IJCRR - 5(11), June, 2013
Pages: 87-93
Date of Publication: 18-Jun-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
INCREASING PREVALENCE OF EXTENDED SPECTRUM BETA LACTAMASES (ESBLS) PRODUCING E.COLI AND KLEBSIELLA SPP IN OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENTS (OPDS) PATIENTS IN URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS (UTIS) IN TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
Author: Gopal Kashyap, Sweta Gupta, Ved Prakash Mamoria, Pushpa Durlabhji, Dinesh Jain
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Extended-spectrum \?-lactamases (ESBLs) are plasmid-mediated group of fast growing enzymes synthesized by the Gram negative bacteria that are causing medicinal crisis. At present, ESBLs has been increasing as a serious pathogen having the property multidrug resistance. So, The present study was undertaken to find out the prevalence of ESBLs positive E. coli and Klebsiella in urinary isolates obtained from various In-patient Departments (IPDs) , Outpatient Departments (OPDs) and Intensive Care units (ICUs). Methods: Processing of 251 non- repetitive urine samples received during a period of about one year for detection of ESBLs positive Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. was done. All suspected isolates of ESBLs producers were confirmed by the Double Disc potentiating discs test, Double disc synergy test and E-Test. Results: Out of Two fifty one urinary isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. 93 (37.1%) were confirmed as ESBLs producers and 158(62.9%) were non ESBL producers by all the three tests of confirmation. 61 out of 93 (65.6%) were from OPDs and in all IPDs maximum ESBLs producing urinary isolates were obtained from Medicine wards 12/93 (12.9%). Conclusion: Results indicate that now ESBL producers are increasing in community. So, routine ESBL detection should be made mandatory not only in indoor patient but also in outdoor also. Appropriate use of third generation cephalosporins must be encouraged to reduce the risk of multidrug resistant bacteria and to make an antibiotic policy.
Keywords: Extended-spectrum ?-lactamases, Gram negative bacteria, E. coli
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common infectious disease ranking next to Respiratory tract infection [1] and is an important cause of morbidity and mortality. UTI is also the most common hospital acquired infection approx. 35% of total infection.[2] Bacteria are the major causative organism of UTI and E.coli is the most prevalent-causative bacteria of UTI in community as well as hospital acquired UTIs. [3,4] followed by Klebsiella, Staphylococcus, Proteus & Pseudomonas. These bacteria along with other members of Enterobacteriacae are found to produce an arsenal of enzymes known as extended spectrum β- lactamases. UTI can usually be treated with a short course of antibacterial therapy.[4] β-lactamases are enzymes which open β-lactam ring (4 carbon atom ring) of penicillin/cephamycins (i.e cefoxitin & cefotetan). β-lactam antibiotics have 4 atom ring known as β-lactam ring. β-lactamases break the β lactam ring open and therefore deactivate the antibacterial activity of drugs. Gradually with time the property of inactivating the antibiotics spread to other groups of bacteria in Enterobacteriacae and also larger group of antibiotics were inactivated. This property was first documented in 1983 in Germany in K. Pneumoniae [5] & spread quickly to Europe and US and was later known as Extended spectrum β-lactamases.[6,7] New threat was proposed by Amp C β- lactamases as they confer resistance to cephamycins (7-2 methoxy cephalosporin) and not affected by commercially available β lactamases inhibitors with loss of outer membrane porins provide resistance to carbapenems [8] ESBLs become clinically important because they destroy cephalosporins given as first line antibiotics in hospital. This may lead to inappropriate treatment and increased mortality. ESBLs producers are multi-resistant to nonlactam antibiotics such as quinolones, tetracyclines, amino glycosides and trimethoprim/cotrimoxazole, narrowing treatment options due to plasmid mediated transfer of resistance and provides therapeutic challenges. [9] Detection of ESBL production by urinary isolates is therefore very important to ensure appropriate antibiotic treatment. As the prevalence of ESBLs differs significantly both geographically and with different risk factors in patients, knowledge of these variations can help in appropriate and timely antibiotic therapy as well as avoidance of preventable antibiotic use. With reports of high prevalence of ESBL producers and lack of information in India, the present study was carried out to find out the distribution of ESBL producing bacteria isolate from urine in different units of a tertiary care hospital in Jaipur and in community acquired UTIs presenting to this hospital.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
The present study was carried out in the Department of Microbiology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur (Rajasthan).The test group selected was the population of patients from various Out Patient Departments, different wards, and Intensive care units in the hospital regardless of their age, sex, occupation, religion and ethnicity. A Proforma was filled accordingly. Sample collection Processing of 251 non- repetitive urine samples received during a period of about one year for detection of ESBLs positive Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. was done. Sample was collected with Universal precautions by prescribed sterile technique. Samples were transported to the laboratory as soon as possible maintaining optimum transportation conditions. Routine microscopy of all urine samples was done and samples with more than /equal to 5 white blood cells /HPF were selected. Sample culture All culture Medias were obtained from Hi media Laboratories Mumbai, India. Primary inoculation was done on the Blood agar, MacConkey agar which was incubated 18-24 hrs at 370C aerobically. Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. from samples were finally identified by standard techniques based on Colony morphology, Gram’s staining, Hanging drop for motility and Biochemical tests as per CLSI guidelines. Antimicrobial susceptibility test using modified Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method was done of all isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. All the strains identified were tested for ESBLs production as per CLSI guidelines. Following criteria were used in isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. for selection of ESBLs producers: Screening Isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. were examined for their susceptibility to 3rd generation cephalosporins Cefotaxime and Ceftazidime antimicrobial discs.
