IJCRR - 5(16), August, 2013
Pages: 47-53
Date of Publication: 28-Aug-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
VALUE OF RAPID ANTIGEN ASSAY IN DIAGNOSIS OF PYOGENIC AND PARTIALLY TREATED MENINGITIS
Author: Shalini Bajaj, Deepandra Garg, Manish bajaj, Neha Agrawal, S.L. Mandowara
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: To assess the usefulness of rapid antigen assay in diagnosis of pyogenic meningitis and to compare CSF culture with Rapid antigen Assay in pyogenic meningitis in terms of percentage recovery of the pathogen. Research Design and Methods: The prospective observational study was conducted on all suspected cases of meningitis, admitted in Bal Chikitsalaya, Department of Paediatrics, RNT Medical College, Udaipur over a period of 6 months. A total of 20 children with pyogenic meningitis were enrolled in our study. Their haematological and CSF cytochemical findings, management, clinical course during illness and outcome were also recorded and analyzed. Rapid Antigen detection by Latex Agglutination Test was compared with CSF culture. Results: In our study, the overall positivity on Rapid Antigen assay was 85% of cases with a sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 100% respectively. This in sharp contrast to CSF gram's stain and culture where the results were positive in 55% and 40% cases respectively.Streptococcus pneumoniae was the commonest organism isolated on Rapid antigen assay in 47.06% followed by Neisseria meningtidis in 35.29% and Hemophilus Influenzae in 11.76% .Case fatality rate was 15% in our study. Conclusions: We concluded that Rapid antigen asssay has high sensitivity and specificity .So, it can be advised as an additional laboratory investigation to found etiology of bacterial meningitis mainly in pretreated cases and also differentiate partially treated cases from that of tubercular meningitis as it is a common dilemma encountered by the clinicians.
Keywords: C–Reactive Protein, Neonatal Septicemia
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Acute bacterial meningitis, also referred to as pyogenic meningitis, is one of the most serious illnesses leading to high morbidity and mortality all over the world, especially in developing countries such as in India.(1)In the pre antibiotic era of the previous century the epidemics and endemic potentials of this disease with a predominate fatal outcome, were recognized particularly in children.(2)With the availability of antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents, mortality has substantially reduced, but still remains the major cause of death in paediatric age group. Mortality rate due to acute bacterial Meningitis remains significantly high in India and other developing countries ranging from 16-32 %. (3) The mortality in untreated cases of pyogenic meningitis is nearly 100%. There are significant complications in as many as 50% of patients of pyogenic meningitis in spite of treatment (4) Prompt diagnosis is the corner stone for effective management. Lumbar puncture and CSF examination remains most important early diagnostic test. (5) The conventional methods of diagnosis like Gram staining and bacterial culture do not always yield positive results. The CSF become sterile on culture because frequent administrations of antibiotics before a specific diagnosis. (6) Gram staining of the CSF smear is a very helpful and cheap method and can be rapidly and accurately performed. CSF protein > 100 mg /dl and CSF sugar < 40mg /dl are suggestive of bacterial meningitis, but can also be seen in other causes of meningitis. The only reliable method is bacterial culture of CSF .However; positivity by this method varies from only 30-60% cases to 70-80% (7,8) The CSF culture is time consuming and can give false negative results if the specimen has been transported and stored under unsatisfactory conditions or if an antibiotic therapy has been initiated before the specimen was taken.(9)Therefore, there is an urgent need for finding an alternate method of diagnosis. Detection of microbial antigens in cerebrospinal fluid may be the single most important test in partially treated meningitis since Gram’s stain and culture may be negative and it is a valuable aid when choosing antimicrobial therapy.(9) Not many studies have been performed in India to assess the role of rapid antigen assay .The present study is ,therefore, being planned to find out the usefulness of rapid antigen assay in diagnosis of pyogenic meningitis as well as its role in detection of partially treated meningitis and differentiating it from tubercular meningitis.
