IJCRR - 9(5), March, 2017
Pages: 22-25
Date of Publication: 20-Mar-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence of Leptospirosis among paddy field workers in Pune, Western India
Author: Potdar Gayatri A.1, Pol Sae S.2, Bharadwaj Renu S.3
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Leptospirosis has been under-reported and under-diagnosed in India. Certain occupational groups such as agricultural labors, animal handlers, sewage workers, abattoir workers and miners etc. constitute high risk groups for acquiring Leptospirosis.
The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence of anti-Leptospiral antibodies among paddy field workers reporting with fever to a rural hospital in Pune district and thus to ascertain the extent of the problem in paddy field workers in Maharashtra , India.
Settings and Design: This was a cross-sectional prospective study. A total of 160 paddy field workers were included in the study, during year 2013 to2014.
Materials and Methods: All patients who presented with clinical features were tested with IgM ELISA and MAT tests.
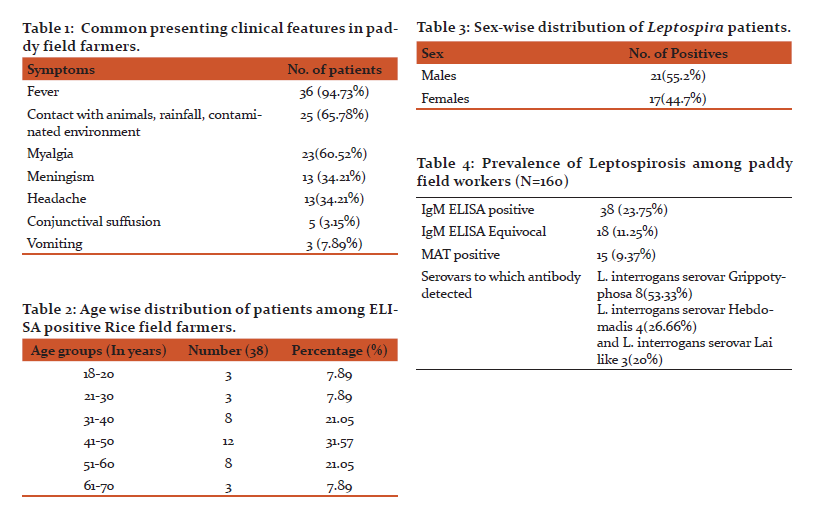
Results: The common clinical presentation amongst the paddy farmers was myalgia and headache in association with fever. Majority of patients were in the age group 30-50 years. Total 55.2% males and 44.7% females were affected. IgM ELISA was positive in 23.8% of the patients. Total 9.4 % were positive by MAT test. The commonest serovars to which antibodies were detected was Grippotyphosa. Total 60.52% of patients with laboratory confirmed leptospirosis gave evidence of leptospirosis by Faine's Criteria.
Conclusions: Leptospirosis is thus an important cause of febrile illness in paddy field workers at risk and must be kept in mind in the management of such patients. The major prevailing serovars in Maharashtra, western India are Grippotyphosa and Hebdomadis, which differs from the prevalent serovars in urban areas. Adequate foot covers in the form of closed shoes and rubber gloves must be advised for farmers working in the paddy fields to prevent infection.
Keywords: Leptospirosis, ELISA, MAT, Paddy field workers
Full Text:
Introduction:
Leptospirosis is a global public health problem, the severity of which can vary from mild to a rapidly fatal illness. The extent of the problem in tropical and subtropical regions can be chiefly attributed to climatic and environmental conditions. The causative bacteria, Leptospira species, are responsible for a wide spectrum of clinical symptoms (1,2).
Due to unavailability of appropriate laboratory diagnostic facilities in most parts of the country, lack of awareness of the disease, and inadequate epidemiological data, Leptospirosis has been under-reported and under-diagnosed in India. (3)All available evidences recommend that , Leptospirosis is emerging in India as an important public health problem(4) .The disease is currently endemic and deeply entrenched in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. High risk areas include Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Goa and West Bengal(5–9).
Certain occupational groups such as agricultural labors, animal handlers, sewage workers, abattoir workers and miners etc. constitute high risk groups for acquiring Leptospirosis(10–12). Local agricultural practices, poor housing and waste disposal give rise to many sources of infection in the rural setting.