In our isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. the diameter of zone of inhibition was measured for Cefotaxime (30µg) & Ceftazidime (30µg) antimicrobial discs. Diameter of ≤ 22mm for Ceftazidime and/or ≤ 27mm for Cefotaxime was considered as ESBLs suspects as per NCCLS guidelines. [10] All suspected isolates of ESBLs producers of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella were confirmed by the Double Disc potentiating discs test, double disc synergy test and few suspected isolates were also be confirmed by E-Test. Quality control with Standard strains for Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Klebsiella spp. 700603 was also done.
RESULTS
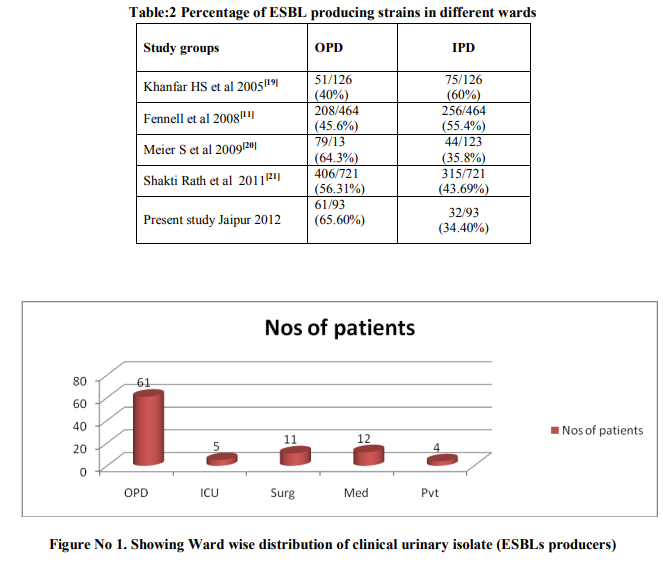
The present study was under taken to detect the prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of ESBLs positive Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. in urinary isolates obtained in Department of Microbiology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College, and Jaipur. The samples were obtained from OPDs, IPDs and ICUs of various Department from Mahatma Gandhi Hospital,Jaipur. 251(Two fifty one) urinary isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. were processed for ESBL detection. In primary screening of 251 isolates 97 were found to be resistance to Cefotaxime and/or Ceftazidime antibiotic discs. Those 97 suspects of ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp.in urinary samples were further tested for confirmation by Double Disc Synergy test and Double Disc Potentiation test .Out of 97 suspects of ESBL producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp.in urinary samples 75 (77.32%) were confirmed by Double Disc Synergy test and 90 (92.78%) were confirmed by Double Disc Potentiation test.25 suspected ESBL producing urinary isolates were tested with E-Test. All except four isolates were tested positive by E-Test. 4(four) isolates were not confirmed positive by any of the three tests hence they were considered non ESBLs producers. Out of 251(Two fifty one) urinary isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. 93 (37.1%) were confirmed as ESBLs producers and 158(62.9%) were non ESBL producers by all the three tests of confirmation. Out of 93 confirmed ESBLs producers Escherichia coli (89/93) (95.7%) was the predominating organism.52/93 i.e. 56% of ESBLs producing isolates were obtained from female patients. Maximum ESBLs producing isolates were from patients of 20-40 yrs age group followed by 10-20 yrs age group. Maximum ESBLs producing urinary isolates i.e. 61/93 (65.6%) were from Outpatient Departments of various clinical disciplines. Of all In-patient Departments maximum ESBLs producing urinary isolates were obtained from Medicine wards 12/93 (12.9%).