MATERIAL and METHODS
The Study of was carried out on all suspected cases of meningitis, admitted in Bal Chikitsalaya, Department of Paediatrics, RNT Medical College, Udaipur over a period of 6 months. Each patient evaluated on the bases of detailed history, clinical examination and Relevant laboratory investigations including-Complete blood counts, ESR, Lumbar puncture- complete CSF analysis, CSF culture for pyogenic organism, Rapid Antigen detection by Latex Agglutination Test ,Blood Sugar, Ultrsonography (USG) Skull, cranial CT scan, MRI whenever required,
SELECTION OF CASES
Inclusion Criteria
All suspected cases of meningitis will be included in the study Group I – Cases.-This group will include: (A) All definite cases of pyogenic meningitis (10) as suggested by history, clinical examination, Radiological investigations and CSF analysis. (B)"partially treated pyogenic meningitis", where the meningitis symptoms, signs and CSF findings are modified after receiving antibiotics. When this happens, CSF findings may resemble those of viral meningitis or early tubercular meningitis. A total of 20 cases will be included in this group. Group II- Control group-This group will include: ? Definitive cases of tubercular meningitis (meningoencephalitis) (11)based on history, clinical examination, Radiological investigations and CSF analysis ? Viral encephalitis/meningoencephalitis ? Cerebral Malaria etc. 10 patients will be included in this group.
Exclusion Criteria:
Traumatic lumbar puncture. The CSF was collected with aseptic technique by lumbar puncture in 3 sterile containers and transported to the laboratory as soon as possible. In case of delay in transportation CSF was kept in an incubator at 35-37OC. In all the patients Rapid Antigen Assay of Cerebrospinal Fluid by Latex Agglutination test will be performed. Latex agglutination test will be used using Pastorex kit for CSF samples only. (12)
RESULTS
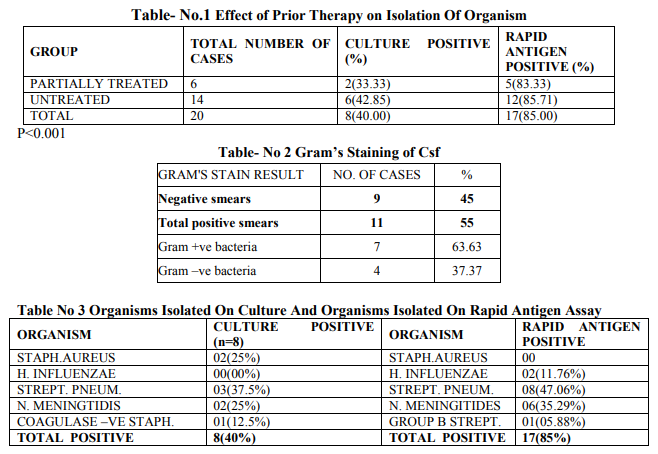
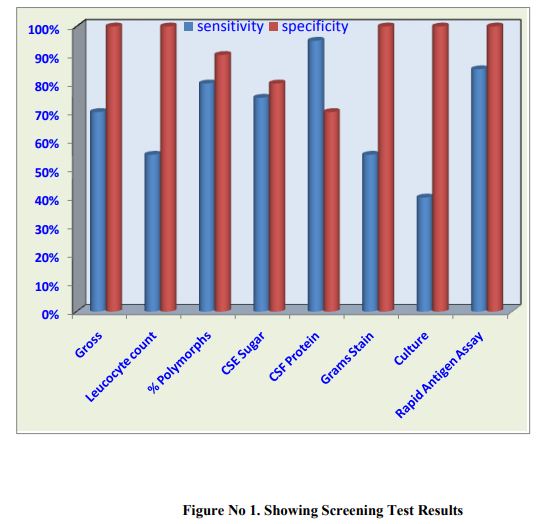
20 cases and 10 controls were enrolled and were studied for clinico-microbiological profile as per the inclusion and exclusion criteria mentioned above. Majority of the patients 11 (55%) were in the age group >5 Years. Males were 11 (55%) as compared to Females 9 (45%) in the present study. (p >0.3) Male to Female ratio was 1.22:1.. (x2 = 2.86, p >0.3) In the present study fever was the commonest symptom in 19 (95%) followed by convulsion in 15 (75%).When various clinical sign at admission were analysed in the present study, Signs of meningeal irritation were present in 11 (55%) cases, bulging fontanallae were seen in 5(25%) cases. Leucocytosis was higher in untreated patients as compared to partially treated ones, with a coefficient of linear regression value of 0.91. A higher CSF protein and lower glucose level was also found in untreated as compared to partially treated patients. (r 0.91) It was observed positivity of CSF culture among untreated patients 6 (42 %) was higher in comparison to partially treated patients 02 (33.33%).Positivity of Rapid antigen test among untreated patients {12(85.71%)} was slightly higher than among partially treated patients {5(83.33%)}.Overall, Rapid antigen assay led to more isolation of organisms {(in 17 cases (85%)} as compared to culture {in 8 cases (40%)} [Table No.1]. This difference was statistically significant (p5 Years. Males were 11 (55%) as compared to Females 9 (45%) in the present study.However, the difference was statistically insignificant (P value >0.3). The male to female ratio in the current study was 1.22:1. Similar to our study and Rao et al (1998) from Libya reported male to female ratio of 1.2:1. (13) It was observed that there is a higher admission rate of males as compared to that of females. Moreover, because of social and cultural bias in favour of males, they are provided with earlier and better medical and social care. In the present study, Fever was the commonest symptom (95%) followed by convulsion (75%), Vomiting (55%) Similarly Gupta and Dhande (2002) also observed fever (98.28%) as the commonest symptom followed by convulsion (67.24%) and vomiting (31.03%). (14) In the present