IJCRR - 4(14), July, 2012
Pages: 79-84
Date of Publication: 31-Jul-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
AWARENESS AND PRACTICES OF BIOMEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT AMONG NURSING STAFF OF A HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO A TEACHING INSTITUTE
Author: Mohan M Raut, Umesh S Joge, Vilas R Malkar, Sonali G Choudhari, Harshada M Ughade
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Title: Awareness and Practices of Biomedical Waste Management Among Nursing Staff of A Hospital Attached To A Teaching Institute Objectives -1) To study the awareness and practices about biomedical waste management among nursing staff 2) To assess the use of personal protective measures against biomedical waste. Methodology: A hospital based cross-sectional study conducted among 152 nursing staff. Information regarding awareness and practices of biomedical waste management such as of BMW rules, biohazard symbol, colour coded containers and use of personal protective devices was collected. The actual practice of handling biomedical waste in wards was observed during the morning hours of OPDs. Results: In the present study knowledge about biomedical waste management rules was found in
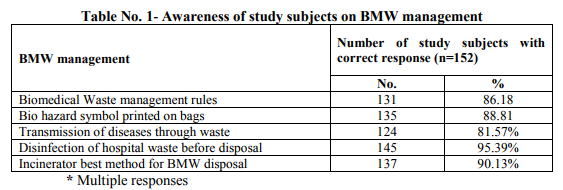
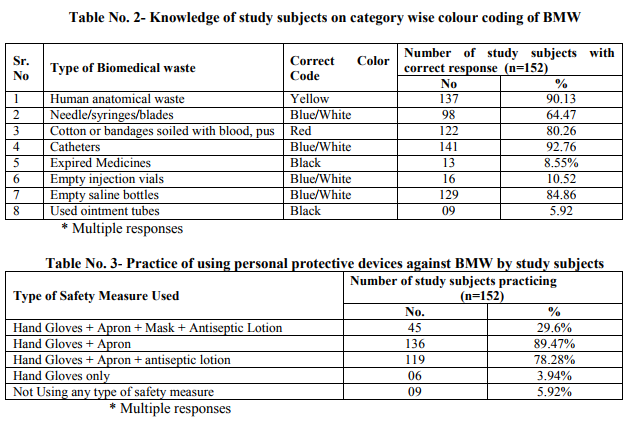
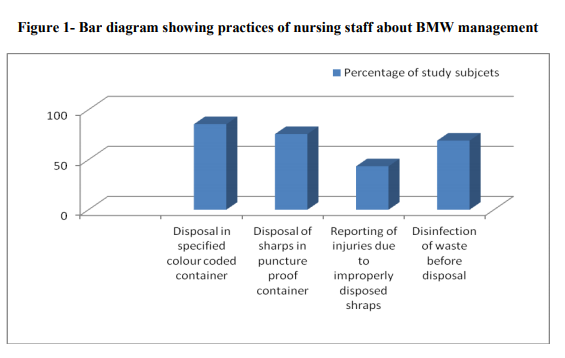
131(86.18%) study subjects while about 135(88.81%) were aware about bio-hazard symbol printed on bags. About 124(81.57%) nursing staff were aware about risk of transmission of various diseases including HIV/Hepatitis B and injuries due to hospital waste. Knowledge of color code of containers for segregation of biomedical waste in study subjects was good. Most of the study subjects gave a correct answer for Human anatomical waste 137(90.13%), cotton or bandages soiled with blood, pus 122(80.26%). As far as practice of biomedical waste management is concerned it was revealed that 130(85.52%) disposed the biomedical waste in specified colour coded container correctly. Only 66(43.42%) reported injuries due to improperly disposed sharps. With regard to use of personal protective measures 45(29.6%) study subjects used a combination of hand gloves, apron, mask and antiseptic lotion for prevention of disease. Conclusion: Continuous monitoring and evaluation of biomedical waste management is necessary to ensure that policies and procedures are followed. Even a small proportion of badly managed waste can potentially be dangerous.
