that computer is termed a ?general purpose? processor because it was designed to perform well different tasks as opposed to an embedded system that has been built to perform a few specific tasks either very well or within very strict parameters.
a) Real time embedded systems:
Embedded systems are often wrongly classified as real-time systems. However, most systems simply do not require real-time capabilities. A real time system (defined by IEEE) is a system whose correctness includes its response time as well as its functional correctness. In other words, in a real-time system, it not only matters that the answers are correct, but when the answers are produced is also taken into consideration. Therefore, it can be defined as a system that performs its functions and responds to external, asynchronous events within a specified amount of time. It is an operating system capable of guaranteeing timing requirements of the processes under its control. While time-sharing OS like UNIX strive to provide good average performance, for a real-time OS correct timing is the key feature. There are hard and soft realtime systems depending on time constrains[1].
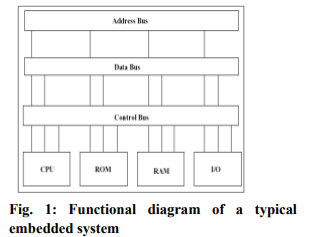
b) Embedded Processors:
With so many applications, all major microprocessor manufacturers are building their own embedded processors. Many companies have started using existing microprocessor cores and modifying them to suit embedded devices. AMD, for example, recently introduced its AMD-K6-2E processor in two flavours for embedded applications. Motorola has been a significant player in the embedded processors field over the last couple of years. They have the 68K cores at the low-end, Cold Fire in the midrange and PowerPC for higher-end applications. Another contender for the market share is Intel, who went the embedded way with its i960 processor, based on 1.0 micron technology. The same team was then put into developing the Strong Arm, which is based on 0.18 micron technology. This processor became quite popular, and found its way into devices like the Compaq iPAQ pocket PC, HP Jornada handheld PC, mobile phones and various digital imaging products.
c) Embedded Hardware Trends:
With the increase in interest and research of embedded systems, has come a flood of new design trends. It is hard to envision that five years from now embedded systems will bear much resemblance to the systems today, other than their basic functionalities and even those may be replaced in the future. Two of the current trends in the embedded systems world that is discussed here are that of application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and systems on a chip (SOC)[2].
- Application Specific Integrated Circuits
As the title suggests, this is an IC that has been designed for a specific application. In ASICs, the drawback is that they need heavier investments and longer time spans to develop. Apart from this, they can‘t be customized later as the software instructions for them are put on a ROM, which is difficult to modify.
- System -on- a-Chip
A system-on-a-chip offers all the functions of a computer, but with a difference-all these features including a processor, chipset, video encoder, graphics processor, super I/O, clock generator, and the various buses used to interconnect, except the host memory of the system, are integrated on a single silicon chip . Like all forms of SOC, it reduces the number of chips in a system, allowing the product to be smaller and less expensive.
d) Embedded software:
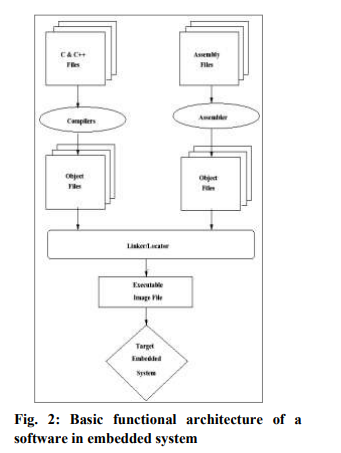
C has become the language of choice for embedded programmers, because it has the benefit of processor independence, which allows programmers to concentrate on algorithms and applications, rather than on the details of processor architecture. However, many of its advantages apply equally to other high-level languages as well. Perhaps the greatest strength of C is that it gives embedded programmers an extraordinary degree of direct hardware control without sacrificing the benefits of high-level languages. Compilers and cross compilers are also available for almost every processor with C. Any source code written in C or C++ or assembly must be converted into an executable image that can be loaded onto a ROM chip. The process of converting the source code representation of your embedded software into an executable image involves three distinct steps, (as in given figure 2) and the system or computer on which these processes are executed is called a host computer. There are some very basic differences between conventional programming and embedded programming[3].
REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEM AND EMBEDDING LINUX:
Embedded systems demand extremely high reliability (for non-stop, unattended operation), in addition to the ability to customize the OS to match an application's unique requirements. General purpose desktop OSes (like Windows) aren't well suited to the unique needs of appliance-like embedded systems. However, commercial RTOSes, though designed to satisfy the reliability and configuration flexibility requirements of embedded applications, are increasingly less desirable due to their lack of standardization and their inability to keep pace with the rapid evolution of technology. Fortunately, a new and exciting alternative has emerged: open source Linux. Linux offers powerful and sophisticated system management facilities, a rich cadre of device support, a superb reputation for reliability and robustness, and extensive documentation. Linux is available at no charge -- and with completely free source code. Open-source Linux has created a new OS development and support paradigm wherein thousands of developers continually contribute to a constantly evolving Linux code base. In addition, dozens of Linuxoriented software companies have sprung up – eager to support the needs of developers building a wide range of applications, ranging from factory automation to intelligent appliances Linux distributions are variations on the same theme -- that is, they are collections of the same basic components, including the Linux kernel, command shells (command processors), and many common utilities. The differences tend to centre based on which of the many hundreds of Linux utilities have been included, what extras are included, and how the installation process is managed. Some of the special capabilities being developed include:
- Installation of tools to automate and simplify the process of generating a Linux configuration that is tuned to a specific target's hardware setup.
- A variety of Windows-like GUIs to support a wide range of embedded requirements.
- Support for the specific needs of various embedded and real time computing platforms and environments (e.g. special Compact PCI system features).
a) Embedded Linux systems:
More recently, there has been a growing interest in tailoring Linux to a very different hardware and software needs of the embedded applications environment. A minimal embedded Linux system needs just these essential elements:
I. a boot utility
II. the Linux micro-kernel, composed of memory management, process management and timing services
III. an initialization process, to make it do something useful
IV. drivers for hardware
V. one or more application processes to provide the needed functionality
VI. a file system (perhaps in ROM or RAM)
VII. TCP/IP network stack
VIII. A disk for storing semi-transient data and swap capability[4].
b) Real time operating systems:
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) are commonly used in the development, production, and deployment of embedded systems. Unlike the world of general purpose computing, realtime systems are usually developed for a limited number of tasks and have different requirements of their operating systems. This section first gives the requirements of real-time operating systems followed by how real time performance is achieved in Linux[4][5].
- Real-Time Operating Systems: The Requirements
A good RTOS not only offers efficient mechanisms and services to carry out real-time scheduling and resource management but also keeps its own time and resource consumption predictable and accountable. A RTOS is responsible for offering the following facilities to the user programs that will run on top of it. The first responsibility is that of scheduling: a RTOS needs to offer the user a method to schedule his tasks. The second responsibility is that of time maintenance: the RTOS needs to be responsible in both providing and maintaining an accurate timing method. The third responsibility is to offer user tasks the ability to perform system calls: the RTOS offers facilities to perform certain tasks which the user would normally have to program on its own, but the RTOS has them included in its library, and these system calls have been optimized for the hardware system that the RTOS is running on. The last thing that the RTOS needs to provide is a method of dealing with interrupts: the RTOS needs to offer a mechanism for handling interrupts efficiently, in a timely manner, and with an upper bound on the time it takes to service those interrupts.
- Linux and real time
Many (if not all) embedded applications have some sort of real time performance requirement. Many of these real-time requirements prove to be ?soft‘ - missing a deadline once in a while does not impact the overall system viability. A GPOS typically suffers from several challenges to real-time applicability: determinism in general, and response under load in specific. GPOS schedulers, optimized for time-sharing, can induce unpredictably long blocking times; drivers developed by a mix of GPOS-vendor engineers, peripheral-board vendors, and other third parties add their own variable latencies. Linux, developed for desktops and servers, is also a GPOS, but enjoys a promising future in real time embedded designs. Two primary paths existing to provide a real-time Linux: by inserting a second kernel into the system, and by refining the standard Linux scheduler and tuning Linux device drivers first to characterize the performance of standard versions of Linux. Before even attempting to enhance Linux responsiveness, it is important to measure its real-time performance thoroughly in terms familiar to real-time/embedded designers: worstcase interrupt latency, context switch, and maximum blocking times.
- Comparison with existing embedded operating Systems
RTOS like QNX, PSOS, and VxWorks are designed from the ground up for real-time performance, and provides reliability by allocating certain processes a higher priority than others when launched by a user as opposed to by system-level processes. The demands for real- time performance were addressed during the initial design phase. As a result, commercial non-Linux embedded operating systems have tended to be more scalable at the low end and have better real-time performance. However embedded Linux has now evolved to the point where it can address, at low or zero cost, all but the most demanding of embedded applications .The real time performance issue can be important in the market, and embedded Linux vendors are working hard to match the real time capabilities of established products[6].
- EMBEDDING LINUX:
One of the common perceptions about Linux is that it is too bloated to use for an embedded system. The standard Linux kernel is always resident in memory. Each application program that is run is loaded from disk to memory where it executes. When the program finishes, the memory it occupies is discarded, that is, the program is unloaded. In an embedded system, there may be no disk. The two ways to handle the removal of dependency on a disk are the complexity of the system and the hardware design. In a simple system, the kernel and all application processes reside in memory when the system starts up. This is how the traditional embedded systems works and is also supported by Linux.
