IJCRR - 5(15), August, 2013
Pages: 111-118
Date of Publication: 17-Aug-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF RICE HUSK FILLER ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF POLYETHYLENE MATRIX COMPOSITE
Author: Atuanya C.U. , Olaitan S.A. , Azeez, T.O. , Akagu C.C. , Onukwuli O.D., Menkiti M. C.
Category: Technology
Abstract:In the present work, the effect of rice husk filler loading (10%, 20%, 25%, 30%, and 35%) on the mechanical properties of recycled low density polyethylene (RPE) and mixed with 20 percent weight fraction of virgin polyethylene (MPE) composites was aimed to be investigated. The waste polyethylene was blended with virgin polyethylene and the composites of RPE and MPE were moulded with the addition of rice husk filler using injection moulding machine at a pressure 150MPa and temperature 160oC. The composites were cut into specified dimensions and mechanical properties were conducted on them. Tensile strength increased up to 10 percent weight fraction of rice husk filler in the composites and later decreased above 10 percent filler loading. Tensile modulus, flexural strength and modulus, and Brinell hardness increases with increased filler loading, but impact strength decreases with increased in filler loading. The rice husk filler loading had significant effect (p < 0.05) on the mechanical properties of MPE composite compared with RPE composite which indicated that rice husk filler may be used for reinforcement of Polyethylene.
Keywords: Rise husk filler, Polyethylene, Mechanical properties
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The material strength of the polymers required the reinforcement of the polymer matrices for purpose of improving the mechanical strength and performance of the polymer materials. Many researchers have worked on the use of natural fibers and fillers (jute, stalk, baggase, groundnut shell, palm kernel, banana and coconut, wood etc.) to strengthen the properties of the polymer in many applications (Sui et al, 2008; Hardinnawirda and SitiRabiatull, 2012; Behzad, 2011; Raju et al, 2012; Chantara et al, 2010; Luyt, 2009). Natural fillers due to its compositions (cellulose, pectin, hemicelluloses and lignin) contributed greatly to the structural performance of polymer composites (Raju et al, 2012; Kim et al, 2004; Yang et al, 2004). Currently, natural fibers form an alternative for glass fiber, the most widely applied fiber in the composite technology. The advantage of the natural fibers over synthetic fibers like aramid, carbon or glass fiber are not only due to its low densities, non abrasive, non-toxic, high filling levels possible resulting in high stiffness, specific properties, biodegradable, inexpensive, good thermal and acoustic properties, good calorific value, enhanced energy recovery and reduces biomass in the environment (Raju et al, 2012; Kim et al, 2004; Yang et al, 2005; Gacitua et al, 2005 ) but also due to the fact that natural filler prevents thermal expansion of composites. Rice husk is among natural materials that have been used in polymer composites (Imoisili et al, 2012) and contains 35% cellulose, hemicellulose 25%, lignin 20% and ash 17% (94% silica) by weight (Panthapulakkal, 2005). Researchers have shown that rice husk filler used in thermoplastics and thermosets composite improves mechanical and structural performance of the composites but studies on its benefit are limited to density, tensile strength and thermogravimetric analysis (Kim et al, 2004; Yang et al, 2004; Yao et al, 2008) without considering the waste polyethylene. This study was to investigate the effects of rice husk loading on the mechanical properties of recycled low density polyethylene (LDPE) matrix blended with virgin LDPE so as to reduce biomass of rice husk fiber and to conserve polyethylene waste in the environment.