DISCUSSION
ESBLs are an example of the increasing number and diversity of the enzymes that inactivate β- lactam antibiotics. Multi drug resistance and ESBLs enzymes producing E.coli & Klebsiella spp. are major threat to treat urinary tract infections. A dramatic increase in the frequency of ESBL producing E.coli & Klebsiella spp. has been observed in last decade. Frequent and inappropriate use of antibiotics in human led to increasing resistance rate making the treatment of urinary tract infections more complex. ESBLs has become a major problem worldwide as is confers resistance to the third generation broad spectrum cephalosporins. Although CLSI guidelines exist for detection of E.coli & Klebsiella spp., no such recommendation exists for other ESBLs producing organisms. Failure of empirical therapy, which is usually, initiated with third generation cephalosporins due to resistance of ESBL producing E.coli & Klebsiella spp. lead to increase in mortality rate in Hospital settings.
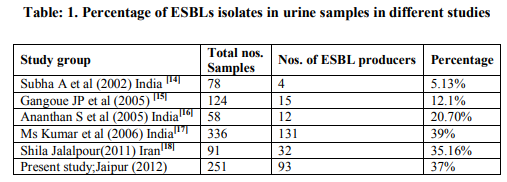
Emphasized must be laid on developing rapid screening method for ESBL detection by clinical laboratories so as to report ESBLs producing organisms in appropriate time. Combination of Antibiotics with their clavulanate salt confirms ESBLs production. Clinical microbiologist play an important role in devising ways and means of rapidly identifying these ESBLs producing organisms and help institutions to initiate appropriate therapy. Detection become more important by the fact that resistance to one of the 3GC cephalosporins means therapeutic resistance to all cephalosporins up to 3GC even when in vitro sensitivity may be detected otherwise. In this study observed that female have a higher probability (56%) of predisposition to UTIs. These findings were in accordance with the study by Fennell et al (2008) from Ireland and it was 65.5%.Another study by Babypadmini S et al (2004) from India where they found 56.62 %.[11,12] Therefore our study correlate with various other studies which shows higher percentage of isolates were from female patients. [11,12,13] Most of the patients in our study were from the age group 20-40yrs (43 %), which shows that UTI is more common in middle age group person in our population compare to Tada Dharmistha G et al 2012 study in which most of the patients were from the age group 10-20 yrs (30%).[13] The prevalence of ESBLs production in India varies from 5-60%in urinary isolates. In present study the prevalence of ESBLs production was 37% which correlates with MS Kumar et al and S Jalalpour. [17,18] The prevalence of ESBLs producers organisms are on the rising trend as seen in various studies since 2002 to 2012. The prevalence of ESBLs producing E.Coli is 35.45% which correlates with Babypadmini S et al & Shila Jalalpour. Prevalence of Klebsiella spp. is 1.59% which correlates with Joseph Gangoue et al. [12,18] Our study showed that most of the ESBLs producing isolates were from the Out Patient Departments (Community Acquired).Various studies show that prevalence of Community Acquired UTIs is increasing in recent times. In the beginning ESBLs were in a good number identified to be a hospital based crisis but it is now becoming more common along with community acquired isolates, especially Esch. coli (Shila Jalalpour(2011) Iran[18] Parul Agarwal et al 2008 Pune [22]. In the present study Esch.coli and Klebsiella spp. were found 35.45% and 1.59% respectively. This was due to illogical and ample use of third generation cephalosporins in both the hospital and community and is alleged to be the main cause of mutations in these enzymes that lead to the appearance of the ESBLs. [23] Initially ESBL producers were restricted to hospital –acquired infections only, but they have now also been isolated from outpatient departments. Major outbreaks involving ESBL producing strains have also been reported from all over the world.
CONCLUSION
Considering various findings of the present study, it can be concluded that Extended Spectrum beta lactamases are gradually increasing in community in India. ESBL producing organisms have become clinically important in last two decades because of increasing trend in prevalence leading to increase in antimicrobial resistance. Increase antimicrobial resistance result in increase morbidity, mortality and cost of health care. In order to prevent and control the emergence of antimicrobial resistance in ESBL producing organisms it is of utmost importance to limit the misuse and overuse of antibiotics especially broad spectrum antibiotics. ESBL producing strains were previously common in Inpatient Departments few years back but nowadays they are commonly isolated in Outpatient Departments therefore early detection is of clinical importance for effective management of patients. To conclude, early and sensitive methods to detect ESBL producing strains should be practiced so that appropriate antibiotics may be given to treat the patients and further decrease the spread of ESBL producing microorganisms. It is also utmost important to formulate appropriate hospital antibiotic policies and taking adequate precautionary measures to decrease the spread of ESBL producing microorganisms.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors are grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
1. Nachimuthu R ,Chethpalayam SS,Balasubramanium V,Ravichandran Palamappam K,Kannan VR.,2008.Urinary tract Infection and Antimicrobial susceptibility patternof Extended Spectrum Beta Lactamase producing Clinical isolates,Adv in Biol Research.,2(5-6):78- 82.