Keywords: Biomedical waste, Nursing staff, Awareness, Practices
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
According to Biomedical Waste (BMW) Management and Handling rules, 1998 of India ?Biomedical Waste? means any waste which is generated during the diagnosis, treatment or immunization of human being or animal in research activities pertaining thereto or in the production or testing of biological.(1) In the persuasion of the aim of reducing health problems, eliminating potential risks and treating sick people, healthcare services inevitably create waste which itself may be hazardous to health. The waste produced in the course of healthcare activities carries a higher potential for infection and injury than any other type of waste. Inadequate and inappropriate knowledge of handling of healthcare waste may have serious health consequences and a significant impact on the environment as well. (2) Advances in medical facilities with the introduction of sophisticated instruments has increased the waste generation per patient in health care units. The rapid mushrooming of hospitals has increased the quantity of hospital waste production. Appropriate waste management system have been developed and installed globally to handle both hazardous and non-hazardous BMW. The Ministry of Environment and Forests notified the BMW (Management & Handling) law in 1998. (3) Though legal provisions exist to mitigate the impact of hazardous and infectious hospital waste on the community, still these provisions are yet to be fully implemented. The absence of proper waste management, lack of awareness about the health hazards from BMW, insufficient financial and human resources and poor control of waste disposal are the most critical problems connected with healthcare waste.(4) Nursing staff is a first level professional who provides direct patient care during duty shift and assist in management of wards/departments. While attending to the above activities BMW is generated. The role of nurses in BMW management is very important. The head nurse should keep an inventory of materials required and check for an adequate supply. Nursing staff should enquire that waste bags are tightly closed. Senior nursing officer is responsible for training new nurses in BMW handling and management. (5) Hence to explore the various issues in safe management of healthcare waste the present study was undertaken among nursing staff with the objectives to study the awareness and practices about BMW management and to assess the use of personal protective measures against BMW. MATERIAL AND METHODS The present hospital based descriptive cross sectional study was conducted in 500 bedded hospital attached to a teaching institute in district Akola of Maharashtra state during the period 1st October to 31st December 2009. The hospital generates about 250 gm waste per bed per day. The permission from head of institution and clearance from ethics committee was obtained before starting the study. Survey started with the necessary consent of the matron and verbal consent of the respective study participants. Total 152 nursing staff were interviewed by predesigned and pretested questionnaire. Before administering the questionnaire the purpose of the study was explained to all participants. The questionnaire was prepared in local language and had a set of questions based on knowledge and practices regarding BMW management. Initially the introductory information of study subject was filled in and then one to one interview began and it took approximately 15 minutes for each participant. Information regarding awareness and practices of BMW Management such as of BMW rules, biohazard symbol, colour coded containers and use of personal protective devices was collected. The actual practice of handling BMW in wards was observed during the morning hours of OPDs i.e. 9:00 a.m. to 1.00 p. m. and noted in observation checklist. All data forms underwent scrutiny for logical inconsistencies, skip patterns and missing values. The data were coded and double entered into a database. The data entry interface was designed to check for referential integrity, missing values and acceptability constraints. Errors identified at any level were referred back to the field for correction. Analysis was done by using suitable statistical methods Anonymity of the participants was maintained throughout the study RESULTS In the present study knowledge about BMW management rules was found in 131(86.18%) study subjects while about 135(88.81%) were aware about bio-hazard symbol printed on bags. About 124(81.57%) nursing staff were aware about risk of transmission of various diseases