- The file systems -high availability:
An embedded Linux file system, unlike desktop or server implementations, must offer user independent support for recovery in the event of power failure. Also, power consumption, size and failure rate considerations mean that the file system is likely to be running from some variant of flash or ROM rather than hard disc or other rotating media. The Linux kernel must be rebuilt to support this device, but, again depending on the file system used, corruption can occur. Another is to make use of on-board flash memory with Disc on Chip devices, drivers must be added to Linux kernel -but there is the option of using the Journaling Flash File System (JFFS). This is a ?log structured ?file system, which means that old data is not lost when new data is written to flash.
ADVANTAGES/DISADVANTAGES OF USING EMBEDDED LINUX:
Although most Linux systems run on PC platforms, Linux can also be a reliable workhorse for embedded systems. A fully featured Linux kernel requires about 1 MB of memory. However, the Linux micro-kernel actually consumes very little of this memory, only 100 K on a Pentium CPU, including virtual memory and all core operating system functions. With the networking stack and basic utilities, a complete Linux system runs quite nicely in 500 K of memory on an Intel 386 microprocessor with an 8-bit bus (SX). Another benefit of using an open source operating system like Embedded Linux over a traditional real-time operating system (RTOS) is that the Linux development community tends to support new IP and other protocols faster than RTOS vendors do. For example, more device drivers, such as network interface card (NIC) drivers and parallel and serial port drivers are available for Linux than for commercial operating systems[7].
The core Linux operating system, the kernel itself has a fairly simple micro-kernel or monolithic architecture, meaning the whole operating system-process management, memory management, file system and drivers is contained within one binary image which is in compressed form. This provides a highly modular building block approach to constructing a custom embeddable system, which typically uses a combination of custom drivers and application programs to provide the added functionality. Linux is also well suited for embedded Internet devices, because of its support of multiprocessor systems which lends its scalability. This capability gives the designer an option of running a real-time application on a dual processor system, increasing total processing power. So you can run a Linux system on one processor while running a GUI, for example, simultaneously on another processor. The only disadvantage to running Linux on an embedded system is that the Linux architecture provides real-time performance through the addition of real-time software modules that run in the kernel space, the portion of the operating system that implements the scheduling policy, hardware-interrupts exceptions and program execution. Since these real-time software modules run in the kernel space, a code error can impact the entire system‘s reliability by crashing the operating system, which can be a very serious vulnerability for real-time applications.
APPLICATIONS
Embedded software is present in almost every electronic device you use today. However, a common obstacle for developers has been the need to develop different sets of hardware and software for different devices. In addition, the software running on the hardware chip is different. This often results in increased costs and time taken for development. Defence services use embedded software to guide missiles and detect enemy aircrafts. Communication satellites, medical instruments, and deep space probes would have been nearly impossible without these systems. Embedded systems cover such a broad range of products that generalization is difficult. Here are some broad categories.
1) Aerospace and Defence electronics (ADE)
2) Automotive
3) Broadcast and entertainment
4) Consumer/internet appliances
5) Data communications
6) Digital imaging
7) Industrial measurement and control
8) Medical Electronics
9) Server I/O
10) Telecommunications
CONCLUSION
The developments of embedded systems have been fairly dynamic over the past couple of years with the rapid digitization of various parts of our day-to-day utility items. The trend of embedded systems now involves the miniaturization of electronics so that it can fit into compact devices. In the future these systems will be moved by the forces of nature. Soon we will see more digitization of appliances, and these will be fuelled by human need. Embedded developers are a flexible, forward-looking bunch, and despite the need to reorient itself technically, they are flocking to Linux like penguins to their nesting ground. They are choosing Linux for the technical advantages cited above, for its greater reliability, for the comprehensive set of standard APIs, and to lower their cost. Linux has already altered the embedded and real-time operating system landscape in a fundamental and irreversible way.
Developers now have greater control over their embedded OS; manufacturers have spared the costs and headaches of software royalties with the users getting more value.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. L. Thiele and R. Wilhelm. Design for timing predictability. Real-Time Systems, 28(2- 3):157–177, 2003.
2. H. Kopetz. Real-Time Systems: Design Principles for Distributed Embedded Applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1997.
3. A. Burns and A. Wellings. Real-Time Systems and Programming Languages. Addison-Wesley, third edition, 2001.
4. http://www.dedicatedsystems.com/encyc/buyersguide/rtos/rtosme nu.htm for an RTOS Buyer's Guide
5. T.A. Henzinger, E.A. Lee, A.L. Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, S.S. Sastry, and J. Sztipanovits. Mission Statement: Centre for Hybrid and Embedded Software Systems, University of California, Berkeley, http://chess.eecs.berkeley.edu, 2002
6. http://www.opensource.org for general Open Source propaganda.
7. Embedded Systems, Linux, and the Future by Karim Yaghmour , author of Building Embedded Linux Systems 06/09/2003.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License