Rice field workers spend the major part of their day in rice fields flooded with water. This water is often contaminated with rodent urine and leptospira from the urine enter the skin through minor cuts and abrasions on the hands of these workers making them more prone to get leptospirosis.
The present study was conducted with the objective to estimate the prevalence of anti-Leptospiral antibodies among paddy field workers reporting with fever to a rural hospital in Pune district and thus to ascertain the extent of the problem in paddy field workers in Maharashtra , India.
Materials and Methods:
This was a cross-sectional prospective study conducted at B J Govt Medical College Pune and the study was approved by the institutional ethical committee. Patients were recruited to the study after written informed consent was obtained.
Adult Paddy field workers presenting with febrile illness to Rural Hospital, Pawana Nagar, Pune were included in this study. Faine’s criteria were used for suspecting leptospirosis, wherein patients with fever, headache, jaundice, cough and breathlessness, sub-conjunctival suffusion, signs of meningeal irritation were included(2).
The presenting complaints of the farmers, duration of pyrexia and history of contact with animals were recorded. Their age, sex and address was noted. A detailed clinical examination was done and the routine investigations such as Widal test for typhoid, IgM ELISA for dengue and Peripheral Blood Smear for Malaria Parasites, were done. The score as per Faine’s criteria (2)were noted .
A total of 160 paddy field workers were included in the study.
Blood samples were collected from these 160 paddy field workers attending Rural Hospital, Pawana Nagar, Pune, during year 2013 to2014. Samples were collected aseptically using sterile 5 mL syringe. Serum was separated by centrifugation of blood at room temperature; the sera were transferred into 1.5 mL sterile micro tube (Eppendorf) and tested for evidence of leptospira infection.
Commercially available Leptospira IgM ELISA (Panbio Pty., Ltd., Queensland, Australia) was used for the detection of IgM antibodies to Leptospira species. The method was followed as per the manufacturer’s protocol .The absorbance of each well was read at a wavelength of 450 nm with Erba reader (Transasia, India). The results were expressed as Panbio units and interpreted as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
MAT: Samples were sent to National Leptospirosis Reference Centre, Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), Port Blair, for Microscopic Agglutination Test as per standard protocol against common Indian strains (13).
Statistical methods:
Percentage is taken into consideration in common presenting clinical features, age wise distribution of patients among ELISA positive patients, sex-wise distribution, and for results of ELISA and MAT test.
Results:
The common clinical presentations amongst the paddy farmers were Myalgia and headache in association with fever (Table1). Majority of the study group were patients in the age group 30-50 years (Table 2). 55.2% males and 44.7% females were affected (Table 3). Evidence of recent infection by leptospires could be found in Leptospirosis was found in 23.8% of the patients. Only 9.4 % of the infections could be confirmed by MAT. The commonest serovars to which antibodies were detected was Grippotyphosa (Table 4).
60.52% of patients with laboratory confirmed leptospirosis gave evidence of leptospirosis by Faine’s Criteria.
Discussion:
Leptospirosis is a zoonotic and an occupational disease. National Reference Centre, Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), Port Blair, during the period 2000–2001, conducted a countrywide study in India (14). The positivity rate was highest in South India at 25.6%, followed by 8.3%, 3.5%, 3.1% and 3.3% in northern, western, eastern and central India respectively (7).
However, little data is available regarding epidemiology of the disease, even in those individuals who are at risk of acquiring the disease. These individuals include farmers, sewer workers, abattoir workers and veterinarians etc. as they work in environments which could be contaminated with leptospires. New risk groups may be formed as a result of changes in agricultural or social practices or in the reservoir animal population in the area.
Paddy field workers work in rat infested muddy damp conditions, often contaminated with rat urine. Abrasions are common in body extremities, which are likely, serve as a portal of entry for leptospira. Intermittent rains and repeated flooding of rodent nests lead to the contamination of surface water and paddy fields.