including HIV/Hepatitis B and injuries due to hospital waste. Majority 145(95.39%) of subjects were in favour of disinfection of waste before disposal and 137(90.13%) agreed that incinerator is the best method for BMW disposal. (Table 1) Knowledge of color code of containers for segregation of BMW in study subjects was good. Most of the study subjects gave a correct answer for colour code of containers for BMW such as Human anatomical waste 137(90.13%), cotton or bandages soiled with blood, pus 122(80.26%), catheters 141(92.76%), empty saline bottles 129(84.86%). But on the other hand very few 13(8.55%) and 9(5.92%) study subjects knew the color code of expired medicines and ointment tubes respectively. (Table 2) As far as practice is concerned it was revealed that 130(85.52%) study participants disposed the BMW in specified colour coded container correctly and 115(75.65%) disposed sharps in puncture proof containers. Only 66(43.42%) nursing staff reported injuries due to improperly disposed sharps and 105(69.07%) correctly disinfected waste before disposal. (Figure 1) With regard to use of personal protective measures, 45(29.6%) nursing staff used a combination of hand gloves, apron, mask and antiseptic lotion for prevention of diseases while most of the study subjects used one or other device. Surprisingly 9(5.92%) of the study subjects did not use any type of safety measure while handling biomedical waste. (Table 3) Gross observation in wards: Syringe and needle cutter were available in 80% wards while IEC regarding BMW was depicted in about 50% wards. BMW was transported from ward to segregation room in plastic color bags put in trolley and then finally it was sent to final disposal site. The duty of waste collection was entrusted to sanitary staff. Though most of the staff knew the importance of incineration in BMW management but unfortunately the incinerator in hospital is not working since a considerable amount of years. The hospital has a sound record keeping system about amount of hospital waste generation and its disposal. DISCUSSION In present study knowledge about BMW management rules was found in 86.18% study participnats. Similar findings were reported by Mathur V et al(2) (91.7%), Saini S et al(6) (60%) and Mathew S et al(7) (73.7%) while findings by Sharma S(8) (25.1%) contradicts the present finding. About 88.81% of nurses were aware about bio-hazard symbol printed on bags which was consistent with the results of Mathew S et al(7) (86.8%), Naik A et al(9) (90%). Health care waste is hazardous because of its composition and ability to transmit infectious diseases including HIV/AIDS and hepatitis B and C.(10) About 81.57% study participants knew about risk of transmission of HIV/Hepatitis B and C, injuries due to BMW and similar findings (82%), (83.33%), (91%), (92.1%) were reported by(2,7,9,11) respectively. 95.39% participants knew the importance of disinfecting the hospital waste before disposal which is more or less in agreement with Mathur V et al(2) (78.3%). Under BMW law 1998, the heart of the law is segregation at origin. Segregating potentially infectious material from the other waste at the point of generation may reduce both volume and cost. (12) Segregation and color coding of containers is probably the most important pivotal point and crucial for further waste management. Improper colour coding ultimately results in an incorrect method of waste disposal. This may lead to failure of the whole system.(2) It is expected that nursing staff should have 100% knowledge of colour code of containers of BMW. In present study it ranged from 5.92% to 92.76%. Findings of the present study are more or less in accordance with the studies conducted by Saini S et al (5) , Naik A et al (6) while these are in contrast with(2) . Low level of knowledge is mainly attributed to poor training facilities which can be improved by intensive training of health worker at all levels. About 85.52% nursing staff disposed waste in specified colour coded container and 75.65% nurses disposed sharps in puncture proof containers which is in agreement with Mathur V(2) (73.3%) and (71.6%) respectively. The practice of reporting of injuries resulting from improperly disposed biomedical waste was found to be low (43.42%) among the study subjects. Stein et al (12) in their study revealed only 37% nurses reported that they ever suffered needle stick injury while(2,8) got the figure as 30% and 40% respectively. Low reporting of injuries may be attributed to the fact that most of the staff are unaware about a formal system of injury reporting which should be established within all the health facilities. It