METHODOLOGY
Both virgin and recycled polyethylene was used in the study. The waste polyethylene (PE) was obtained from the industrial waste of IBETO Group of Companies and crushed using the fabricated crushing machine at National Engineering Design and Development institute (NEDDI) both in Nnewi, Anambra State, Nigeria. The virgin PE was obtained from chemicals line in Ugah market, Onitsha, Anambra state, Nigeria. The rice husk used was a by-product of a local rice mill in Otolo Nnewi and Kpoko Bros., Atani Road, Onitsha, Nigeria. Composite Preparation The rice husk used was sun-dried and then ovendried at 1100C for 2 days to a moisture content of almost 3.0wt% and finally, sieved to 18-mesh size. The composites were prepared in mixingratio of virgin polyethylene, recycled polyethylene and rice husk as shown in the Table 1. Composite Processing The rice husk filler and polyethylene were manually mixed and then fed into an injection moulding machine of the reciprocating screw type to produce the composite samples. The operating pressure and temperature of the injection moulding machine was 150MPa and 1600C respectively. Process time for each sample is 30 – 60 seconds averagely. The following mechanical tests were carried out to assess the influences of the rice husk on the mechanical performance of polyethylene after conditioning to 65% Relative Humidity and temperature of 25oC. Samples of the rice husk filler - polyethylene composites were cut into specified dimensions and tested at room temperature in accordance with ASTM 638-90 standards.
Tensile Testing
Tensile properties were carried out on the specimens using a KAOH TIEH Instron Testing Machine, in accordance with ASTM 638-90, at a cross-head speed of 200rev/min. The dimensions of each sample were 150mm (length) x 30mm (width) x 5mm (thickness) and held by the gripping heads, the samples were pulled till failure and the respective loads and extensions noted. The values thus gathered were used to calculate the strain, tensile strengths, and modulus of the samples A to L using the equation (1) and (2) as reported by Raju et al (2012).

Flexural Testing Flexural properties were carried out by 3-point bending tests on composite samples with dimensions 60mm (span) x 20mm (width) x 5mm (thickness) using a WP 300.4 bending device in accordance with ASTM 790 – 90. Equation 3 and 4 was used to obtain the flexural strengths and modulus respectively of the samples.

Impact Testing
The unnotched impact properties were conducted on all specimens in accordance with ASTM D 256-90. Prepared samples were subjected to fracture by a pendulum – Type Impact Testing Machine and the unnotched toughness values of the composites obtained by reading off the energy expended to rupture each sample.
Hardness Testing
Brinell Hardness Test was conducted on samples using a manually-operated Universal Testing Machine. A hardened steel ball with a diameter of 10mm was used in performing the test. The indentations on the specimens were measured (diameter-wise) and appropriate mathematical methods used for conversion to obtain the Brinell Hardness Values. The equation for the Brinell Hardness Number (HBN) is written as:
 ???????
???????
Where P is the applied Load measured in kg, D is diameter of steel ball (10mm) and d is the diameter of indentation (mm). Statistical Analysis The statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS Version 17.0 with bivariate correlations. The Pearson’s correlation coefficient test was used for the test of significance with two tail of p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant between RPE and MPE composites.
RESULTS
Effect of rice husk filler loading on tensile property of polyethylene composites
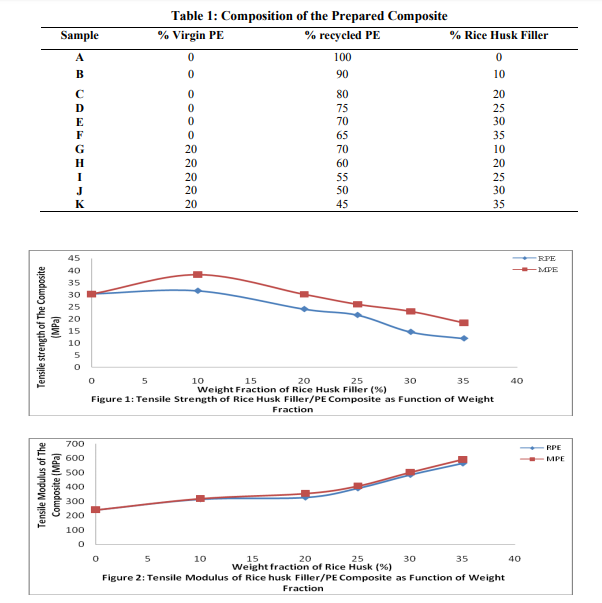
