IJCRR - 6(19), October, 2014
Pages: 42-46
Date of Publication: 10-Oct-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFICACY OF DISTRACTION TECHNIQUE IN REDUCING PAIN AMONG CHILDREN RECEIVING VACCINATION
Author: Richa Talwar, Anita Yadav, Rupinder Deol, Jasbir Kaur
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Vaccination is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infection. Routine vaccination is a universal phenomenon which is administered repeatedly throughout infancy, childhood and adolescence. It is the common source of iatrogenic pain in childhood. Pain from injection is a source of distress for children, their parents and vaccinators, and if not addressed, can lead to pre-procedural anxiety in future, medical fears and healthcare avoidance behaviours. So, there is a great need to study the methods of alleviation of vaccination related pain in children. Objectives: The study was undertaken with the objective to assess the efficacy of distraction technique in reducing level of pain among healthy children during vaccination. Methods: A quasi experimental study design was used to evaluate the efficacy of distraction technique in reducing level of pain among healthy children receiving vaccination at well baby clinic in selected hospital, Ludhiana. Sample size of 200 healthy children using convenience sampling (100 in each group) was used. The standardised FLACC (face, leg, activity, cry, consolability) - Behavioral Pain Assessment scale was used to observe level of pain among the healthy children during vaccination. A sound and light producing movable toy was used as distraction technique in experimental group during vaccination. Video recording of the children receiving vaccination was done and the pain score was calculated. Results: Findings revealed that 7% of the children in experimental group as compared to only 1% in control group experienced no pain during vaccination. The mean pain score among experimental and control group were 4.02\?1.694 and 4.89\?1.503 respectively (p< 0.001). Conclusion: The distraction technique significantly reduces the level of pain in healthy children receiving vaccination (p< 0.05). Therefore, it is recommended that distraction technique should be used during every painful procedure among children.
Keywords: Distraction technique, Pain, Vaccination, Children, FLACC (face, Leg, Activity, Cry, consolability) Behavioral Pain Assessment scale
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Immunity is a biological term that describes a state of having sufficient biological defences to avoid infection.1 Children have immature immune response against diseases unlike adults. To develop the immune response and to impart the immunity, there is a need of vaccination.2 Parents want their child to be safe from diseases. So, they choose vaccination as a preventive measure.3 Routine vaccination is a universal experience which is painful and children show behavioural distress to pain.4 Despite the benefit of vaccination5 the pain associated with vaccination is a source of great anxiety and distress for many children.5-6 Reports from children, parents and nurses consistently indicate that many children do indeed fear the “shot”4 which is often manifested by the child’s distress behaviour such as crying, temper tantrums, untoward behaviour and refusal to cooperate, which is upsetting not only for the child but also for both parents and professionals that makes it difficult to complete the needed procedure.4,7 Many mothers withhold scheduled vaccines out of concern for the excessive pain from vaccination.8 Unfortunately, despite an increased focus on pain assessment and management, vaccination related pain remains largely untreated.9 Many children are so preoccupied with the possibility of pain from vaccination that this worry dominates the entire visit. Every nurse or physician who works with children, find a cowering child whose first question is, “Am I going to get a shot?” The needle is a powerful negative symbol for many children, is a phobia for some, and unfortunately has become an icon of medical/nursing care.10-11To ensure adequate pain relief, to make pain more tolerable and to give the children a sense of control over the situation, non-pharmacological methods are widely accepted that may be used independently or in addition to