was noticed that the though the nursing staff knew about the disinfection of waste before disposal, not all were practicing it. Lack of effective supply is the reason stated by majority. In the present study about 29.6% nursing staff used a combination of hand gloves, apron, mask and antiseptic Lotion for prevention. Most of the study subjects used one or other preventive device like gloves by 143(94.08%) which is similar to study by Tuduetso Ramokate and Debashis Basu(11) where out of 150 study participants 122(95%) always used gloves while handling BMW. The current status of employees‘ awareness about safety measures practices for BMW management will help the authorities to create strategy for improving the status in future. The BMW management practices in the hospital were satisfactory, except for a deficiency in supply of needle-cutters in a few wards. This is a typical example of an obstacle coming in the way of a mandatory practice, due to a problem of logistics. It is incumbent upon those responsible for procurement of supplies to ensure timely replacement of such items. Again the IEC material regarding BMW was also lacking in significant number of wards. In such a case it would be better to include all these supplies in the stock items like other disposables and items of regular use, which are stocked in the hospital and provided on demand immediately without loss of time. CONCLUSION Thus continuous monitoring and evaluation of BMW management is necessary to ensure that policies and procedures are followed. Even a small proportion of badly managed waste can potentially be dangerous. Recommendations The WHO acknowledges BMW management as a problem and observes that the human element is as important as technology in waste management. There should be institutional initiatives, sustained dialogues, training and interactions of hospital staff regarding biomedical waste management so that the personal protective measures could be used meticulously and safety management of hospital waste would be possible.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author would like to thank all the study participants for sharing their time for the interview. Authors also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. The Gazette of India; Extraordinary, Ministry of Environment and Forest, Notification, New Delhi, 20th July 1998,http//delhigovt.nic.in/dept/health/bmwco m.pdf or http://envfor.nic.in/legis/hsm/biomed.html.
2. Vanesh Mathur, S Dwivedi, MA Hassan, and RP Misra: Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices about Biomedical Waste Management among Healthcare Personnel:Indian J Community Med. 2011 Apr-Jun; 36(2): 143–145.
3. Bhagya Bhaskar, Hema Nidugala, Ramakrishna Avadhani: Biomedical waste management – knowledge and Practices among healthcare providers in mangalore: Nitte University Journal Of Health Science. Vol 2,No 1,March 2012,ISSN 2249-7110.
4. Plianbangchang PH. W.H.O. Publication; ?A Report on Alternative Treatment and NonBurn Disposal Practices?; Safe Management of Bio-medical Sharps Waste in India.
5. Bio- Medical Waste Management- Self Learning Document for Nurses and paramedical. WHO, India country office , New Delhi
6. Saini S, Nagarajan SS, Sarma RK: Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Biomedical Waste Management Amongst Staff of a Tertiary Level Hospital in India. Journal of the Academy of Hospital Administration, 2005; 17 (2): 1 – 12.
7. Savan Sara Mathew, A. I. Benjamin, Paramita Sengupta. Assessment of biomedical waste management practices in a tertiary care teaching hospital in Ludhiana. Health line, 2011 Dec; 2(2): 28-30.
8. Shalini Sharma. Awareness about biomedical waste management among healthcare personell of some important medical centers in Agra. International Journal of Environmental science and Development. Vol 1, No 3, August 2010-251-255.
9. Ashish Naik, Bhautik Modi, Bansal R K. Biomedical Waste Handling practices in urban health centre of Surat Municipal Corporation. National Journal of Community Medicine; Vol 3, issue 1 Jan-March 2012.
10. World Health Organization. WHO Fact Sheet no. 281. 2004. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization. http://www.who.int.org.
11. Tuduetso Ramokate, Debashis Basu. Health care waste management at an academic hospital: knowledge and practices of doctors and nurses. Health - South African Medical Journal, June 2009.
12. Stein AD, Makarawo TP, Ahmad MF. A survey of doctors‘ and nurses‘ knowledge, attitudes and compliance with infection control guidelines in Birmingham teaching hospitals. J Hosp Infect. 2003; 54:68–73.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License