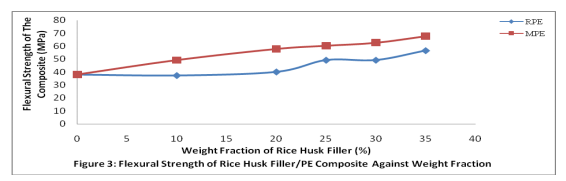
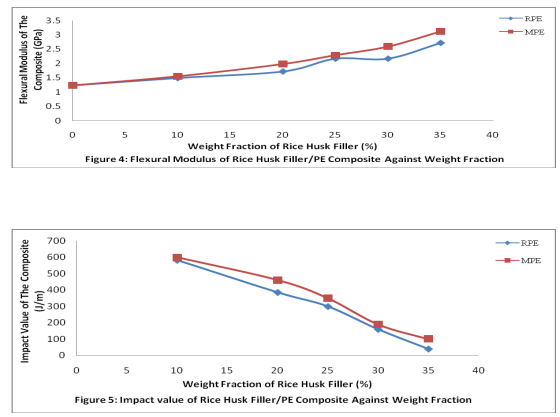
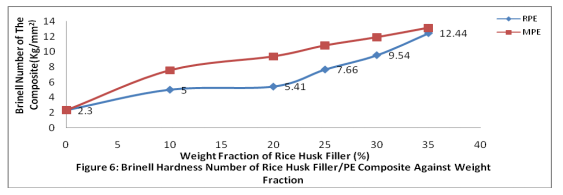
Tensile strength and modulus of the PE composite as a function of the weight fraction of the rice husk filler for both recycled polyethylene (RPE) and recycled polyethylene with 20 % virgin polyethylene (MPE) are illustrated in the Figure 1 and 2 respectively. Effect of rice husk filler loading on the flexural property of the polyethylene composites The flexural strength increases steadily from 38 MPa to 67.7 MPa and 56.6 MPa for RPE and MPE respectively with increased rice husk filler loading as illustrated in the Figure 3 as well as flexural modulus as shown in the Figure 4. Effect of rice husk filler loading on the impact strength of the polyethylene composites Figure 5 depicts that the impact strength of the polyethylene composites decreases steeply from 600J/m to 100J/m for RPE and 583J/m to 40J/m for MPE with increased weight fraction of the rice husk filler in the composite as shown in the Figure 5. Effect of rice husk filler loading on the brinell hardness of the polyethylene composites The magnitude of Brinell hardness of the rice husk filler polyethylene composites increases from 2.3N/mm2 to 13.15N/mm2 and 12.44N/mm2 for RPE and MPE respectively with increased weight fraction of rice husk filler loading as shown in Figure 6.
DISCUSSION
It can be deduced that the tensile strength of the composite increases with increased rice husk filler loading in both RPE and MPE as illustrated in Figure 1 and 2. The tensile strength of RPE and MPE composite with 10 percent of weight fraction of the rice husk filler loading increases from 30.33 MPa to 38.4 MPa and 31.58 MPa which amounted to 4.1 and 26.6 percent respectively. It was observed also that the tensile strength decreased to 18.37 MPa and 11.88 MPa for RPE and MPE respectively with increased rice husk loading up to 35 percent filler loading as illustrated in Figure 1. The increased tensile strength attributed to an effective creation of an interfacial adhesion bond between filler (hydrophilic) and PE (hydrophobic), which resulted to morphological changes as reported by many researchers (Luyt, 2009; Yao et al, 2008; Yang et al, 2004; Ratnam et al, 2010). The observation is contrary to the case of unsaturated polyester resin as reported by Hardinnawirda and SitiRabiatull (2012). This is an indication that rice husk filler has a better interfacial adhesion with polyethylene matrix compared with unsaturated polyester resin. It was also obtained that there is significant effect of 0.007 (p < 0.05) with a correlation coefficient of 0.932 between MPE and RPE composite which indicated that the incorporation of 20 percent of virgin PE was significant in the composite applications. The tensile strength of the composites decreases after ten (10%) percent of filler loading was due to the inability of the filler to support stresses transferred from the polyethylene matrix. The tensile modulus also increases with increased weight fraction of the rice husk filler loading as illustrated in the Figure 2 and similar to the report of many researchers (Yang et al, 2004; Imoisili et al, 2012; Raju et al, 2012). The flexural strength increases steadily from 38 MPa to 67.7 MPa and 56.6 MPa with 78.2 and 48.95 percent for RPE and MPE respectively with increased rice husk filler loading as illustrated in the Figure 3 as well as flexural modulus as shown in the Figure 4. This indicated that the increased filler loading, increases the stiffness of the rice husk filler/polyethylene composite. This is a common phenomenon and similar to the report of many researchers (Zaini et al, 1996; Yang et al, 2004; Imoisili et al, 2012). The 20 percent addition virgin PE on the flexural strength of the composite