study, a sign of meningeal irritation (in 55% cases) was the commonest observed sign. Comparable to our study, Gupta and Dhande (2002) also observed the same. (14)In contrast to our study, Chinchankar et al (2002) reported meningeal irritation signs in 26% cases only. (15) The variation observed in incidence of clinical features in patients with pyogenic meningitis depends upon age of patients, duration of onset, host resistance and infectivity of organism. In the present study (30%) patients received preadmission antibiotics. The TLC in untreated patients was found to be more as compared to patients who had received prior antibiotic therapy but the difference was statistically insignificant (P >0.8). In current study, >60% polymorphs were seen in 83.33% of partially treated cases and 78.57% of untreated cases of pyogenic meningitis respectively. Similar observation was found by Gupta and Dhande (2002). (14) On cytochemical examination of CSF, it was observed that CSF cell count was higher in untreated cases. A linear regression analysis revealed a significantly higher cell count in untreated patients(r 0.91).This is expected as partial treatment with antibiotics is likely to alter the CSF picture. However, in the study conducted by Gupta and Dhande (2002), such a difference was not found.(14) The CSF protein was also high in untreated patients compared to partially treated.CSF glucose was also lower in untreated as compared to partially treated group (r 0.91). (Table .2) The culture was positive for organism in 33.33% of partially treated as compared to 42.85% of untreated patients. However, the difference between these two groups was statistically insignificant (P>0.1). Similarly Gupta and Dhande (2002) also observed culture positivity in partially treated (21.42%) as compared to 46.66% in untreated cases.(14) Yang et al (1993) from China observed that only 2.5% of partially treated patients had culture positivity.(17) (Table no.3) In our study Streptococcus pneumoniae was the commonest organism cultured (37.5%) followed by Staphylococcus aureus and Niesseria meningtidis (25% each).Gupta and Dhande (2002) isolated Staphylococcus aureus and Khaliq and Salam (2002) recovered Klebsiella (33.33%), as the predominant organism respectively.(14,18) In contrast to above mentioned studies many authors reported that the most common causative organism in pyogenic meningitis grown on CSF culture was H. influenzae (Rao et al, Choo et al).(Table no.3) . (13, 19) This could be a difference in the geographic distribution of H. Influenzae. In current study it was observed that commonly isolated organisms on Rapid Antigen Assay were Streptococcus pneumoniae(47.06%), Nisseria meningtidis(35.29%), and Hemophilus influenza (11.76%).[Table no.3 ] Chavez-Bueno et al(2005) observed that, in infants and children worldwide, S.pneumoniae, N.meningtides, H.influenzae were the common organisms causing bacterial meningitis(20) Similar to our study, Das et al(2003) observed that common etiological organisms were S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae type b and N. meningitidis.(21) In contrast a study by Drow et al(1983) using coagglutination revealed H. influenzae, 97%; group B Streptococcus, 75%; S. pneumoniae, 71%; and N. meningitidis,58% as most common organisms.(22) Rapid Antigen Assay showed a sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 100% in diagnosis of bacterial meningitis in our study. In contrast Gram’s stain and culture were positive in 55% and 40% cases respectively. Similarly, in a study by Das et al (2003), an etiological diagnosis could be made by LPA in 83% cases of bacterial meningitis as compared to 6% by culture and 36% by gram's stain respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of LPA test were 83% and 100%, respectively, very similar to our study. (21) In our study 70% patients were discharged on recovery while 15% of cases expired. Higher mortality has been observed by many workers (Kumar et al and Bhat et al,). (7, 16) Earlier detection of the organism by Rapid Antigen assay and prompt institution of the appropriate antibiotics could have contributed to our lower case fatality rate.