In the present study 23.8% of paddy field workers reporting to hospital with a febrile illness had serological evidence of leptospirosis. A total of 18(11.25%) samples showed equivocal results (Table 4). In 11.25% of the cases the result were equivocal, a convalescent sample taken after two weeks is required to confirm the results. A limitation of using a single serum sample in the demonstration of IgM antibodies is the absence of antibodies very early on in the infection or the persistence of antibodies.
Serological evidence in present study is definitely higher than the previous report of urban studies in western Maharashtra. Total of 18.6% cases were seropositive in cases of Pyrexia of unknown origin(15). The reason for high prevalence of leptospirosis in this area may also be due to the overuse of fertilizers commonly used for agriculture, which makes the pH of the water and soil alkaline, thereby allowing Leptospira to survive for a longer time and thus facilitating its transmission. The prevalence of leptospirosis is higher in rural as compared to the urban population, mainly due to greater exposure to livestock.
A study conducted in Vietnam found a seroprevalence rate of 18.8% in the rice growing areas of the country. Studies conducted to detect the prevalence of leptospirosis in various occupational groups have shown a range of 7% to 56% in various occupational groups. In a study carried out by Everard et al(16), the seroprevalence rates were 7% in meat processors, 33% in rice field workers and 45% in sugarcane farmers.
In Swapna et al study seropositivity rates were, hospital sanitary workers (56.2%) and fishermen and fisher folk (52.8%) followed by construction workers (40%), agricultural workers (30%)sewage workers (28.2%), veterinarians (13.3%) and laboratory staff (3.3%)(17). Occupational groups having a direct or indirect contact with animals are more likely to be infected as these animals at as reservoirs of leptospires.
The preponderance of cases occurred in the age groups of 30 to 60 years of age shows that this disease is common in the working population who are most likely to be exposed to this organism (Table 2). No sex preponderance was noticed in the current study as males and females are equally involved in field activities and so are at same risk of acquiring the infection. In contrast to this, in Kalimuthusami et al study, of 329 rice mill workers, who were tested for seropositivity 80.9% were males and 19.1% were female(18).
The commonest symptoms of those who were detected as having leptospirosis were fever, headache, Myalgia. This triad was seen in 34.21% of the patients. These results were comparable with Patil, et al study, Clinical profile and outcome of leptospirosis(19).
The overall seropositivity of leptospirosis by MAT was 9.37%. This may be due to the fact that the samples were collected in the acute phase when IgM antibodies appear while MAT detects a combination of IgM and IgG and may be positive a little later in the illness. In a study by Shekatkar et al.also the IgM ELISA gave more positivity as compared to MAT. (20).
The serovars which were predominantly observed in this area were Grippotyphosa (53.3%), followed by Hebdomadis (26.7%) and Lai (20%). In urban Pune, Autumnalis and Copenhaegeni are common infecting serovars(21). The geographical variation in the distribution of serovars is related with the predominance of animal reservoirs. Grippotyphosa has been implicated as the predominant serogroup in Andaman and Kerala also (22).
According to the Thai Ministry of Public Health, Bureau of Epidemiology (BOE) report on leptospirosis a total of 1779 cases and 27 fatalities were reported from 70 provinces over eight month period. The attack rate was 2.80 per 100 000 population. The case fatality rate (CFR) was 0.04 percent. The majority of cases (58.5 percent) were rice farmers(23).
Conclusion:
Leptospirosis is thus an important cause of febrile illness in paddy field workers at risk and must be kept in mind in the management of such patients. The major prevailing serovars in Maharashtra, western India are Grippotyphosa and Hebdomadis, which differs from the prevalent serovars in urban areas. Adequate foot covers in the form of closed shoes and rubber gloves must be advised for farmers working in the paddy fields to prevent infection.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. P. Vijayachari of National Leptospirosis Reference Centre, Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), Port Blair, India for performing MAT test. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature of this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
References:
Bibliography:
1. Heath CWJ, Alexander AD, Galton MM (1965) Leptospirosis in the United States: Analysis of 483 cases in Man. N Eng J Med 273: 857-64.
2. Faine S (1982) Guidelines for the control of leptospirosis. WHO Offset Publication No. 67, Geneva.
3. Muthusethupathi MA, Shivkumar S, Suguna R, Jayakumar M, Vijaykumar R, Everard COR, et al. (1995) Leptospirosis in Madras: a clinical and serological study. JAPI 43: 456-58.