was significant with 0.035 (p < 0.05) and correlation coefficient of 0.844. Though, there is no significant effect on the flexural modulus between RPE and MPE since significant level 0.556 (p > 0.05) which indicated that 20 percent of weight fraction of the virgin PE in the composite was insignificant on flexural modulus. The result of unnotched Izod impact test depicts that the impact value decreases steeply with increased weight fraction of the rice husk filler in the composite as shown in the Figure 5. The addition of up to 35 weight fraction of rice husk weight filler loading causes the reduction in impact strength of the RPE and MPE to 40J/m which is 93.1% and 100 J/m which is 83.3% respectively. This observation could be attributed to the poor wetting of the rice husk filler by the PE blends, which lead to poor interfacial adhesion between the fiber and polymer matrix resulting in weak interfacial regions. Poor interfacial adhesion between hydrophobic matrix and hydrophilic nature filler usually results in decrease toughness as reported by Raju et al (2012). Thus, the decline in impact strength with increased rice husk filler loading is attributed to the poor interfacial adhesion between the hydrophobic polyethylene matrix and hydrophilic (rice husk filler). In addition, the incorporation of the filler resulted to reduction in polymer chain mobility, thereby lowering the ability of the system to absorb energy during fracture propagation. The significant effect of 0.001(p < 0.05) with correlation coefficient of 0.994 was obtained between RPE and MPE composites which attributed to 20 percent of virgin polyethylene. It is apparent from Figure 6 that the increase of 5 to 35 weight fractions of rice husk filler increases the hardness of both RPE and MPE composite from 2.3 to 12.44 and 13.15 N/mm2 which is equivalent to 440.9 percent and 471.7 percent for RPE and MPE respectively with Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.944 and significantly 0.009 (p < 0.05) with correlation coefficient of 0.923. This trend of results is expected because as more filler is incorporated into the polymer matrix, the elasticity of the polymer chain reduced resulting in more rigid composites.
CONCLUSION
Based on the result obtained, there is significant effect on mechanical properties of rice husk filled RPE and MPE composites with exception of flexural properties. The upward trend exhibited in tensile strength with the 10 percent rice husk filler for both RPE and MPE coupled with the enhancement in tensile modulus, flexural strength and modulus, and hardness indicated that rice husk filler may be used for the reinforcement of RPE and MPE up to 10 percent filler. However, a reduction in tensile strength at above 10 percent rice husk filler loading and the gradual drop in impact strength with increased rice husk filler loading may be due to poor interfacial bonding and agglomeration of rice husk filler. Also, Rice husk filler showed superior tensile strength properties in MPE composites due to addition of 20 percent weight fraction of virgin polyethylene compared with the low tensile strength recorded in the rice husk filler – RPE composite. Therefore, rice husk not only helpful for reinforcement of waste polyethylene but reduces biomass level of rice husk and polyethylene waste in the environment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank IBETO Group of Companies, National Engineering Design and Development institute (NEDDI) and Nnamdi Azikiwe University, Awka, Nigeria for both materials and financial support.
References:
1. Sui, G, Zhong, WH, Yang, XP, Yu, YH, Zhao, SH. Preparation and Properties of Natural Rubber Composites Reinforced with Pretreated Carbon Nanotubes. Polymers for Advanced Technologies (Pat) 2008, 1-7.