medication. Distraction, electro-analgesia, imagery, relaxation technique, hypnosis and cutaneous stimulation are common non-pharmacological techniques used to alleviate pain.12 Distraction is a non-pharmacological intervention that diverts attention from a noxious stimulus by passively redirecting the child’s attention or by actively involving the child in the performance of diversion task.13 Distracters that can be commonly used for children include sound and light producing movable attractive toys, picture books, talking with the child and music etc.14 Related to the quality of the distraction, Mac Laren and Cohen found that, more the children engage in distraction, the lower is the pain experienced by them regardless of the type of distraction stimuli.15It was observed by the researcher that because of this, sometimes parents do not get their child vaccinated or postpone the vaccination. Hence the need to assess the efficacy of distraction during painful procedure was felt as Infant procedural distress is largely understudied in child health nursing literature. The purpose of the study was to assess the efficacy of distraction technique in reducing level of pain among healthy children receiving vaccination. In future, this distraction technique may allow the parents to stick with the immunisation schedule and decrease the fear of shot in children. Material and Methods: A quasi experimental (post test only) research design was used to assess the efficacy of distraction technique in reducing level of pain among healthy children receiving vaccination at well baby clinic in selected hospital Ludhiana. The distraction technique (sound and light producing movable toy) was introduced to the experimental group during vaccination and withheld in the control group. The target population included all the healthy children up to the age of 3 years. The sample size of 200 healthy children were selected by convenience sampling technique. To assess level of pain during vaccination, FLACC (face, leg, activity, cry, consolability) - Behavioral Pain Assessment Scale was used. This is a standardised scale which includes the observation of five parameters i.e. face, leg, activity, cry and consolability, which indicate behavioral pain responses of the child. The video was recorded starting from the time when child lied down on vaccination table till 1-5 minutes after vaccination and videos were graded for pain accordingly. The maximum pain score of the tool was ten and minimum was zero. Informed written consent was taken from the parents. In intervention phase, sound and light producing movable toy was shown as a method of distraction to healthy children of experimental group during vaccination. Standard needle size of twenty six gauge and thigh as a site of vaccine was used for all the children. Simultaneously, video recording of the whole procedure was done by a trained person. Videos were encoded by another person with research background. An intervention was involved in the study, so it was conducted after approval from the ethical committee of DMC and Hospital, Ludhiana. Analysis of data was done in accordance with the objectives of the study. Null hypotheses (H0 ) of the study was that there will be no significant reduction in level of pain among experimental group at 0.05 level of significance.
Statistical Methods
Both descriptive and inferential statistics were Statistical Methodsused; calculations were carried out manually, with the help of calculator, Microsoft excel and SPSS version16. Descriptive statistics such as percentage, mean, standard deviation and inferential statistics like ANOVA, ‘t’ test and chi square were used for analysing the collected data. The level of significance was set at 0.05.
RESULTS
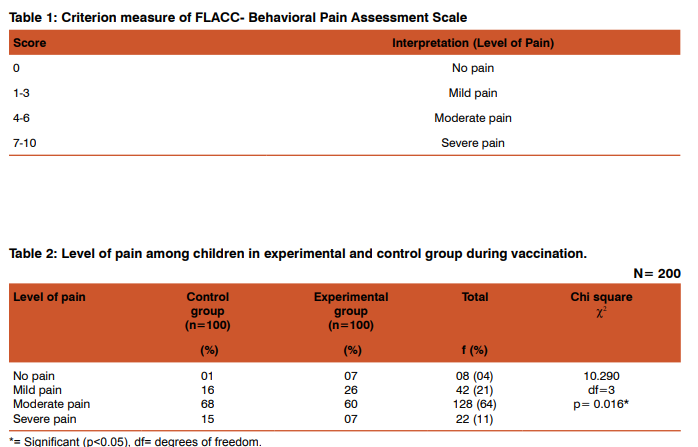
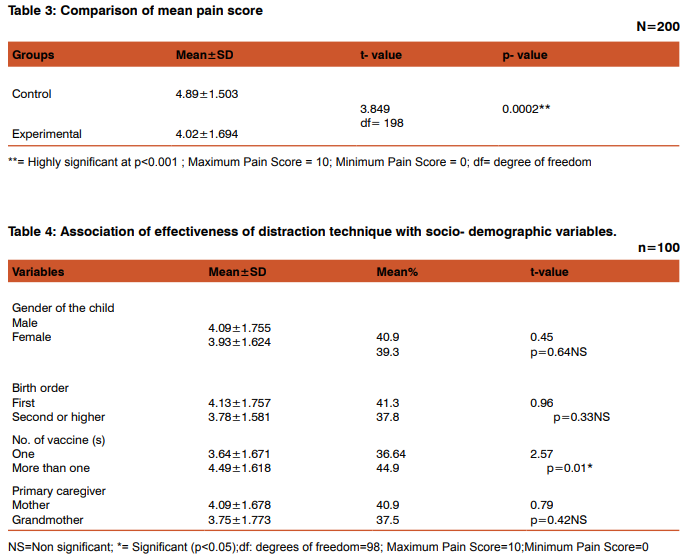