2. Bailey and Scott?s Diagnostic Microbiology.12th Edition .
3. Walter E. Stamm, Urinary Tract Infection,Pyelonephritis,and Prostatitis. Harrison’s Principle of Internal Medicine.17th Edition(Vol 2):1820-1827
4. Paterson, D.L., W.C. Ko, Von Gottberg, et al., 2001.Outcome of cephalosporin for serious infection due to apparently susceptible organisms producing extended spectrum Beta-lactamases: implications for the clinical microbiology laboratory, J.Clin Microbiol.,39:2206-2212.
5. Knothe H, Shah P,Kremery V et al.(1983).Transferable resistance to cefotaxime,Cefoxitin,Cefamandole and Cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens.Infection II(6):315-317
6. Quinn JR,Miyashiro D,Sahm D et al.Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM10) conferring selective resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1989;33:1451-6.
7. Jacoby GA ,Medeiros AA,O Brien TF, et al. Broad spectrum transferable beta lactamases.N Eng J Med 1988;319:723-4
8. Phillipon A,Arlet B,Jacoby GA.2002.Plasmid-Determined AmpC-Type β-Lactamases.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.,2002;46:1-11.
9. Matsumoto, Y., and M. Inoue. 1999. Characterization of SFO-1, a plasmidmediated inducible class A beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:307-31.
10. Rosenthal VD, Maki DK, Jamulitrat S, et al. International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium report ,data summaryfor2003-2008,issued June 2009.Am J Infect Contr2010;38:95-106.
11. Jerome Fennell, Akke Vellinga et al (2012) “Increasing prevalence of ESBL production among Irish clinical Enterobacteriaceae from 2004 to 2008: an observational study”; BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:116
12. Babypadmini S, Appalaraju B. Extendedspectrum β-lactamases in the urinary isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae – prevalence and susceptibility pattern in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Med Microbiol 2004; 22(3): 172-74.
13. Tada Dharmishtha G, Gandhi Paragi J, Patel Kiran N.A study on antibiotic related resistance in UTI patients: a comparison between community acquired and hospital acquired E. Coli. National Journal of Community Medicine. Vol 3 Issue 2 AprilJune 2012 Page 255.
14. Subha A, Ananthan S. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) mediated resistance to the third generation cephalosporins among Klebsiella pneumoniae in Chennai. Indian J Med Microbiol 2002; 20:92-95
15. Joseph Gangoue P, Branka bedenic et al . Extended spectrum β-lactamases producingEnterobacteriaceae in Yaunde,Cameroon.J Clin Microbio,july 2005,3273-77.
16. Ananthan S, Subha A. Cefoxitin resistance mediated by loss of porin in clinical strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Indian J Med Microbio, (2005) 23(1):20-23
17. MS Kumar, V Lakshmi, R. Rajagopalan. Occurrence of Extended –spectrum β- lactamases among Enterobacteriaceae ssp. Isolated at a tertiary care institute. Indian J Med Microbio, (2006) 24(3): 208-211
18. Shila Jalalpour (2011) “ Survey frequency of extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia strains isolated from urinary tract infection in Iran”; African Journal of Microbiology Research vol 5(22) pp. 3711- 3715, 16, December 2011.
19. Husam S. Khanfar, Khalid M. Bindayna, Abiola C. Senok, and Giuseppe A. Botta. Extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL) in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae: trends in the hospital and community settings. J Infect Dev Ctries 2009; 3(4):295-299.
20. S. Meier, R Weber et al “Extendedspectrum β-lactamase-producing gramnegtive pathogens in community acquired urinary tract infections: an increasing challenge for antimicrobial therapy”; Infection(2011) 39:333-340.
21. Shakti Rath, Debasmita Dubey , Mahesh C. Sahu,et al.Surveillance of multidrug resistant Escherichia coli in a hospital in India.
22. Agrawal P, Ghosh A N, Kumar S, Basu B, Kapila K. Prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamases among Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2008;51:139-42
23. Chaudhary, U, Aggarwal, R.Extended spectrum beta lactamases(ESBL)- An emerging threat to clinical theraputics, Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology,2004;.22(2): 75-80.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License