2. Hardinnawirda, K, Sitirabiatull, IA. Effect of Rice Husks as Filler in Polymer Matrix Composites. Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Sciences (JMES) 2012, 2: 181-6.
3. Behzad K. Investigation of Reinforcing Filler Loading on the Mechanical Properties of Wood Plastic Composites. World Applied Sciences Journal 2011, 13 (1): 171-4.
4. Raju, GU, Kumarappa, S, Gaitonde, VN. Mechanical and Physical Characterization of Agricultural Waste Reinforced Polymer Composites. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3 (5): 907-16.
5. Raju, G, Ratnam, CT, Ibrahim, NA, Rahman, MZ and Wan – Yunus, WMZ. Enhancement of PVC/ENR Blend Properties by Poly (Methyl Acrylate) Grafted Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110 (1): 368-75.
6. Kim, H-S, Yang, H-S, Kim, H-J, Park, H-J. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Rice Husk Flour Filled Thermoplastic Polymer Composites. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2004, 76: 395–404.
7. Yang, H-S, Wolcott, MP, Kim, H-S, Kim, HJ. Thermal Properties of Lignocellulosic Filler-Thermoplastic Polymer Bio-Composites. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2005, 82: 157–60.
8. Yang, H-S, Kim, H-J, Son, J, Park, H-J, Lee, B-J, Hwang, T-S. Rice-husk flour filled polypropylene composites; mechanical and morphological study. Composite Structures 2004, 63: 305–12.
9. Hassan, SA, Ani, FN, Abubakar, A. Oil-palm fiber as natural reinforcement for polymer composites. Society of plastics engineers plastics research online 2009, 1-3.
10. Gacitua, WE, Ballerini, A, Zhang, J. Polymer Nanocomposites: Synthetic and Natural Fillers A Review. Maderas. Ciencia Y Tecnología 2005, 7(3): 159-78.
11. Ratnam, CT, Fazlina, RS, Shamsuddin, V. Mechanical Properties of Rubber-Wood Fiber Filled PVC/ENR Blend. Malaysian Polymer Journal 2010, 5 (1): 17-25.
12. Luyt, AS. Editorial corner – a personal view Natural fibre reinforced polymer composites – are short natural fibres really reinforcements or just fillers? eXPRESS Polymer Letters 2009, 3 (6): 332.
13. Imoisili, PE, Ukoba, KO, Ibegbulam, CM, Adgidzi, D, Olusunle, SOO. Effect of Filler Volume Fraction on the Tensile Properties of Cocoa-Pod Epoxy Resin Composite. International Journal of Science and Technology 2012, 2 (7): 432-4.
14. Deepa, B, Pothan, LA, Mavelil-Sam, R, Thomas, S. Structure, properties and recyclability of natural fibre reinforced polymer composites. Recent Developments in Polymer Recycling 2011: 101-20.
15. Imoisili, PE, Olunlade, BA, and Tomori, WB. Effect of Silane Coupling Agent on the Tensile Properties of Rice Husk Flour (RHF) Polyester Composite. The Pacific Journal of Science and Technology 2012, 13 (1): 457 - 62.
16. Yao, F, Wu, Q, Lei, Y, Xu, Y. Rice straw fiber-reinforced high-density polyethylene composite: effect of fiber type and loading. Industrial Crops and Products 2008, 28(1): 63–72.
17. Zaini, MJ, Fuad, MYA., Ismail, Z, Mansor, MS, Mustafah, J. The Effect of Filler Content and Size on the Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Oil Palm Wood Flour Composites. Polymer International 1996, 40: 51-5.
18. Kim, HS, Yang, HS, Kim, HJ, Park, HJ. Thermogravimetric analysis of rice husk flour filled thermoplastic polymer composites, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 76: 395-404.
19. Panthapulakkal, S, Sain, M, Law, S. Effect of coupling agents on rice husk filled HDPE extruded profiles, Polym. Int. 2005, 54: 137- 42.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License