Out of total 200 subjects, the percentage of male children in experimental and control group were 57% and 60% respectively. Three-fourth of children (75%) in control group and nearly two-third (67%) in experimental group were first born children in the family. More than half of the children (56%) in control group and 58% in experimental group weighed between 6.1-12 kg. More than half of the children (56%) in the experimental group and slightly less than half (44%) in the control group belonged to the age group of 0-6 months. Regarding the vaccination related data, most of the children (90%) in control group and majority of the children (80%) in experimental group had their mother as a primary caregiver. Mothers of more than one-third of children (44%) in control group and 40% in experimental group were present during vaccination. More than half of the children (54%) in control group and less than half (45%) in the experimental group received more than one vaccine. Majority of the children (82%) in control group and 83% in experimental group received vaccination by intramuscular route whereas only 12% in control group and 9% in experimental group received vaccine by both intramuscular and subcutaneous route. Regarding the level of pain during vaccination, only 1% of children in control group showed no pain whereas 7% of children in experimental group demonstrated no pain. Findings revealed that 16% of children in control group and 26% children in experimental group experienced mild pain. More than two-third (68%) of children in control group and less than two-third (60%) of children in experimental group experienced moderate pain during vaccination. Further findings reveals that 15% of the children in control group demonstrated severe pain, whereas only 7% of the children in experimental group demonstrated severe pain. There was statistically significant difference in the level of pain among experimental and control group (p<0.05) (Table II).The mean pain score of control group was 4.89±1.503 whereas the mean pain score among experimental group was 4.02±1.694 (p<0.05) (Table III).
DISCUSSION
Pain is a sensory and emotional experience, which is considered unpleasant. Pain in infancy is poorly understood. Nursing and medical staff often have difficulty in assessing whether an infant is in pain. An important responsibility of nurses, who care for children, is eliminating pain and suffering, if possible. The most common type of pain experienced by children is acute pain resulting from vaccination, any kind of injury, illness and necessary medical procedures. Although focus on acute pain is the obligation of primary care nurses, physicians, general paediatricians, paediatric surgeons and paediatric subspecialists to recognize and address all types of pain (e.g., procedure-related pain, acute pain, chronic pain, recurring pain and pain associated with terminal illness). A sound and light producing movable toy was used to distract the children of experimental group during vaccination. Regarding the comparison of mean pain score among experimental and control group, it was found that the mean pain score among control group was 4.89±1.503 as compared to the mean pain score (4.02±1.694) of experimental group during vaccination. This finding revealed that the distraction technique was effective in reducing the level of pain among experimental group. French MG et al. (1994) conducted a study at Children Hospital, Ohio, to study the effect of an active distraction technique, blowing out air during vaccination. These findings also supported the present study findings in which the mean pain score was less among the children of experimental group (4.02±1.694) as compared to the mean pain score of children in control group (4.89±1.503).16 Bellieni CV et al. (2006) at University of Siena, Italy conducted a study on the analgesic effect of watching television during venipuncture. The findings revealed that the procedures performed while watching TV were less painful (p<0.05). These findings support the findings of present study.17 The findings of present study revealed that there was a significant association of effectiveness of distraction technique with number of vaccine(s) received at a time among children. The mean pain score (4.49±1.618) was more in children who received more than one vaccine as compared to mean pain score (3.64±1.671) of children who received only one vaccine while receiving distraction (Table IV). A study conducted by Allen KD et al. (1996) support these findings that the children who received sucrose or water during vaccination cried less if they received only one injection rather than two injections (F=3.36, p<0.05).18 Therefore, it is concluded that distraction technique was effective in significantly reducing the level of pain among experimental group during vaccination (p<0.001). Thus the review of different studies support the study findings.