CONCLUSION
From above mentioned facts observed in the present study, we concluded that pyogenic meningitis is certainly contributing to pediatric mortality and morbidity, especially because of changing causative microbiological pattern. Streptococcus pneumoniae infection is the most significant cause of pyogenic meningitis in all pediatric ages. Rapid antigen assay has high sensitivity and specificity and is rapid enough to guide the clinician for instituting proper antibiotics. So, it can be advised as an additional laboratory investigation to found etiology of bacterial meningitis mainly in pretreated cases and also differentiate partially treated cases from that of tubercular meningitis as it is a common dilemma encountered by the clinicians. We hope that the present study will go a long way in improving the quality of survival of patients with pyogenic meningitis.
References:
1. Srivastava JR. Srivastava VK, Mehrotra SN and Samuel KC. Clinical and bacteriological study of pyogenic meningitis in children. Indian J Pediatric 1968: 35:423-28.
2. Vancent J, Quagliarello and Scheld WM, New perspective on bacterial meningitis Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 7: 603-608.
3. Mani R, Pradhan S, Nagarathna S, Wasiulla R, Chandramukhi A. Bacterio,logical profile of community acquired acute bacterial meningitis a 10 year retrospective study in a tertiary neurocare centre in South India. Indian J Med. Microbiology 2007; 25: 108-14
4. Sinha KK.Acute pyogenic meningitis. Some important aspect. Hospital Today 1999;4:209- 216
5. Dean A. Seehusen, M.D., Mark M. Reeves, M.D., And Demitri A. Fomin, M.D. Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis. American Family Physician 2003;68(6):1003-1008
6. Pandit L, Kumar S, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I. Diagnosis of partially treated culture-negative bacterial meningitis using 16S rRNA universal primers and restriction endonuclease digestion. J Med Microbiol 2005; 54: 539-542.
7. Kumar L. Chitlangia S, Ayyagari A.The current status of pyogenic meningitis in children. Ind.Paediatrics. 1980; 17:438-444
8. Converse GM, Gwaltney JM, Strassburg DA, Handley JO.Alteration of cerebrospinal fluid findings by partial treatment of bacterial meningitis.J Pediatrics. 1973; 83(2): 220-225
9. Surinder K, Bineeta K, Megha M. Latex particle agglutination test as an adjunct to the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Indian J Med Microbiol 2007;25:395-7. 10. Prober CG. Central Nervous system infections .Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 2004;(17 ): 2038 -2044
11. Munqj FM, Starke JR. Tuberculosis. Nelson textbook of Pediatrics, 2004; (17):958-972 12. Forbes, B.A., D.F. Sahm, A.S. Weissfeld, eds. 2002. Meningitis and other infections of the central nervous system .Bailey and Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology, 11th ed. p. 907-916
13. Rao BN, Kashbur IM, Sembesh NM, Bargathy SM. Etiology and occurrence of acute bacterial meningitis in children in Benghazi, Libyan Arab Jamahiriya 1998; 4 : 50-57. 14. Gupta BD, Dhande NR, An epidemiologic and clinical study of Pyogenic meningitis in children submitted to University of Rajasthan for MD (Ped.) 2002. 15. Chinchankar N, Mane M, Bhave S, Diagnosis and outcome of acute bacterial meningitis in early childhood. Indian Pediatrics 2002; 39: 914-921.
16. Bhat BV, Verma IC, Puri RK, Sinivasan S and Naini P. Prognostic indicator in pyogenic meningitis. Indian Pediatr. 1987; 24: 977-983. 17. Yang Y.H, Fu S.G. Penh H et al. Abuse of antibiotics in China and its potential interference in determining the etiology of pediatric bacterial disease. Pediatr. Infect Dis J 1993; 12:986-988. 18. Abdul Khaliq A Sallam. Etiology and presentation of acute bacterial meningitis in children at Al-Thawrah Hospital, Sana`a, Yemen J Ayub Med Coll Abottabad Oct - Dec 2004;16(4):40-3. 19. Choo K.E, Ariffin W.A, Ahmed T, Linn W.L, Gururaj A.K. Pyogenic meningitis in hospitalized children in Kelantan, Malaysia. Ann Trop Pediatr. 1990; 10(1) : 89-98. 20. Susana Chávez-Bueno, George H. McCracken Jr, Bacterial Meningitis in Children. Pediatric Clinics of North America 2005;52(3):795-810 21. B.K. Das, Rajesh Lal Gurubacharya, T.M. Mohapatra and O.P. Mishra. Bacterial Antigen Detection Test in Meningitis. Ind J Pediatrics 2003; 70 (10) : 799-801. 22. Doris L. Drow,David F. Welch, Diane Hensel,Kathy Eisenach,Earl Long And M. Slifkin Evaluation of the Phadebact CSF Test for Detection of the Four Most Common Causes of Bacterial Meningitis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, Dec. 1983, p. 1358- 1361.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License