4. Shekatkar SB, Harish BN, Menezes GA, Parija SC. Clinical and serological evaluation of Leptospirosis in Puducherry, India. J Infect Dev Ctries 2010;4:139-43.
5. Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Siozopoulou V, Christou L, Akritidis N. The globalization of leptospirosis: Worldwide incidence trends. Int J Infect Dis 2008;12:351-7.
6. Christopher AM, Mohapatra AK, Binay, Dutta TK, Kanungo R, Das AK. Pulmonary manifestations of leptospirosis. In: Souvenir, 3rd Annual Conference of Indian Leptospirosis Society, Pondicherry, 2002. 32.
7. Kamath S. Leptospirosis In: Das S Ed. API Medicine update, Mumbai.2003; 13:1008-11.
8. Olszyna DP, Jaspars R, Speelman P, van Elzakker E, Korver H, Hartskeerl RA. Leptospirosis in the Netherlands 1991-1995. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1998; 142: 1270-1273.
9. Koutis CH. Special Epidemiology. Athens, Greece: Technological Educational Institute of Athens; 2007.
10. Padre LP, Watt G, Tuazon ML, Gray MR, Laughlin LW. A serological survey of ricefield leptospirosis in central Luzon, Philippines. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Pub. Health 1988; 19: 197-199.
11. Chan OY, Paul DR, Sng EH. Leptospirosis among abattoir workers- a serological study. Singapore Med. J. 1987; 28: 293-296.
12. Levett PN. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001; 14(2): 296-326.
13. ThaipadungpanitJ,ChierakulW,WuthiekanunV,Limmathurotsakul D, Amornchai P, Boonslip S, Smythe LD, Limpaiboon R, Hoffmaster AR, Day NP, Peacock SJ, 2011. Diagnostic accuracy of real-time PCR assays targeting 16S rRNA and lipl32 genes for human leptospirosis.
14. Christopher AM, Mohapatra AK, Binay Dutta TK, Kanungo R, Das AK (2002) Pulmonary manifestations of leptospirosis. In: Abstracts, 3rd Annual Conference of Indian Leptospirosis Society, Pondicherry, p32.
15. Sandhya A Kamath, Shashank R Joshi. March 2003Re-emerging of Infections in Urban India - Focus Leptospirosis. JAPI vol. 51.
16. Everard COR, Hayes RJ, Fraser Chanpong GM. A serosurvey of leptospirosis in Trinidad among urban and rural dwellers and persons occupationally at risk. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985; 79(l): 96-105.
17. Swapna RN, Tuteja U, Nair L, Sudarsana J. Seroprevalence of leptospirosis in high risk groups in Calicut, North Kerala, India. Indian J Med Microbiol 2006;24:349-352.
18. Kalimuthusmi Natarajaseenivasan, Marimuthu Boopalan, Krishnaswami Selvanayaki, Sudalaimuthu Raja Suresh, ans Sivalingan Ratnam 2002.Leptospirosis among rice mill workers of Salem, South India. Jap J Infect Disease, 55; 170-173.
19. Patil VC, Patil HV, Agrawal V. Clinical profile and outcome of leptospirosis at tertiary care centre in western Maharashtra. J Acad Med Sci 2012;2:30-7.
20. Smita B. Shekatkar, Belgode N. Harish, Godfred A. Menezes and Subhash C. Parija. Clinical and serological evaluation of leptospirosis in Puducherry, India. J Infect Dev Ctries 2010; 4(3):139-143.
21. Bal AM, Bharadwaj RS, Joshi SA, Kagal AS, Arjunwadkar VP. Common infecting leptospiral serovars in and around Pune, Maharashtra. Indian J Med Res 2002 Jan;115:14-6.
22. Ratnam S, Subramanian S, Madanagopalan N, Sundararaj T, Jayanthi V (1983) Isolation of leptospires and demonstration of antibodies in human leptospirosis in Madras, India. Trans Roy Soc Trop Med Hyg 77: 455-58.
23. National News Bureau of Thailand Public Relations Department.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License