CONCLUSION
Regarding the comparison of mean score of pain among experimental and control group, it was found that the mean pain score among control group was 4.89±1.503) as compared to the mean pain score (4.02±1.694) of experimental group. This difference was found statistically significant (p<0.001). This finding reveals that the distraction technique was effective in reducing the level of pain among experimental group. A statistically significant association was effectiveness of distraction technique and number of vaccine(s) received at a time by the children during vaccination (p=0.01) exact. Children among experimental group demonstrated less pain if they received only one vaccine (3.64±1.671) as compared to those who received more than one vaccine (4.49±1.618; p<0.05).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. OP, Gupta P and Paul VK.Ghai. Essential Pediatrics. 6th ed. New Delhi: CBS Publishers, 2008.p.181.
2. FDA/NIH/WHO Workshop. Immune response in children to influenza vaccination;[cited 2011 July 28].Available from: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/NewsEvents/WorkshopsMeetingsConferences/ ucm090464 pdf.
3. Abbot K and Fowler-Kery S. The use of a topical refrigerant anaesthetic to reduce injection pain in children. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 1995; 10: 584-90.
4. Agras S, Sylvester D andOliveau D. The epidemiology of common fear and phobias. Comprehensive Psychiatry; 1969:1511-56.
5. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases. Recommended childhood and adolescent immunization schedule-United States, 2003.Pediatrics 2003;111: 212-16.
6. Schechter NL, Zempsky WT, Cohen LL, McGrath PJ, McMurtry CM, Bright NS. Pain reduction during paediatric immunisations: evidence-based review and recommendations. Paediatrics 2007 May; 119(5):1184-98.
7. Schecter NL, Altman A and Wiseman SJ. An introduction: American Academy of Paediatrics report of the subcommittee on management of pain associated with procedures in children with cancer. Paediatrics 1990; 86:813.
8. Help. Eliminate pain in kids. Clinical practice guidelines for pain management during childhood vaccination, Technical report, http://www.cdha.nshealth.ca/default retrieved on 25-03-2011.
9. Anand KJS, Thrivikraman KV, Engelmann M, Su Y andPlotsky PM. Adult rat behaviour and stress responses following pain in the neonatal period. Pediatr Res 1995; 37:57A.
10. Fassler D. The fear of needles in children. Am J Orthopsychiatry 1985; 55:371–77.
11. Hamilton JG. Needle phobia: a neglected diagnosis. J FamPract 1995; 41:169-75.
12. Ball JW andBindler RC. Clinical handbook for pediatric nursing. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby Publication; 1998.
13. Fernandez E. A classification system of cognitive coping strategies for pain; 1986; 26,141,151.
14. McCarthy MA andKliebre C. A conceptual model of factors influencing children’s response to a painful procedure when parents are coaches. Journal of Paediatric Nursing 2006; 21.
15. MacLaren JE and Cohen LL. A comparison of distraction strategies for venipuncture distress in children. JPediatrPsychol 2005; 30:387–96.
16. French MG, Painter CE and Larry LD. Blowing away shot pain: a technique for pain management during immunisation. Paediatrics 1994 Jun; 6:210-7.
17. Bellieni CV, Cordelli DM, Raffaelli M, Ricci B, Morgese G andBuonocore G. Analgesic effect of watching TV during venipuncture. Arch Dis child. 2006 December; 91(12):1015- 1017.
18. Allen KD, White DD andWalburn JN. Sucrose as an analgesic for infants during immunisation injections. Arch PediatrAdolesc Med 1996 Mar; 150
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License